Amphetamines: the effects and mechanisms of action of this drug
This stimulant substance can generate serious side effects, especially in recreational use.
The use of products with stimulant effects is frequent in today's society. Coffee, tea, chocolate, energy drinks... all of them have an activating effect on our organism that helps us to be more awake and energetic and that help to maintain our mood.
But apart from those mentioned above, there are other substances considered drugs, whose potency is much greater than those mentioned above.. These are substances that although they originated for medical use today are also used recreationally, illegally because they pose a health risk due to their addictive potential and side effects.
Within these stimulants we find cocaine and the type we are going to talk about in this article, amphetamines.
Amphetamines: type of substance and characteristics.
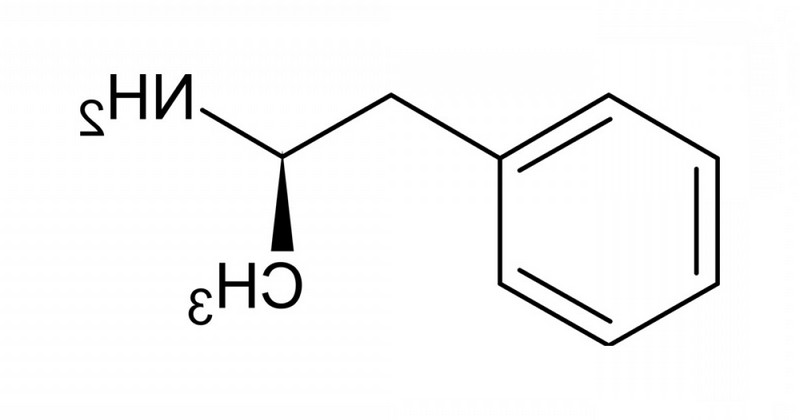
The amphetamines are a type of substance classified within the group of excitatory or psychoanaleptic. They are synthetic chemical compounds derived from beta-phenyl-isopropylamine, although in origin they are derived from substances derived from the Catha edulis plant.
The term "amphetamine" in question usually refers to the group of substances derived from amphetonic acid. substances derived from amphetaminic acid or similar in composition, although within the amphetamines, the term "amphetamine" usually refers to the group of substances derived from amphetamine.The term "amphetamine" in question usually refers to the group of substances derived from amphetaminic acid or similar in composition, although within the amphetamines there is a subgroup called amphetamines. As psychoactive activating agents, they cause an increase in the functioning of the nervous system, increasing wakefulness, alertness and physical and mental energy.
Their effects on the organism
Their effects on the organism suppose at the first moment a feeling of euphoria and a considerable increase in energy.The subject remains awake and his or her cognitive abilities seem to be faster and enhanced. The subject remains awake and his cognitive abilities seem to be faster and enhanced. The user tends to increase his level of awareness, attention and concentration.
Amphetamines generate the sensation of increased controllability and self-confidence, as well as giving the impression of clarity of vision.and gives the impression of clarity of thought. They also generate an increase in motor activity, increasing heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate. They reduce sleepiness, tiredness and hunger.
Amphetamines have been used in a wide variety of circumstances: from medicinal use to treat a variety of conditions. medicinal use to treat a variety of conditions to the enhancement of athletic or even academic performance, as well as purely recreational use. They are usually consumed orally, although they can be administered intravenously or inhaled in powder form. Their effects are very similar to those of cocaine, although they present fewer risks than cocaine.
Mechanisms of action
The mechanism of action of amphetamines is based on the blocking of monoamine reuptake. blocking the reuptake of monoamineswith particular emphasis on those of dopamine and noradrenaline. In addition, they also influence the synthesis of these substances, causing more of them to be generated. This causes the effects of these neurotransmitters to last longer as they remain longer in the synaptic space and are utilized by the postsynaptic neurons.
Amphetamines are therefore agonists of dopamine and noradrenalinThis causes the pleasurable and energy-enhancing sensations typical of this group of substances. It is also serotonin, but to a much lesser degree.
Medical uses
Amphetamines are substances which, like most illegal drugs, originally had medicinal purposes. In the specific case of amphetamines, these medicinal uses are still in force in a large number of cases, with the following often being employed based on or derived from this type of substance are often used to treat different ailments.s are often used to treat different ailments.
Specifically, they are nowadays used in some treatments against obesity (since they cause an increase in activity while reducing feelings such as fatigue and appetite), narcolepsy (their excitatory effects can combat sleep episodes) and even attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or adhd (in these cases amphetamine derivatives are used since they improve attentional capacity and reduce impulsive symptoms in this type of population).
Side effects and risks
While the consumption of amphetamines can be beneficial in some cases and generates a temporary increase in the performance of physical and mental abilities, recreational and continuedWhile the recreational and continued use of these substances can cause serious effects in both the short and long term, especially if intoxication or dependence occurs.
1. Dependence
Although they are not as addictive as cocaine, amphetamines have a high addictive potential due to their action on the brain's reward system and the progressive acquisition of tolerance. and the progressive acquisition of tolerance, which which makes it necessary to consume more and more amphetamines to feel the same effects.
Withdrawal syndrome
Abrupt withdrawal from amphetamine use can lead to withdrawal syndromes, which usually generate effects contrary to those produced by its use. Thus, fatigue and decreased energy are often observed, fatigue and loss of energy, nightmares, insomnia, insomnianightmares, insomnia, craving, motor agitation, anxiety and depression, inability to concentrate or emotional lability.
3. Sleep problems
Whether or not it is limited to withdrawal, one of the problems that amphetamine use may cause is difficulties in falling asleep or the fact that it does not produce a feeling of rest.
4. Hallucinations and perceptual disturbances
Although the action of amphetamines is not focused on this aspect, sometimes the following have been reported the presence of visual hallucinations.
5. Cardiorespiratory problems
Amphetamines have effects on the cardiovascular system, increasing blood pressure, heart rate and respiratory rate. Especially when intoxication occurs, it can lead to tachycardia, sweating and increases in blood pressure which can lead in severe cases to cardiorespiratory arrest.
6. Appetite
As mentioned above, amphetamines cause a decrease in appetite. While this may be beneficial for some people and is in fact used to treat obesity, this loss may lead to nutritional problems such as anemia.
7. Motor disturbances
Both in intoxication and in abstinence, amphetamines frequently cause alterations in the locomotor system. It is possible that weakness and sluggishness or, on the contrary, agitation and tremors may be generated, and in cases of severe intoxication may lead to epileptic seizures.
8. Altered language
It is common that amphetamine use can cause logorrhea derived from the state of physical excitement. The subject has a rapid and profuse speech, although there may be leakage of ideas.
9. Emotional problems
It is frequent that in the long run the consumption of these substances generates emotional lability, going from happiness to sadness with great ease and can generate anxiety or depression in the consumer. Also they can generate suicidal ideations.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)