Angular gyrus (cerebrum): areas, functions and associated disorders.
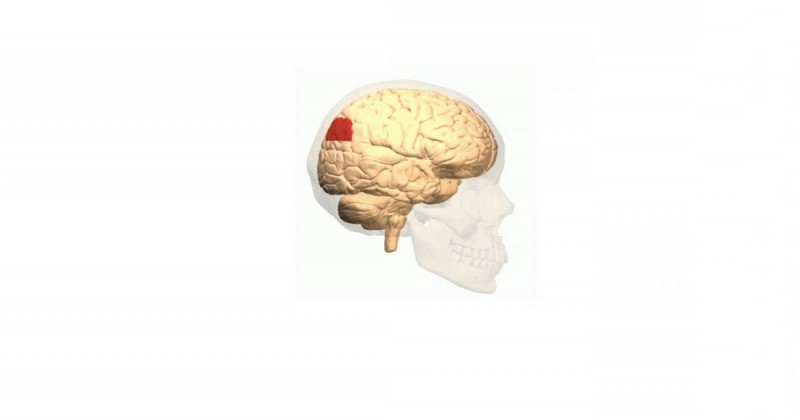
This part of the cerebral cortex is involved in mental processes related to language and calculation.
A person's ability to understand what he or she hears or reads is something that is done so automatically that we rarely stop to think about which brain structures make this possible.
These and many other functions are specific to the angular gyrus of the brain. Throughout this article we will talk about what it is, where it is located, what are its functions and what happens when it does not work properly.
What is the angular gyrus?
The cerebral gyri refer to those mounds formed in the brain, caused by the folds of the cerebral cortex.. One of them is the angular gyrus, this gyrus is located in the posterior area of one of the cerebral convolutions; specifically in the one located between the intraparietal sulcus and the horizontal branch of the Sylvian fissure.
In addition, the angular gyrus corresponds to Brodmann's area 39which, together with area 22 and 40, form Wernicke's area. This region of the temporal lobe is the so-called auditory associative cortex and its main function is to enable people to understand words and have the ability to produce meaningful speech.
A lesion in this area of Wernicke's can cause both verbal deafness and blindness.. Verbal blindness, or alexia, is the inability to understand written words, while verbal deafness, or auditory-verbal agnosia, is the inability to understand heard words.
Finally, the angular gyrus is associated with language interpretation as well as with mathematics and cognition, integrating information from other areas of the brain.It integrates information from other areas of the brain. Next, we will see what implications the angular gyrus has on the different brain functions.
What are its functions?
As mentioned above, the angular gyrus is responsible for aspects related to language production, calculation and mathematical skills, visuospatial ability and some cognitive aspects. These are functions acquired through experience, but which are supported by the Biological predispositions of the human brain when it comes to learning. That is, without proper stimulation, this part of the brain will not develop well.
The following is a breakdown of all the functions that the angular gyrus performs in the brain, these functions are presented below.
1. Language
Given its involvement in the functions of Wernicke's area, the angular gyrus plays a fundamental role in the production of meaningful sentences and phrases. a fundamental role in the production of meaningful sentences and phrases..
It is also one of the areas responsible for written verbal comprehension. That is, thanks to it, people can understand what we read.
2. Calculation
Regarding the functions related to calculation and mathematics, the angular gyrus intervenes in the person's ability to perform the mathematical operations necessary to obtain a result, a value, a value, a value, a value, a value, a value. necessary to obtain a result, a value or to solve any type of mathematical problem.
On the other hand, it is also involved in the learning of arithmetic or basic mathematical operations and in the interpretation of numerical quantities and dimensions.
3. Visual
The angular gyrus is involved in the spatial focusing of attention, that is, in the orientation and spatial search of visual stimuli.
In addition, it is also responsible for visuospatial processing, it is also responsible for visuospatial processing.. Thanks to visuospatial processing, people can identify where objects are located in space, as well as the distance between them or between us and them.
4. Other functions
Finally, there are a multitude of functions in which angular gyration plays a more or less significant role.
Among these functions, the following stand out:
- Involvement in creative verbal tasks.
- Executive control of behavior..
- Processing of sequences of actions.
- Symbol reading and coding.
- Involvement in Theory of Mind.
Theory of mind is a term that refers to a person's ability to perceive and identify the thoughts and purposes of others and assign them to the possible person who emits them.
What if it is injured: Gerstmann's syndrome?
If due to an injury or a neurodegenerative process, the angular gyrus suffers some kind of damage, the above functions can be seriously affected.
There is also a specific syndrome associated with an injury or impairment of this area known as Gerstmann's syndrome.
This neurological disorder has been associated with damage or defective activity of the angular gyrus.. It is characterized by presenting very little incidence in the population and by manifesting itself through a set of symptoms related to sensation, perception and the codification of information coming from the different senses.
Symptoms of Gerstmann's syndrome
Among the most representative symptoms of this condition we find the following.
1. Digital agnosia
This is one of the main symptoms of Gerstmann syndrome. This type of agnosia is distinguished by causing in the person the inability to distinguish or identify the fingers of the hand, both their own and others.
This agnosia is not associated with any type of fragility or lack of tactile perception of the fingers. or lack of tactile perception of the fingers. The person is simply unable to name, choose, identify or orient his or her own fingers.
2. Acalculia
Acalculia consists of the appearance of difficulties related to mathematical and arithmetic skills. Within this symptom, the person may manifest different types of deficits:
- Inability to perform mathematical operations both written and mental.
- Problems interpreting mathematical signs.
- Problems to maintain or continue numerical orders or series.
- Inability to design sequences.
- Difficulties in using numbers correctly..
3. Agraphia
As far as written language is concerned, people with Gerstmann syndrome suffer from a deficit in the ability and capacity for writing. Also known as agraphia.
These patients show problems in the transcription of heard words, in spontaneous writing and in copying.
Also, other symptoms of agraphia are:
- Alteration in the ability to correctly trace letters.
- Lack of symmetry of the letters.
- Changes in the orientation of the lines in writing.
- Use of several typographies.
- Invention of own characters.
4. Spatial disorientation
Patients with lesions in the angular gyrus may also present problems in distinguishing between left and right.. Thus, there appears to be a deficit in the lateral orientation of one's own body in space.
In addition, these patients present great problems in identifying the left or right plane of any object, place, spatial situation or even the parts of one's own body.
Bibliographical references:
- Hirnstein, M.; Bayer, U.; Ellison, A.; Hausmann, M. (2011). TMS over the left angular gyrus impairs the ability to discriminate left from right. Neuropsychologia. 49(1): pp. 29 - 33.
- Lee, H; Devlin, J.T.; Shakeshaft, C.; Stewart, L.H.; Brennan, A.; Glensman, J.; Pitcher, K.; Crinion, J.; Mechelli, A.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Green, D.W.; Price, C.J. (2007). Anatomical traces of vocabulary acquisition in the adolescent brain. J Neurosci. 27(5): pp. 1184 - 1189.
- Vatansever, D.; Manktelow, A. E.; Sahakian, B.J.; Menon, D. K.; Stamatakis, E.A. (2017). Angular default mode network connectivity across working memory load. Human Brain Mapping. 38(1): pp. 41 - 52.
- Rushworth, M.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H. (2006). Connection patterns distinguish 3 regions of human parietal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 16(10): pp. 1418 - 1430.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)