Tarlov’s cysts: symptoms, causes and treatment
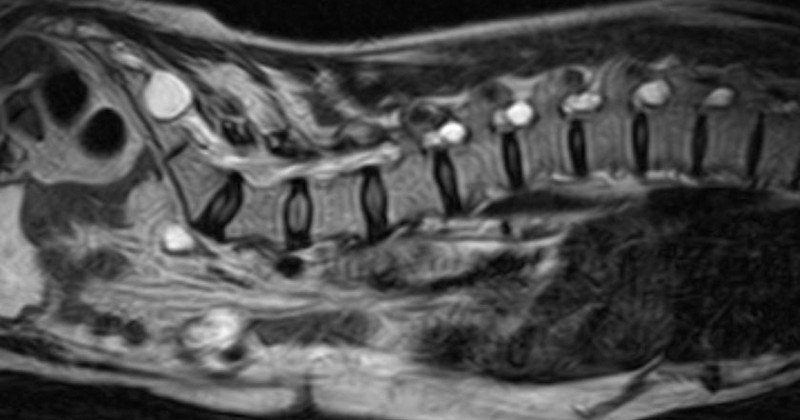
This pathology appears in the form of a malformation in the dura mater, a membrane of the meninges.
Occasionally and due to certain types of organic anomalies, our body produces and develops a series of abnormal masses formed by membranous bags that house substances or liquid elements produced by the body itself. Although in most cases they do not pose a danger to the physical integrity of the person, their effects can be quite annoying. This is the case of Tarlov cysts, which are abnormal formations that are produced by the body itself.abnormal formations that can appear in the lumbar or sacral area.
Throughout this article we will discuss the characteristics of these malformations, as well as the symptoms associated with them, their causes and possible treatments.
What are Tarlov cysts?
Also diagnosed as perineural, periradicular or extradural perineural, periradicular or extradural arachnoid cysts, Tarlov's cysts are small bodies containing a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid.Tarlov's cysts are small bodies containing a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
These cysts are formed by a dilatation of the dura mater, so they are classified as a pathology of this. They are anomalous formations that also have a stalk or prolongation that a stalk or prolongation that keeps them connected to the spinal subarachnoid space.They are also located around the nerves of the sacral and lumbar area, which are pressed or compressed by these cysts.
Although, as just mentioned, Tarlov's cysts usually affect the nerves located in the lower spinal column, these anomalous bodies are completely asymptomatic in the first phase of their development. That is to say, they do not necessarily entail the appearance of symptoms that give them away.
However, in cases in which the person suffers some trauma or inflammation, or when the compression of the nerves is very serious, the patient may experience pain in the lumbar areas. As well as symptoms of sciatica, urinary incontinence or headaches among many others that will be mentioned in the following point.
These pathological formations of the dura mater, which are are named after the North American neurosurgeon Isadore TarlovThese pathological formations, named after the American neurosurgeon Isadore Tarlov, have a much higher incidence in women and their symptoms can be reduced by means of a diet or an alkaline diet, among many other treatments.
What is the symptomatology?
The main characteristic of Tarlov cysts is that they are usually asymptomatic, at least in 70% of the people who suffer from them. However, in the remaining cases they can be highly annoying.
Due to the discretion with which they develop, they are most often discovered accidentally when the person undergoes some type of neuroimaging test such as a nuclear magnetic resonance and tend to be evaluated as formations without any type of pathological significance.
In some cases, during the early stages of their formation, symptoms may appear and develop either gradually or, on the contrary, a painful clinical picture may appear. a painful clinical picturesuddenly. Likewise, the severity or intensity with which the symptoms affect the individual will depend largely on the size to which the Tarlov cysts develop.
In most patients, symptoms begin with mild pain experienced at the same level at which the cyst is located.This is followed by a series of alterations in all those organs or functions related to the nerve on which the pressure is exerted.
Although at first they do not pose a threat or danger to the physical health of the person, without effective treatment, Tarlov cysts can cause very severe complications that seriously compromise the quality of life of the patient, who is susceptible to develop any kind of dependence or partial or complete physical disability.
Among the main symptoms that can manifest themselves are:
- Pain in the lumbar or sabra area.
- Pain of sciatic character.
- Pain at the level of the buttocks.
- Pain in the hip.
- Muscular pain in the thighs due to a decrease in blood flow.
- Complications in the excretory organs.
- Alterations in the reproductive organs.
- Decreased sensitivity or hypoesthesia.
- Tingling sensation or paresthesia.
As a result, people suffering from Tarlov cysts experience great difficulty in experience great difficulty in carrying out certain movements or postures, such as standing or attempting to sit. such as standing or attempting to sit. Likewise, walking, bending over or lying down can be a great torment due to the painful sensations they cause.
What causes it?
At the moment, a completely reliable cause of Tarlov's cysts has not been established. However, different theories have been developed over time, the main hypotheses of which relate these cysts to a traumatic, congenital and hemorrhagic origin.
1. Congenital hypothesis
This first theory points to the idea that certain irregularities in the formation of the membranes that envelop the brain known as meninges may be the main cause of the formation of these cysts; or a congenital alteration in the most superficial of these membranes, the dura mater.the dura mater;
2. Traumatic hypothesis
On the other hand, the traumatic hypothesis describes that injuries caused by spinal punctures, anesthesia applied in the peridural area or in the spinal area, as well as trauma involving the sacral area, are the most common causes of this condition. trauma involving the sacral area may also be the origin of the may also be the origin of the appearance of these cerebrospinal fluid masses.
3. Hemorrhagic hypothesis
As its name suggests, the hemorrhagic hypothesis is based on the assumption that the cyst is produced by hemorrhage. is produced by a subarachnoid hemorrhage..
How can it be diagnosed?
As noted above, Tarlov's cysts are most often diagnosed accidentally when the patient has a subarachnoid hemorrhage. are usually diagnosed accidentally when the person undergoes some type of neuroimaging test in the area where the cyst is located. performed in the area where the masses are located.
However, in cases where the person begins to experience the first symptoms, a functional MRI will be necessary. functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) will be necessary.. In addition, in order to rule out the possibility of any other type of condition, a computerized myelography should be performed to reveal a connection between the cyst and the subarachnoid space.
Is there a treatment?
The choice of one of the possible treatments available for Tarlov cysts is subject to the type of effects and symptoms experienced by the patient, as well as the size of the cyst and the results of physical tests.
In smaller cysts that do not cause very large or bothersome symptoms, intervention is usually resorted to by means of physiotherapy, together with the administration of Anti-Inflammatory or analgesic medication. or analgesic medication. Recent studies have shown that gabapentin, traditionally used for the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain, is highly effective in reducing the effects of cysts.
However, in more severe cases, the patient may have to undergo surgery. By means of a technique known as fenestration, the surgeon is able to the cyst and drain the cerebrospinal fluid inside. inside the cyst. The cyst is then sealed to prevent the possibility of the fluid replenishing.
Finally, a treatment that has proven to be quite effective in alleviating the pain of Tarlov cysts is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. This procedure has no side effects and consists of the application of small electrical currents through the skin.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)