Cerebral angiography: what is it and what disorders can it detect?
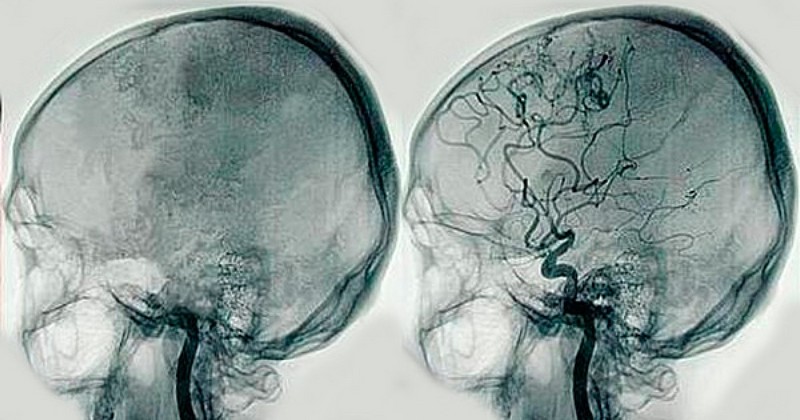
This diagnostic technique allows us to know how Blood flows in the brain.
All our organs need the performance of the cardiovascular system to survive, because thanks to it they receive the oxygen and nutrients necessary for their subsistence and correct functioning.
This includes our nervous system, which requires a continuous supply of these elements. But sometimes there may be alterations that damage the vascular system that irrigates the brain or symptoms that suggest the existence of such damage.
It is therefore necessary to have different techniques that allow us to observe and analyze the blood flow of the brain, one of the best known being angiography. one of the best known is cerebral angiography..
- Recommended article: "The 15 most common neurological disorders".
What is cerebral angiography?
Cerebral angiography is a medical evaluation technique that allows the study and analysis of brain flow and the health of the cerebrovascular system. It is a technique in which X-rays are X-rays are used to visualize, by injecting a contrast agent into the main cerebral blood vessels, the flow and state of the the flow and state of the circulatory system. The images obtained are generally very clear and make it possible to accurately identify alterations in the blood circulation of the brain.
The procedure is as follows: after placing the patient on the X-ray table, the head is immobilized and a sedative is administered while cardiac activity is monitored. After that, a catheter is inserted into the arteries of the arm or leg, which will be guided through the artery to the neck with the help of the X-ray. Once there, a contrast solution is injected through the catheter in order to subsequently take images of the blood circulation by means of X-rays. After that, and unless some kind of intervention has to be performed through it, the catheter is removed and pressure is applied to the area through which it has been introduced in order to prevent bleeding.
Although it is generally used as a technique for the diagnosis and monitoring of cerebrovascular disorders, the fact that a catheter is used to perform it allows therapeutic procedures such as the administration of drugs to be used in addition, which may obviate the need for other treatments.
Types
Cerebral angiography is a technique that has several variants depending on the mechanisms used to evaluate the state of the patient's blood vessels. Some of the best known are the following.
1. Conventional angiography (by intra-arterial digital subtraction).
This is the procedure described above, in which the catheter is placed in the artery and guided to its target. It is an invasive procedure that is usually the most common due to its efficiency and the high level of sharpness it allows. The catheter is usually introduced via the femoral route, through the groin to the aortic arch, where, after an initial injection of contrast, the catheter is placed in the artery to be analyzed.
As regards digital subtraction, it refers to the fact that the skull is often digitally removed from the image taken in X-rays, so that the image of the blood vessels can be seen more clearly.
2. Helical Computed Tomography Angiography
In this case, no catheter is introduced into the subject's body, but it does require the injection of a contrast agent in order to obtain the CT image. It is less invasive than its conventional counterpart.
3. Magnetic resonance angiography
In this type of angiography no catheter is used either, and it is not an invasive technique. It involves the performance of a magnetic resonance, not using radiation as in other cases.
What can be diagnosed?
Cerebral angiography is a test that is still used today as one of the main tests to diagnose is still used today as one of the main tests to observe the circulatory flow and the state of the blood vessels of the brain.. There are many disorders and diseases that the application of this technique allows to observe.
1. Cerebrovascular accidents or strokes
Angiography makes it possible to observe the existence of extravasation and ruptures of blood vessels, or the absence or obstruction of circulation in some area of the brain. It is for this reason that is a valid technique both to detect ischemia and to visualize cerebral hemorrhages.. (More information on strokes).
2. Aneurysms
The use of angiography allows to detect the presence of aneurysmsThe use of angiography makes it possible to detect the presence of aneurysms, bulges in the arterial wall filled with blood and with a relatively weaker wall that can rupture. (More information on aneurysms).
3. Tumors
The presence of tumors in the brain tends to cause disturbances in the blood flow of the brain, as well as to cause phenomena such as brain tumors.and cause phenomena such as cerebrovascular accidents. For this reason, angiography makes it possible to observe the presence of abnormalities generated by the presence of tumors. (More information on brain tumors).
4. Malformations
The existence of congenital malformations, as occurs in AVM, can also be assessed by this evaluation and diagnostic technique.
5. Arterial or venous alterations
Cerebral angiography can be used to determine whether the blood vessels of the brain are in good health, whether they are inflamed or whether disorders such as atherosclerosis are present.
6. Brain death
Cerebral angiography is also used to assess whether or not brain death is present. Specifically, it evaluates whether or not there is blood flow, observing an absence of irrigation in cases of encephalic death.
7. Other disorders
Cerebral angiography can be used to observe the presence of different disorders and diseases other than those mentioned above. For example, alterations can be found in neurosyphilis, or in people with disorders such as Kleine-Levine syndrome.
Risks and possible side effects of this technique
Cerebral angiography is a generally safe technique that does not tend to cause complications, but this does not prevent it from having risks and adverse side effects that can cause alterations of varying severity.However, this does not prevent it from having risks and adverse side effects that can cause alterations of varying severity.
One of the risks is the possibility that the patient may be allergic to the contrast applied (generally iodinated). Likewise, it could cause discomfort or even destruction of some tissues if it leaks out of the vein. It may also be risky or harmful for people suffering from kidney problems or diabetes.
The existence of symptoms such as tingling, breathing difficulties, vision problems, infection of the pathway through which the catheter has entered, problems controlling the limb in which the catheter has been inserted, speech problems or hemiparesis are a sign that there may be some type of complication that needs to be treated quickly.
Finally, special caution is necessary in the case of pregnant or breastfeeding women, since the radiation emitted could be harmful. It may also happen that a tear of the artery is provoked that generates some type of hemorrhage or clots that may plug the vessel, although this is very uncommon.
Bibliographic references:
- Camargo, M.; Peralta, A.; Arias, W.; Mercado, C.; Laguna, Y.; Cuellar, J.; Laforcada, C.; Paz, G.; Durán, J.C.; Aramayo, M.; Fortún, F. & Núñez, H. (n.d.). Stroke Protocol. Bolivian Society of Neurology.
- Millán, J.M. & Campollo, J. (2000). Diagnostic value of cerebral angiography in the confirmation of brain death. Advantages and disadvantages. Med. Intensiva, 24 (3); 135-141. Madrid.
- Daroff, R.B.; Jankovic, J.; Mazziotta, J.C. and Pomeroy S.L.. (2016). Bradley's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)