Bloom’s taxonomy: a tool for education
This is a resource created to order objectives in educational proposals.
Education is the process by which training or learning is provided to one or more people with the purpose of developing, training and optimizing their cognitive, affective, social and moral capacities.
Education is an essential element when it comes to generating a common context and learning the different skills necessary to adapt to the environment and to be able to perform different functions, something that has concerned mankind since ancient times.
Despite the fact that access to formal education has not been compulsory and accessible to all until relatively recently, different models or attempts have been made to assess what formal learning is intended to achieve or what objectives it has. One of these models is Bloom's taxonomy.which we are going to talk about in this article.
Bloom's Taxonomy: what is it?
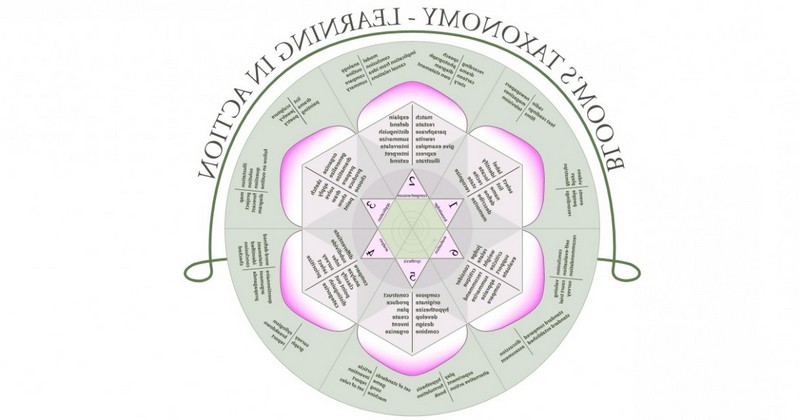
Bloom's taxonomy is a classification of different objectives to be achieved through formal education made by Benjamin Bloom based on the three aspects that different experts in education had reflected in 1948 when trying to establish a consensus regarding the objectives of education: cognition, affectivity and psychomotor skills.
It is a hierarchical classification of objectives, organized according to whether the activity requires more or less complex processing. The author based his classification on the contributions of the prevailing behaviorism and cognitivism of the time.
This taxonomy has been used and valued in the world of education since its conception. In itself, although Bloom's taxonomy is based on the consideration of the three main aspects and these are analyzed and classified, it tends to focus especially on the cognitive aspect, tends to focus especially on the cognitive aspect.This taxonomy was finalized in 1956. Regarding the classification of objectives and the dimensions worked in each of the aspects, in the taxonomy we can find the following.
The cognitive taxonomy
The aspect on which perhaps the greatest emphasis has been placed throughout the history of education, and on which Bloom's taxonomy also focuses especially, is the cognitive sphere.
In this sphere, the aim is to enhance the student's competence in the achievement or attainment of certain cognitive capacities or objectives (specifically, six) based on different intellectual, affective and psychomotor capacities. Although within each of them there may be different actions and aspects to work on, by way of summary we can consider that the main objectives of education according to Bloom's taxonomy are the following.
Knowledge
Although the concept of knowledge may seem very broad, this taxonomy indicates as such the ability to remember what has been previously acquired in a more or less approximate way. It is considered the most basic of the skills and the one that requires the least amount of processing.
2. Comprehension
Acquiring and retaining what we have learned does not require a great deal of processing, but per se it does not help us to adapt to the environment. We need to understand what we have learned. Thus, a second objective is to be able to transform the information as it comes to us. transform the information as it comes to us into something we can understand and interpret. understand and interpret.
3. Application
A more complex step is that of application. At this point the subject must not only grasp and understand what is being said but also be able to use it. It is not the same to know and understand what multiplication is as it is to do it in a practical way and when it is needed.
4. Analysis
The analysis of information implies being able to abstract the knowledge obtained in the previous moments, requiring the ability to fragment the reality of what has been learned in order to distinguish what configures it and allow its application in different fields.
It is able to elaborate hypotheses and contrast them on the basis of the information provided.. Continuing with the multiplication of the previous example, it would be to be able to understand that we can perform a multiplication in a given problem and why it is correct. It requires a lot of processing.
5. Synthesis
Synthesizing involves summarizing a model, combining the information received to create something different from what has been learned (in fact, in later revisions, synthesis is changed to creation). It is one of the most complex cognitive objectives, as it involves not only working with the information not only involves working with the information learned, but also incorporating but also incorporating other elements that help us to obtain its basis and apply it to create.
6. Evaluation
This element involves mainly the fact of being able to make judgments based on a criterion or informed opinion. It may even imply the non-acceptance of what is being taught.This requires a very advanced level of mental elaboration.
Reviewing this educational proposal
Although Bloom's taxonomy has been a reference in the world of education since its conception, this does not imply that different authors have not made any modifications in this regard. Specifically, the one published in 2001 by Lorin Anderson and David Krathwohl, who were students of the original author, stands out.
In this change it was proposed that instead of using nouns to evaluate each of the key categories or objectives, verbs should be used, something that facilitates the understanding that the objective is the fact of doing a certain action and not its result in itself. It is emphasized that we are dealing with an event that requires an active attitude and makes the learner the protagonist of his or her own makes the student the protagonist of his own learning process..
The sequencing of categories was also modified, considering the fact of evaluating a higher order of thinking, but below the process of creation (in the original model, evaluation was considered to be higher than synthesis/creation).
In addition, the model has subsequently been expanded to include different aspects linked to the use including different aspects linked to the use of the new information technologies y la comunicación, asimilándose a otros modelos.
Referencias bibliográficas:
- Bloom, B.S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals: Handbook I, cognitive domain. New York ; Toronto: Longmans, Green.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)