Metacholine: what it is, characteristics, and how it is used in asthma testing
This bronchoconstrictor substance is used in Asthma diagnostic tests. Let's see how it is used.
Asthma is a respiratory problem that is not always obvious. It can occur when there are particles and pollutants traveling in the air environment that trigger the asthmatic response, and sometimes these particles are not so common.
However, given the seriousness of this condition, if it appears, the person can have a serious problem. For this reason it has become necessary to create specific tests to confirm in the most accurate way any case of asthma, and the methacholine test is one of them.
Methacholine is a bronchoconstrictive agent that is agent suitable for generating an asthmatic response in those suffering from the most masked disease. Let's see below what are the properties of this substance and how the test bearing the same name is performed.
What is methacholine?
Methacholine is a bronchoconstrictor agent that is used in the diagnosis of asthma, specifically the main symptom of this medical conditionbronchial hyperreactivity. It has its own test, called the methacholine test, and is indicated when other pulmonary function tests, such as generic spirometry, do not suggest a definitive diagnosis. This substance, once aspirated, produces miosis.
It is a non-selective synthetic cholinergic of the choline ester type.. It acts by binding to and activating the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system. Being very non-selective, this substance is highly activating for all muscarinic receptors and has a very limited effect on nicotinic receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Methacholine is a quaternary amine that is insoluble across the cell membrane. This is why it it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, nor can it be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract.. Once inside the organism, this substance is metabolized slowly, since it is very resistant to the action of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase.
It is hydrolyzed at a very slow rate, slower than that at which acetylcholine is hydrolyzed. This is why its action in the organism is more prolonged and it is almost completely resistant to hydrolysis by choline esterases or non-specific butyrylcholinesterases.
Uses
Methacholine is used as the primary test to confirm suspected asthma. The test in which methacholine is used is called the nonspecific bronchial challenge test or methacholine test. which basically serves to determine the existence of bronchial hyperreactivity, considered the main symptom of asthma.
It is the abnormal sensitization of the airways, caused by an increase in airflow obstruction after contact with specific stimuli.
What is the methacholine test for asthma?
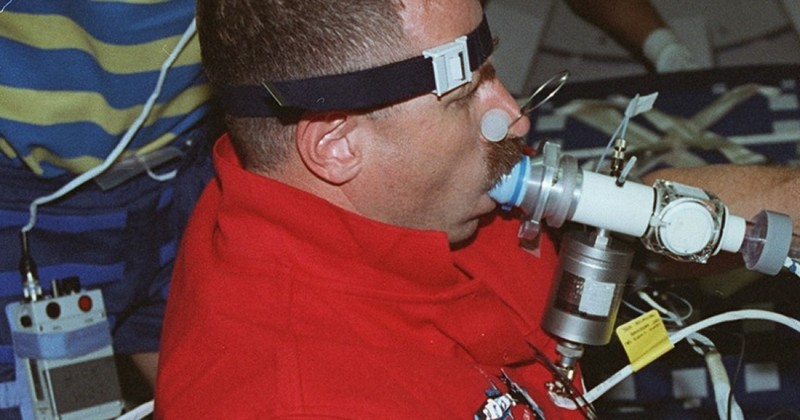
The methacholine test consists of doing, first, an initial spirometry, which will be accompanied by other spirometric testsThe purpose is to check the patient's lung capacity and to see how inhaling methacholine at different doses affects the patient. Methacholine is a drug with bronchoconstrictor action in people with asthma, i.e. it narrows their bronchi when they inhale this substance, reducing their lung capacity for a limited time.
In the initial spirometry, the person's baseline lung capacity is measured.. The patient makes a deep and maximum inspiration, filling as much air as possible in his lungs. Then, the mouthpiece is placed between the lips, exhaling, that is to say, blowing with all his strength the contained air for at least six seconds. This process will be repeated a minimum of three times.
Once the patient's pulmonary capacity is clear, methacholine is administered in increasing doses, and after each in increasing doses, and after each dose a new spirometry will be performed.
If the patient is showing a decrease in lung capacity greater than 20% with respect to the initial spirometry, the methacholine test will be considered positive. That is, it will mean that the patient is reacting to this substance, showing bronchoconstriction and losing lung capacity briefly. The lower the dose needed to drop more than 20%, the greater the degree of bronchial reaction of the patient.. The diagnosis of asthma will be confirmed.
Rarely, an asthmatic person will have a negative result in the methacholine test. Although in many cases the asthma is evident, there are those that are not so obvious, which is why this test is so necessary, making sure the diagnosis. There are people with asthma who may have had a very normal initial spirometry, without showing respiratory problems of any kind and with normal bronchodilation without the use of drugs.
This test is minimally invasive and is usually well tolerated by the patient, who will feel little discomfort.who will hardly feel any discomfort. The only minimally important discomfort is the time it takes to perform the test, and the need to perform several spirometries that require some pulmonary effort.
Requirements to be able to apply the test
In order to apply this test it is necessary for the patient to comply with a series of requirements and guidelines before attending the appointment with the pulmonologist. The patient must indicate if he/she has ever suffered from asthmatic signs or a respiratory infection in the last 6 to 8 weeks, as well as whether he/she has been immunized with vaccines in the last two months.The patient should also inform if he/she has been immunized with vaccines in the last two months. He/she should inform about possible pregnancy, heart disease or if he/she has had urticaria recently.
The patient should have avoided the consumption of the following substances during the following periods of time:
- Caffeinated beverages (coffee and tea): last 6 hours.
- Tobacco: no smoking the day before the test is performed.
- Inhaled bronchodilators: last 12 hours.
- Parenteral bronchodilators: last 12 hours.
- Short-acting oral bronchodilators: last 18 hours.
- Long-acting oral bronchodilators: last 48 hours.
Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions
The main precaution to be taken with the methacholine test is that it is performed under the supervision of a specialized physician. under the supervision of a specialized physicianThe main precaution to be taken with the methacholine test is that it should be performed under the supervision of a specialized physician, and that emergency equipment and medication should be available to avoid any unforeseen event. The risks and benefits of applying the test in cases of epilepsy, cardiovascular disease with bradycardia, vagotonia, peptic ulcer, urinary tract obstruction or other conditions that may be adversely affected by a cholinergic agent should be assessed.
There are several medical conditions in which the use of methacholine, along with the other muscarinic agonists, is contraindicated. Among them we find coronary insufficiency, peptic ulcers, myocardial infarction, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, myasthenia gravis, and myocardial infarction.myasthenia gravis and urinary incontinence. This is because the similar action of this substance with that of the parasympathetic system may aggravate symptoms in these medical problems.
Its use is also not recommended in cases of clinically apparent asthma or in cases in which hypersensitivity to other parasympathomimetic agents has been documented. It should not be used in treatments with beta-adrenergic blocking agents or cholinesterase inhibitors. Treatment for asthma and hay fever inhibit airway responsiveness to the test.
The application of this test may give false positives in diseases such as influenza, respiratory tract infections, very young or very old patients, chronic lung diseases, allergic rhinitis without asthma, smokers or people who have been exposed to airborne pollutants. In these cases, in addition to being able to have a false positive for asthma, there is a risk of severe bronchoconstriction and a highly dangerous reduction in respiratory function..
In case the patient is female and of childbearing age, it is necessary to find out if she is pregnant. No studies on the teratogenic effects of methacholine in animal reproduction have been carried out. It is not known whether methacholine hydrochloride can cause harm to the fetus or affect the patient's fertility. It should only be administered to pregnant women if clearly necessary. It is not known whether methacholine, when inhaled, is excreted in breast milk.
Adverse reactions and interactions
Among the main adverse reactions of methacholine are the following headache, irritation of the pharynx, sensation of loss of consciousness and pruritus (tingling sensation in the skin). The therapeutic use of this drug is limited due to its adverse cardiac effects, such as bradycardia and hypotension, which is doubled due to its function as a cholinergic agonist. Methacholine reacts very toxically in combination with 0.5 to 1 mg of atropine sulfate intramuscularly or intravenously.
Bibliographic references:
- Katzung, Bertram G. (2004). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (9th edition). ISBN 0-07-141092-9.
- Lötvall J, Inman M, O'Byrne P (1998). Measurement of airway hyperresponsiveness: new considerations. Thorax 53: 419-424. PMID 9708238.
- R. Asero, E. Madonini. (2006) Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is a common feature in patients with chronic urticaria. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol; Vol. 16(1): 19-23.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)