Adaptive radiation: what it is, types and examples
This phenomenon studied by biology allows us to understand how species are created.
Perhaps you have ever been in contact with this concept: "adaptive radiation".which is widely used in evolutionary biology. Adaptive radiation, as its name suggests, is an adaptive Biological process in which certain species can fill an ecological niche very quickly.
This phenomenon of domination of the territory of certain species is known as "speciation" and is part of an evolutionary process, since mutations and aspects of natural selection are involved.
In this article we will see in detail what these concepts consist of; ecological niche, mutation and natural selection, fundamental concepts to understand what adaptive radiation is. And finally we will know what is adaptive radiation, what are its causes and origins, characteristics that determine if we are in a situation of adaptive radiation, types of adaptive radiation and some examples.
What is adaptive radiation?
As we have already introduced above, adaptive radiation arises from an adaptive issue of the species. It is very frequent the appearance of this phenomenon in an ecosystem where a new species is introduced, or when species already exist in this ecosystem that manage to survive in this environment that for the moment they had not achieved.
In this process, the appearance of genetic mutations is necessary.. A genetic mutation is a change in the genetic material that makes possible a phenotypic change, that is, in the expression of that characteristic in the organism of that animal. These mutations can give them characteristics that are favorable for survival, or negative.
Therefore, it is normal that if that (random) mutation that occurs in the animal gives it some capabilities that allow them to adapt better to the environment, that group of animals with that mutation will survive longer and pass that mutation to their descendants, and that those that do not adapt to the environment will survive longer.and those that do not adapt (without the mutation), end up disappearing.
Hence the concept of natural selection was born; Darwin, the scientist who postulated this concept, defined that natural selection establishes that the conditions of an environment or ecosystem favor or disfavor, i.e., select, the reproduction of living organisms according to their characteristics. according to their characteristics.
In other words, if in a giraffe ecosystem where the trees with food are very tall, and in this way only giraffes with very long necks have access to food, those that have a mutation in their genetic material that provides them with a longer neck will survive longer because they will feed more and will not die of starvation.
And so, these giraffes, by not dying, will be able to have offspring, and it is very likely that their descendants will inherit this mutation. Little by little the giraffes that do not have the characteristics to eat and not starve will die, and of course they will not be able to pass on their genetic material. These species then fill what are known as ecological niches, which are understood as the functions of the species.which are understood as the functions fulfilled by species within an ecosystem.
Characteristics of this biological phenomenon
There are a series of characteristics that allow us to define a process of adaptive radiation, these are the following.
1. A common ancestor
One of the fundamental characteristics of adaptive radiation is that all derived species have a single common ancestor..
2. Phenotype-environment correlation
The existence of a correlation between phenotype (the characteristics manifested in the organism) and the environment is essential to speak of adaptive adaptation. That is, there must be a significant relationship between the morphological and physiological characteristics of the organism and the environment.
3. Utility character
That is, that the morphological and physiological characteristics of the organism are adapted to the needs of the environment.. That is to say, that these characteristics are useful to the animal for its survival.
4. Speed in the process
That speciation is a response to the need to adapt in the environment, and is a rapid process.
Types of adaptive radiation
Basically three types of adaptive radiation are known.
1. General adaptation
This type of adaptive radiation takes place when a species that develops a radically new characteristic or ability that may result in the invasion of new parts of that environment.. An example of this would be the flight of certain species of birds that facilitates the arrival of these to other spaces.
2. Environmental change
In this case, a species that has the ability to survive in a radically changed environment, compared to others that do not, is very likely toIn this case, a species that has the ability to survive in a radically changed environment, compared to others that do not, is very likely to branch out into new species, covering other ecological niches.
An example of adaptive radiation in response to environmental change would be the rapid expansion and development of mammals with the previous extinction of dinosaurs.
3. Archipelagos
This type of adaptive radiation is centered on archipelagos, which would be isolated ecosystems such as islands or isolated ecosystems such as islands or mountainous areas..
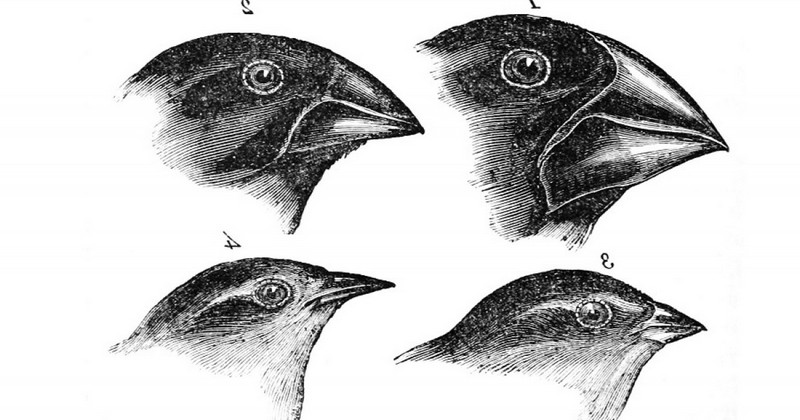
These can be colonized by new species which, if established, follow a rapid evolutionary process in which they diversify. The clearest example would be Darwin's finches, which we will see below.
Examples of adaptive radiation
Real and documented examples of adaptive radiation would be, for example, Darwin's finches of the Galapagos Islands. Darwin's finches were birds that developed and reproduced from a single species of finch that arrived on the Galapagos Islands at a certain point in time. that arrived on the Galapagos Islands at a certain point in time.
In this case, there was a diversity of beaks in the different species of finches. These finches were derived from the same ancestral species, but had been adapted to different ways of feeding, hence their varieties in beak shape.
Other documented cases of adaptive radiation include, for example the introduction by man of predatory mammals in certain regions of Australia, with the survival and expansion of these mammals in certain regions of the world.The development of the dipnoi (fish with lungs) during a period of time that took place around 300 million years ago.
In all these cases there are certain common factors that brand them as examples of adaptive radiation: genetic mutations that result in phenotypic changes, better adaptation to the environment than other species in the same ecosystem, and finally rapid colonization of that species in that ecological niche.
Bibliographical references:
- Carranza, J. (2016). Adaptive ethology: Behavior as a product of natural selection. UCOPress, Editorial Universidad de Córdoba, 1st Edition.
- Gould Stephen, J. (2004). The structure of the theory of evolution. TusQuets Editores.
- Pincheira-Donoso, D. (2012). Selection and adaptive evolution: theoretical and empirical foundations from the perspective of lizards. Ediciones UC.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)