Crouzon syndrome: symptoms, causes and intervention
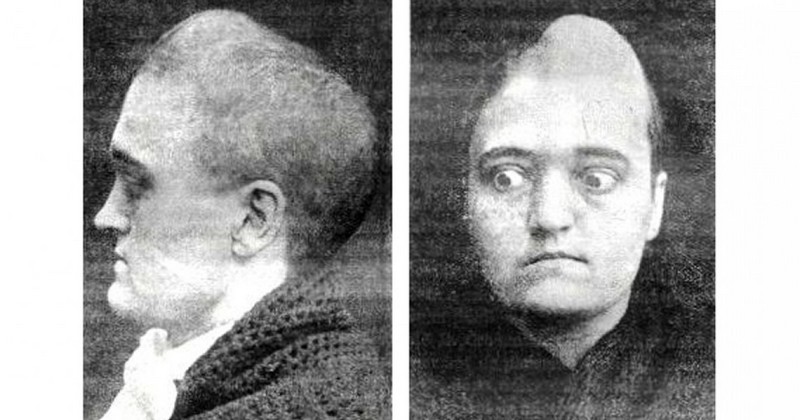
This congenital disease causes the bones of the skull to join together prematurely.
At birth, most human beings have a malleable skull which allows us to come into the world through the birth canal. These bones will close and suture with age, as our brain grows in size and matures.
However, there are cases of different disorders in which this suturing occurs prematurely, which can affect both the morphology and functionality of the brain and various facial organs. One of the disorders being discussed in people with Crouzon's syndrome, a disorder that can affect both the morphology and functionality of the brain and various facial organs. Crouzon syndrome, a hereditary disorder of genetic origin. of genetic origin.
The Crouzon Syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is a disease of genetic origin characterized by the presence of a premature craniosynostosis or suture of the skull bones. This closure causes the skull to grow in the direction of the sutures that remain open, resulting in malformations in the physiognomy of the skull and face.
These malformations can lead to serious complications for the correct development of the encephalon and the and the set of organs that make up the head, problems that will be manifested over time as the child grows.
Symptoms of Crouzon syndrome
The symptoms usually appear around two years of age of the child, not being generally visible at the moment of birth.
The most obvious symptoms are the presence of a bulging of the skull with flattened upper and/or posterior parts, as well as exophthalmos or projection of the eyeball outwards due to the presence of shallow ocular orbits, a compressed nasal cavity that hinders breathing through this route, cleft palate and other facial and oral malformations such as prognathism or forward projection of the jaw or alterations in the dentition.
However, the most relevant and dangerous are respiratory and feeding difficultieswhich can be life-threatening. Hydrocephalus and other neurological disorders are also possible. Intracranial pressure is also higher than usual, and seizures may occur.
All of these difficulties can cause the child to have severe problems as he or she grows, such as dizziness, frequent headaches and perceptual problems. in both vision and hearing.
With regard to ocular ocular alterationsThe prominence of the eyes makes them prone to infections and even to atrophy of the visual system, which can lead to loss of vision.
In addition, facial malformations make it difficult to learn oral communication, which tends to generate a delay in learning. In any case, although these malformations could affect intellectual development, in most of the cases Crouzon syndrome subjects usually have an intelligence in the average corresponding to their developmental age. corresponding to their developmental age.
Causes of this syndrome (etiology)
As mentioned above, Crouzon syndrome is a congenital and hereditary disorder of genetic origin. Specifically, the cause of this syndrome can be found in the presence of mutations in the FGFR2 geneThis gene is involved in cell differentiation, and its mutation causes an acceleration of the suture process of some or all of the skull bones.
It is an autosomal dominant diseaseA person with this mutation has a 50% chance of transmitting the disease to his or her offspring.
Treatment
Crouzon syndrome is a congenital condition with no cure, although some of its complications can be avoided and/or the impact of its consequences can be reduced. Treatment should be interdisciplinarywith the help of professionals from different fields such as medicine, speech therapy and psychology.
Surgery
In a large number of cases part of the problems can be corrected by surgery. Specifically, cranioplasty can be used to try to give the child's head a shape that allows for the normative development of the brain. that allows the normative development of the encephalon and to alleviate the intracranial pressure (thing that also allows to avoid to a great extent the habitual headaches that they usually suffer, product in many cases to this pressure). It can also be used to treat a possible hydrocephalus derived from abnormal brain growth.
Likewise, it can be of great utility in the surgical intervention of the nasal and buccophonatory passagesThis will facilitate breathing and the passage of food through the Gastrointestinal tract and resolve problems such as prognathism and cleft palate. Dental surgery may also be necessary, depending on the case.
The eyes may also benefit from treatment by surgery, reducing exophthalmia as much as possible and thus the possibility of the visual organs drying out or becoming infected.
Speech therapy and education
Because of the difficulties that can be caused by malformations in the malformations of the phonatory systemThe use of the services of speech therapists is very useful. The language can be altered and delayed, so it is necessary to take into account their difficulties and provide appropriate support. In cases of intellectual disability, this should also be taken into account when adjusting the child's education and training.
Psychotherapy
Psychological treatment and counseling for the child, family and educators is essential in order to understand the situation of the affected person and to allow the expression of doubts and fears and the resolution of psychological and educational problems. and the resolution of psychological and emotional problems. The child and his or her environment are affected by the experience of the disorder.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)