Glabellar reflex: what is it and how does it occur?
This physiological phenomenon helps to detect lesions in the nervous system.
Reflexes are rapid reactions that occur upon contact with a specific stimulus, or in a specific manner. The glabellar reflex is one of these reactions, which do not that do not involve the higher functions of consciousness to any extent. Let's see how it is.
What is the glabellar reflex?
As is the case with all reflexes, the glabellar reflex is a process in which the sensory neuron conducts the impulse directly to the motor neuron, which is in charge of sending the impulse to the motor neuron, which sends the impulse to the motor neuron.which is in charge of immediately sending the response to a muscle, which executes the action of the reflex act.
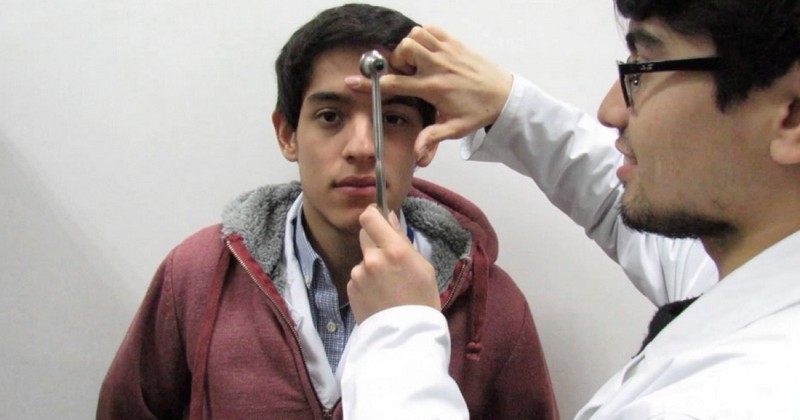
This reflex happens when the center of the forehead is struck repeatedly.The glabellar reflex is produced in the glabellar area, a little above the end of the nose, so that the eyes cannot come into contact with the examiner or with the object that strikes the glabellar area.
Once the glabellar zone has been struck, as described above, in a brief but energetic manner, the glabellar reflex is produced, which consists of a constant and abnormal blinking on the part of the examined subject..
What nerve is involved in this reflex?
During this reaction, the trigeminal nerve, which is the V cranial nerve, is mobilized. This nerve is located in the protuberance of the brainstem, and from there it extends to the ganglion. from there it extends to the Ganglion of Gasser.. This ganglion is the largest sensitive root, and is located in the middle cranial fossa, hence, its neuronal bodies are divided into three parts: the ophthalmic branch (V1), the maxillary branch (V2), and finally, the mandibular branch (V3).
Depending on which branch is stimulated, by means of a contact or a visual stimulus we will be able to observe a different reflex in the eyes or in some area of the subject's face.
When touching the forehead area above the nose (glabellar area), with the tapping and the form described above, what we are doing is to stimulate the ophthalmic branch of the eye. stimulating the ophthalmic branch (V1) of Gasser's ganglion, which is linked to the glabellar ganglion.which is linked to the trigeminal nerve (V cranial nerve).
All these connections must be working properly for the reflex to occur, if there is any interference or anomaly at any point, then the synapse could not occur properly.
Therefore, the afferent neuron of this reflex, which belongs to the facial nerve (III cranial nerve) would not send any signal to the Muscle for it to move, and the reflex would not occur. Taking into account that the III cranial nerve (facial nerve) also intervenes in this reflex, by means of the efferent neuron, then it is understood that the reflex of the glabellar area is of trigeminal-facial origin. is of trigemino-facial origin..
The importance of this physiological phenomenon
This reflex is essential for the protection of exaggerated stretching of the muscles, in this case the muscles of the eyelids. The glabellar zone reflex is responsible for preventing the eyelids from being damaged, which in turn represents an important protection for the eyes.
This evaluation is really simple to perform by the examiner, since it is not invasive. It is part of the person's routine physical examination, and can detect with great accuracy if there is any damage to the spinal cord..
Medical evaluation
The examiner should be attentive to the reflex response in both eyelids; if the blinking is not symmetrical on both sides, it is indicative of neurological damage. is indicative of neurological damage. If so, it will be necessary to determine exactly where the damage is located, whether in the afferent or sensitive pathway, in the reflex processing center (interneuron), the efferent or motor pathway, or in the effector muscle.
For the evaluation of this reflex to be satisfactory, it is necessary for the person being evaluated to be in a state of complete muscle relaxation. Otherwise, the muscle will not react to the stimulus in the expected manner.
Sometimes it is difficult for the it is difficult for the evaluator to get the patient to relax sufficiently. to apply the evaluation method, when these complications occur, a series of techniques can be used to achieve the proper state of relaxation in the subject.
Examples of techniques
Some of these techniques are as follows.
1. Use the Jendrassik maneuver.
This procedure helps to obtain the reflex act by means of abrupt movements in the area where the response is sought.
For example, in the case of the glabellar area, the examiner will ask the subject to blink his or her eyes. will ask the subject to blink rapidly before proceeding with the evaluation..
Relaxation techniques
It is convenient to use them before applying sharp percussion on the muscle tendon.
Bibliographical references:
- Purves (2004). Neuroscience: Third Edition. Massachusetts, Sinauer Associates, Inc.
- Derrickson (2006). Principles of Anatomy and Physiology.
(Updated at Apr 12 / 2024)