Management grid: what it is, and the 5 types of leaders it describes.
A tool that describes the general objectives of management and how to lead.
Also known as a management network, the management grid is a tool used for describing leadership style.. It also specifically identifies five leadership styles that blend different levels of concern for the task and for people.
Leadership dimensions in the management grid
The managerial mesh model was created by Blake and Mouton (1969), who offered a schematic system through which attitudes toward positions are shown in relation to the tasks to be performed and the people involved.
Their theory is based on the 9x9 Grid for which they were responsible for creating a very objective way of graphically represent the two-dimensional view of leadership styles.. Thus, for Blake and Mouton there are two basic dimensions of effective leadership.
On the one hand, there is concern for people, i.e, the concern of managers with human relationsOn the one hand, there is the concern for people, i.e., the concern of managers for human relations, for satisfying the motives of the group's components, which are not necessarily related to the organization's objectives, thus achieving considerable group cohesion.
Concern for production, on the other hand, is the degree to which managers are concerned with human relations, to satisfy motives The interest in production, on the other hand, is the degree to which managers are concerned and interested in the achievement of the objectives of the organization..
These two dimensions are called people orientation and production orientation, respectively. These factors are present in all managers, taking into account that each individual is unique and therefore they are combined in different proportions in each subject.
These dimensions are analogous to the "structure initiation" and "consideration" dimensions of earlier Ohio State University studies and with the typical traits of "employee-centered" leaders formulated by the Michigan University studies.
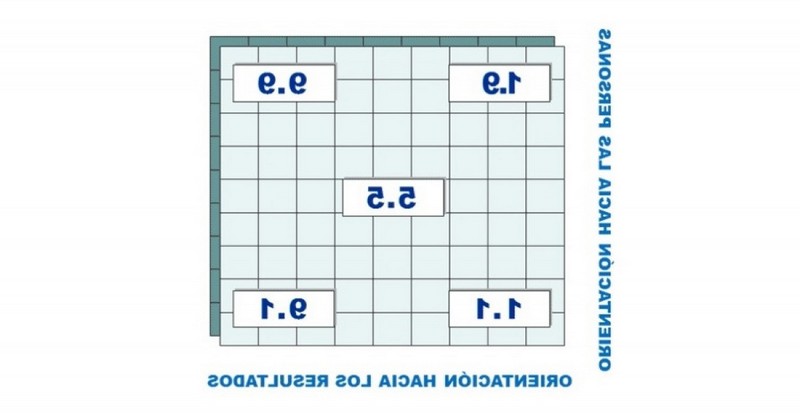
Blake and Mouton's Management Grid
These management styles described in the management grid can take 5 points as a reference:
On the other hand, the leadership styles according to the managerial grid are as follows.
1. Style 1.1: Impoverished
It is characterized by minimal concern for both results and team members.. It cannot be properly called management, since the manager has hardly any influence on the configuration of the work/professional activity of his work group, nor on human relations.
Nor does it seek group cohesion. It follows the law of minimum effort, so it does not try to improve the efficiency of organizations or the welfare of workers. If complications arise, it disappears. It is present and absent at the same time.
2. Style 1.9: Country Club
In the upper left corner of the grid is the "country club style", which is characterized by a large number of employees.which is characterized by a strong concern for people and little concern for production tasks. Managers who employ this style try to create a comfortable and safe environment. They also trust their subordinates to respond with high performance.
Concern for meeting social satisfaction needs leads to a friendly, though not necessarily productive, atmosphere and pace of work..
3. Style 9.1: Produce or perish.
Represents a maximum intensity orientation to results and minimum to people. Production interests are strongly emphasized.
The boss adopts his directive function based on his hierarchical rank, while the personnel under his charge receives instructions on the task to be performed, their main characteristic being obedience.while the personnel under his charge receives instructions on the task to be performed, being obedience its main characteristic.
This style assumes an authoritarian style of managementIn this style, the principle to be followed by the manager is performance, but he is not at all interested in interpersonal relationships, since they may disturb the smooth running of the work.
Subjects are only means to an end, human relations are based on authority and obedience. It would relate to an attitude towards people at work characteristic of Theory X.
4. Style 5.5: Balanced
In the middle of the grid is the "balanced style". Managers who apply this style believe that the needs of people and organizations are in conflict, and therefore it is difficult to satisfy both.
They believe that the best that can be done is to find an acceptable balance between the needs of the workers and the production goals of the organization. of the organization. Ideal performance is achieved by maintaining employee morale at a sufficient level to get an adequate amount of work done.
5. Style 9.9: Team
Finally, in the upper right-hand corner of the grid is the "team style," which is characterized by the utmost concern for the is characterized by the utmost concern for results as well as for human relations..
This direction considers both the interests in productivity and the interests in the motives of the subjects involved in it, it contains a high degree of compatibility between the objectives of the employees and the organization.
Within the five styles of Blake and Mouton's management grid, this turns out to be the ideal one.
Bibliographical references:
- Blake, R.; Mouton, J. (1985). The Managerial Grid III: The Key to Leadership Excellence. Houston: Gulf Publishing Co.
- McKee, R.; Carlson, B. (1999). The Power to Change. Austin, Texas: Grid International Inc.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)