Ethylphenidate: characteristics and side effects of this substance.
This stimulant substance is used in recreational and artistic contexts, but it comes with risks.
Ethylphenidate is a substance with stimulant effects that generates in the consumer a series of effects such as euphoria or mood enhancement, characteristic of other stimulant drugs such as amphetamines or cocaine.
In this article we explain what is ethylphenidate and what effects does it cause?What is its mechanism of action and the doses used, as well as the contraindications and side effects after its consumption.
What is ethylphenidate and what effects does it produce?
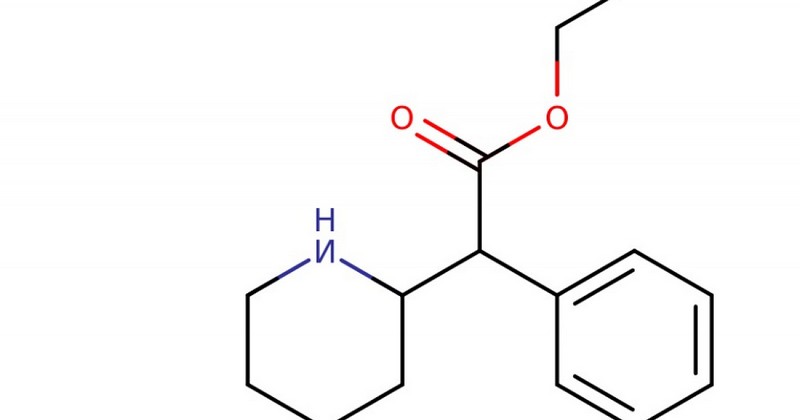
Ethylphenidate or ethyl ester of ritalinic acid is a stimulant compound of the piperidine group. This drug has been considered as a "research chemical". (discussed below), a research chemical that is not controlled by the authorities and, being analogous to others that are, can be considered to be of illegal use. At least until recently.
Although it is a closely related analogue, it should not be confused with methylphenidate, a drug commonly used for the treatment of drug addiction.a drug commonly used for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (under the trade names Ritalin or Concerta, in its long-acting version).
Typically, this drug is used in lethal contexts, this drug is used in recreational contexts (sometimes as an alternative (sometimes as an alternative to other banned stimulant drugs such as cocaine) in search of effects such as euphoria, alertness, mood elevation or improved social skills.
With regard to the legal status of this substance, the Ministry of Health initiated legal mechanisms to include ethylphenidate in the list of psychotropic substances, as it is considered to have no therapeutic utility. has no therapeutic usefulness and that its use would pose a risk to public health. It is currently in Schedule II of psychotropic substances under international control.
Mechanism of action and dosage
The most common routes of administration of ethylphenidate are nasal (snorted) and intravenous, although it can also be consumed orally, smoked or rectally. The intravenous route produces the most potent and immediate effects, while the nasal route is the most common in recreational contexts, attenuates the stimulant "high" and prolongs it over time.
Ethylphenidate acts by inhibiting the presynaptic reuptake of amines, by inhibiting monoamine transporters (such as dopamine and norepinephrine transporters), thus increasing the level of these neurotransmitters in synapses and brain. (such as the dopamine and norepinephrine transporters), thus increasing the level of these neurotransmitters in the synapses and the brain.
This substance has greater dopaminergic selectivityIt has a 16 times greater affinity for dopamine transporter proteins than for norepinephrine, which seems to indicate that it generates a greater euphoric effect, as well as less anxiety and less sympathomimetic effects (such as elevation of heart rate or Blood pressure) than its analogue methylphenidate.
The usual doses for recreational use by intranasal route are usually set at around 25 and 50 mg, and from 50-75 mg as the strongest dose, the adverse effects also increase.
There is also a less recreational consumption and more focused on work or artistic production, in which the user redoses every three or four hours, with oral doses between 2 and 5 mg. in which the user redoses every three or four hours, with oral doses of between 2 and 5 mg, in order to take advantage of the stimulant effects (very similar to those of one or two coffees) without the side effects that would be expected from higher doses or consumption patterns.
Contraindications
The consumption of ethylphenidate and, in general, of any psychostimulant substance that has sympathomimetic effects (acting as an agonist of the sympathetic nervous system) is contraindicated in persons suffering from any of the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity to ethylphenidate.
- Glaucoma.
- If being treated with irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days after discontinuation of treatment, given the risk of a possible hypertensive crisis.
- Hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis.
- Diagnosis or history of major depression, anorexia, suicidal tendencies, psychotic symptoms, severe mood disorders, schizophrenia or personality disorders.
- Diagnosis or history of severe, episodic bipolar disorder.
- Pre-existing cardiovascular disorders, including severe hypertension, heart failure, occlusive arterial disease, angina, congenital heart disease, cardiomyopathies, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias and channelopathies.
- Pre-existing cerebrovascular disorders (e.g. cerebral aneurysm, vascular anomalies and cerebrovascular accidents.
Side effects and adverse reactions
Ethylphenidate, as well as analogous stimulant compounds, can cause a number of side effects and adverse reactions in the user, can cause a series of adverse or side effects in those who consume it.These are the same as those that occur when consuming methylphenidate.
However, as a relatively new substance, the effects of its long-term and continuous use are not yet entirely clear, so caution is alwaysIt should also be borne in mind that, being a recreational substance
It should also be borne in mind that, being a recreational substance, intranasal consumption can cause damage to the nasal passages or bleeding.
However, among the most the most common side effects are the following:
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Insomnia
- Bruxism
- Sweating and tachycardia
- High blood pressure
- Chest pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Visual hallucinations
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Heat stroke or hyperthermia
Research chemicals
The term "research chemicals" refers to all those research chemicals or psychoactive substances that have not been internationally controlled and are generally sold through channels other than conventional pharmaceuticals (on the Internet, for example). They may also be known as "new psychoactive substances".despite the fact that some of them have been synthesized decades ago.
These substances appear on the drug market at a particular time and are often new in their availability, mechanism of action or synthesis. Often, the clandestine chemists who manufacture these new molecules are based on already known drugs and modify the structure of the drug's structure to make it more effective. and what they do is modify their chemical structure to attenuate or enhance certain desired effects.
Many of these compounds were sold and are currently sold on websites in Asian countries, with strange trade names and the appearance of "bath salts" or incense, always under the label that they are not suitable for human consumption, so that in this way the sellers do not have legal problems in certain countries.
Bibliographical references:
- Ho, J. H., Bailey, G. P., Archer, J. R., Dargan, P. I., & Wood, D. M. (2015). Ethylphenidate: availability, patterns of use, and acute effects of this novel psychoactive substance. European journal of clinical pharmacology, 71(10), 1185-1196.
- Krueger, J., Sachs, H., Musshoff, F., Dame, T., Schaeper, J., Schwerer, M., ... & Roider, G. (2014). First detection of ethylphenidate in human fatalities after ethylphenidate intake. Forensic science international, 243, 126-129.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)