Scabies or scabies
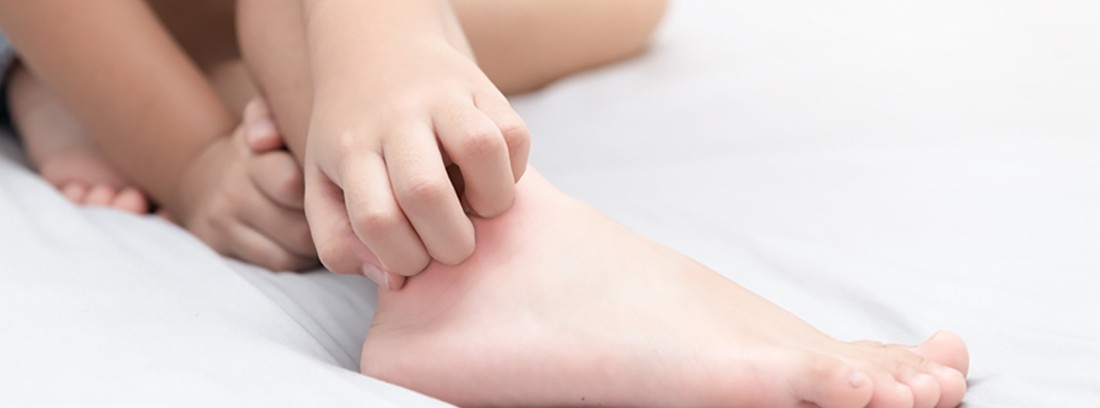
Scabies is an infection caused by a microscopic mite called Sarcoptes Scabiei. It is a very common parasite of humans, spread by close person-to-person contact.
Is it still frequent?
Although the word "scabies" sounds like a bygone era of war or poverty, the disease is prevalent, even in developed countries. It does not necessarily affect people with poor hygiene, but can also be observed in clean and healthy people since to contract it you only need to be in contact with an infected person.
However, it is more common in people who live in crowded conditions and in closer contact, because contagion is easier. It is a more common disease in the third world, but it is not rare in the first world.
What symptoms does it give?
The main symptom that can make you suspect scabies is the one that predominates at night, and that affects someone else who has maintained close contact with the patient.
The diagnosis is easier if there are several affected relatives. The lesions that appear on the skin are not very specific, since most are abrasions and irritations from scratching. The experienced eyes of a dermatologist can detect more specific signs on the skin, such as nodules or lumps in the genital area or the small grooves that the mite makes under the skin and that can be seen mainly on the hands, between the fingers, or on the wrists.
How is it treated?
Scabies requires correct treatment, aimed both at eliminating the mite and disinfecting clothing and belongings that have been in contact with it. In general, it is treated topically, with antiparasitic lotions that should be applied as directed by the doctor.
The clothes should be washed at high temperature to disinfect, with the exception of clothes that cannot be hot washed, which are disinfected when stored in a plastic bag for two weeks. When treating the patient, make sure to explore, and where appropriate treat, the people who live with him, who may also have contracted the disease.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW- It is transmitted by person-to-person contact.
- Main symptom: itching, especially at night.
- Treatment: topical antiparasitic lotion, as directed by the dermatologist.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)