Medulloblastoma: symptoms, causes and treatment.
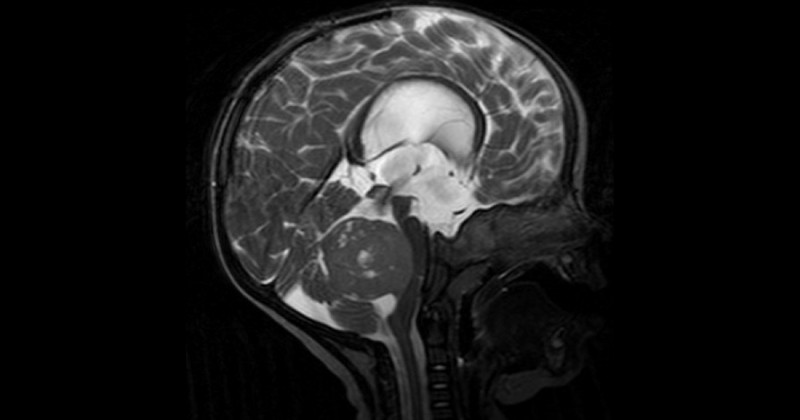
A type of brain tumor that appears especially during childhood, starting in the cerebellum.
Cancer encompasses a group of diseases caused by a disproportionate proliferation of cells in some organ of the body. Cancer affects both adults and children. Specifically, in the pediatric population, the most frequent cancer among brain tumors is medulloblastoma, a malignant tumor that affects both adults and children..
This type of malignant tumor affects the brain and can also reach the spinal cord. It involves excessive proliferation of embryonic stem cells. In this article we will know its characteristics, causes, symptoms, treatments used to eradicate it and survival rates.
Medulloblastoma: characteristics
Medulloblastoma is a type of brain tumor; specifically, it is a malignant, i.e. cancerous, brain tumor. Let us keep in mind that tumors are excessive and abnormal proliferations of cells in some organ of the body; tumors can be benign or malignant (cancer).
Medulloblastoma usually starts in the cerebellum, located at the bottom and back of the cerebellum.located at the bottom and back of the brain. This structure is responsible for coordinating movement and enabling balance. That is why one of its symptoms is impaired coordination, gait and balance.
This type of malignant tumor is usually distributed throughout the brain (and even the spinal cord) through the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a substance that protects these structures. It is rare for medulloblastoma to metastasize (spread of the tumor) to other parts of the body.
Prevalence and distribution.
Another characteristic of medulloblastoma is that it is a rare cancer; on the other hand, although it can appear at any age, it is most common in young children, it is young children who suffer most from it (most medulloblastoma (most medulloblastomas appear before the age of 16).
In the United States, for example, between 250 and 500 new cases of medulloblastoma are diagnosed each year, all of them children. In fact, it is the most frequent malignant brain tumor in children (between 15 and 25% of cases). In terms of gender distribution, it is slightly higher in boys than in girls. In adults, however, it accounts for only 1% of brain tumors.
Symptoms
The symptoms of medulloblastoma may vary from person to person. In addition, they may be caused by the medulloblastoma itself, or by the pressure it exerts on the brain. However, there are a number of frequently occurring symptoms, such as headaches, double vision, dizziness, dizziness, tiredness and fatigue.…
Coordination disturbances also occur. These can result, for example, in an unsteady gait (especially when the tumor has spread to the spinal cord). Both impaired coordination and unsteady gait are related to cerebellar involvement.. In addition, the person with medulloblastoma may manifest clumsiness, fall, drop objects, etc.
Another symptom of medulloblastoma is nausea, which usually appears in the morning.On the other hand, vomiting also appears, which gradually worsens in intensity and frequency.
On the other hand, if the malignant tumor has also reached the spinal cord, the symptoms may be the above plus the following: difficulty walking, back pain and problems controlling the sphincters.
Causes
The origin of cancer remains unknown. There is talk of a multifactorial cause, which varies depending on the type of cancer.. Factors related to the etiology of cancer include genetic factors, lifestyle factors (smoking, diet, exercise, etc.), infectious factors, chemical factors (exposure to substances, radiation, etc.), etc.
It is known, however, that cancer is caused by an excessive and abnormal proliferation of cells, which end up invading underlying tissues and even moving to more distant areas (metastasis). It is also known that the normal mechanisms of cell reproduction and division fail.
In the case of medulloblastoma, it is a type of embryonal tumor; this means that the tumor originates in embryonic stem cells. originates in the embryonic stem cells of the brain.. These cells can synthesize any other type of cell in the body.
Syndromes that increase your risk
We know that medulloblastoma is not hereditary; however, it has been found that some hereditary syndromes (such as Turcot syndrome or Gorlin syndrome) can increase the risk of developing medulloblastoma. some hereditary syndromes (such as Turcot syndrome or Gorlin syndrome) can increase the risk of developing medulloblastoma..
Specifically, Turcot syndrome (also called "brain tumor syndrome") is characterized by the presence of malignant neoplasms in the central nervous system. Gorlin syndrome, on the other hand, involves multiple malignant basal cell tumors and other associated neurological disorders.
Treatment
The treatment of medulloblastoma usually consists of a surgical procedure to remove the tumor, with subsequent sessions of chemotherapy, radiation therapy or both.. The treatment options usually followed are as follows:
1. removal surgery.
This has the objective of removing the medulloblastoma, and is performed by a neurosurgeon. An attempt will always be made not to damage the tissues adjacent to the tumor. Sometimes it is possible to remove the medulloblastoma completely and sometimes not (when it is located in very deep or delicate structures of the brain).
2. Surgery to reduce CSF
The aim of this surgery is to reduce the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, which occurs as a consequence of the growth of the medulloblastoma. This accumulation of CSF puts pressure on the brain, causing hydrocephalus.. This second treatment option is usually combined with the previous one.
3. Chemotherapy
This treatment option consists of administering certain drugs to kill cancer cells. with the aim of killing the cancer cells or to prevent them from dividing further. It is usually administered through an injection into a vein (so-called intravenous chemotherapy), both in children and adults, although drugs administered orally (pills) are also used.
Chemotherapy is generally used after surgery to remove the tumor, and is usually combined with radiotherapy, with the aim of eliminating any remaining tumor.
4. Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy, like chemotherapy, is widely used in patients with different types of cancer. It consists of administering high doses of radiation (X-rays or other types of radiation) with the aim of killing the cancerous cells and reducing or totally destroying the medulloblastoma, as well as stopping the proliferation of the cells.
The disadvantage of this treatment is that it also kills healthy cells, although more and more selective radiotherapies are currently being developed.
Survival rates
The likelihood of surviving a medulloblastoma will vary greatly depending on the type of tumor, age of onset, treatment used, areas affected, etc.
In addition, the survival rate changes if the tumor has or has not spread to the spinal cord; thus, if it has not spread, the survival rate is around 70/80%. If, on the other hand, it has expanded, the rate is around 60%.
Bibliographic references:
- Menon, G., Krishnakumar, K., Nair, S. (2008). Adult medulloblastoma: clinical profile and treatment results of 18 patients. J Clin Neuroscience, 15: 122-126.
- Peris-Bonet, R., Martinez-Garcia, C., Lacour, B., Petrovich, S., Giner-Ripoll, B., Navajas, A., et al. (2006). Childhood central nervous system tumours-incidence and survival in Europe (1978-1997): a report from the Automated Childhood Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer, 42: 2064-2080.
- Rodríguez-Mena, R., Barbella-Aponte, R.A., Gallego-Sánchez, J.M. and Barcia-Mariño, C. (2011). Adult medulloblastomas: surgical series of 11 cases. Neurosurgery, 22(6): 488-497.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)