Adenohypophysis: what is it, functions and hormones it secretes?
This is one of the parts of the brain most closely related to the endocrine system and our hormones.
Our body is made up of a large number of different structures, which in turn are made up of millions of cells.
In this great framework, we can find that there are a series of chemical substances secreted by the organism and whose action regulates to a great extent our behavior and allows phenomena such as growth, sexual behavior or the search for food. These are hormones, which circulate through the endocrine system, in which we can find different structures, some of them at brain level.
In this sense, the pituitary gland stands out, which in turn can be divided into several substructures. One of them, which we are going to talk about in this article, is the adenohypophysis. the adenohypophysis.
Adenohypophysis: definition and main functions
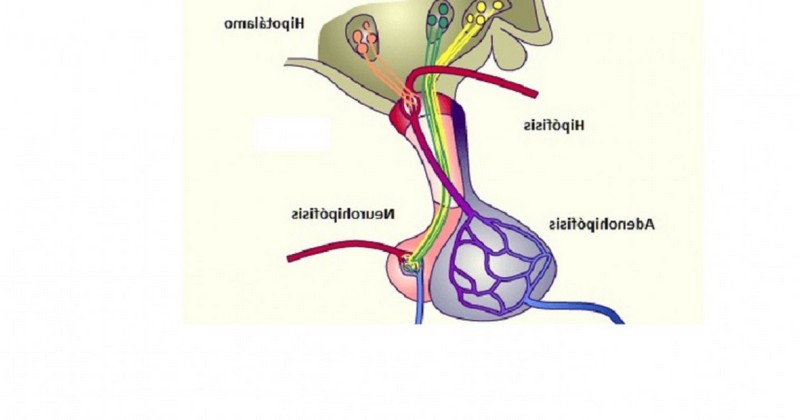
The adenohypophysis is the name given to the the anterior and largest portion of the pituitary gland.. This ovoid-shaped structure is located in the basal part of the brain, below the hypothalamus (to which it is connected by the pituitary stalk) and resting in the hollow of the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica.
It is a small brain region of great importance for our development as human beings, its main function being to regulate the release of a large number of hormones. It is therefore part of the neuroendocrine system, and in particular it is linked to hormones related to growth, metabolism and sexuality..
This brain region is highly vascularized and has a large number of gland-like cells. has a large number of glandular cells.. In this sense the adenohypophysis is made up of six major cell types, of which at least five are known to release the different hormones that the adenohypophysis secretes and regulates: somatotropic (releasing growth hormone), mammotropic (influencing the release of prolactin and thyrotropin), corticotropic (secreting ACTH), gonadotropic (linked to sex hormones), in this case follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone), thyrotropes (stimulate prolactin synthesis, but especially thyrotropin) and chromophobe (believed to serve to renew the possible loss of the previous ones).
Hormones governed by this structure.
The adenohypophysis, as we have seen in the previous section, has as its main function to secrete and regulate the levels of different hormones. These hormones are essential in generating and enabling different Biological processes. Among the different hormones it generates, the following stand out.
1. Corticotropin
Also known as adrenocorticotropic hormone, this substance is fundamental is fundamental in the generation of endogenous glucocorticoids, mainly affecting the glandsmainly affecting the adrenal glands. Its action generates the stimulation of different hormones by this cortex, which allow aspects such as metabolism (for example, it influences insulin secretion), homeostatic balance and inflammatory processes to be regulated.
2. Beta-endorphins
Beta-endorphins are another hormone released by the adenohypophysis. They are substances that act as endogenous opioids, generally associated with moderating, decreasing or even inhibiting the sensation of pain.. In turn, they generate sensations of pleasure and relaxation. It is generated during heavy exertion, pregnancy and childbirth.
3. Thyrotropin
A fundamental hormone that regulates thyroid function, stimulating the secretion of thyroid hormones and their regulation in the body.
4. Prolactin
This hormone is essentially known for being responsible for the production of milk in the mammary glands after pregnancy. after pregnancy (although the hormone itself begins to increase in quantity during pregnancy). Apart from this action, it also influences the growth of the breasts, the inhibition of menstruation and the male refractory period.
5. Follicle-stimulating hormone
An essential substance in the field of reproduction, follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates the production of oocytes and estradiol in women (the same is true for the formation of sperm in men). In addition, it also has an effect on physical development and sexual maturation..
6. Luteinizing hormone
This hormone is deeply linked to reproduction and the corpus luteum, one of its best known roles being that of triggering the ovulation process. In the male it also plays a role in reproduction and sexuality, since it stimulates the production of testosterone. stimulates the production of testosterone by the Leydig cells of the testes. of the testes. It also contributes to the genesis of progesterone, so as to facilitate the implantation of a possible fertilized egg.
7. Somatotropin or growth hormone
This hormone is essential, as its name suggests, for the stimulation of growth and physical development. Muscles and bones are affected by this hormone, among other structures. Also It is also associated with the consumption and metabolism of fats and nutrients and their utilization in the body. and their utilization in the body.
Alterations linked to this brain structure
The adenohypophysis is a fundamental structure for the human being, and its alteration or lesion can generate different disorders and consequences of variable severity.
In this sense it is possible to find that its dysfunction can generate growth alterations, among which we can find various types of dwarfism and gigantism (due to hormone (due to deficit or excess of growth hormone). The role of the adenohypophysis in the generation of thyroid hormones means that its dysfunction is linked to hypothyroidism (by defect) and hyperthyroidism (by excess).
It can also affect reproductive function, affecting both libido (for example, hyperprolactinemia may occur) and the formation of hormones and sex cells themselves. For example, in the case of women, problems could appear or even the cessation of menstruation and the ability to produce eggs. Finally, it can also can generate or affect metabolic alterations (including diabetes) and (including diabetes) and cause problems in metabolizing and utilizing elements such as fats and carbohydrates.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)