Mesocortical pathway: structures, functions and role in psychoses.
This network of interconnected nerve cells is very important for the functioning of the brain.
Within a person's nervous system there are hundreds of thousands of neurons that make up its networks and are responsible for transmitting both electrical impulses and certain substances from one side to the other.
The mesocortical pathway is the network of neurons that runs through the brain and exerts a primary control over the brain. and that exerts a primordial control in the thought, the emotions and the feelings.
What is the mesocortical pathway?
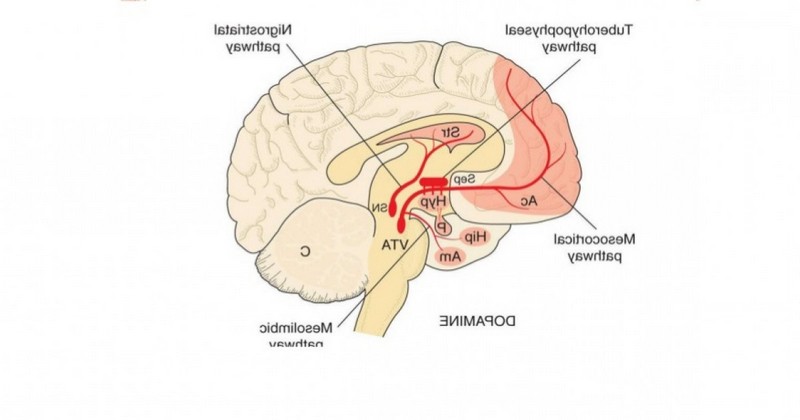
It is known as mesocortical pathway to the route or bundle of neurons that unite the ventral tegmental area and the cerebral cortex, especially at the level of the frontal lobe. The mesocortical pathway is one of the most important pathways of the dopaminergic system, playing an extremely important role in cognition, as well as in emotions and affectivity.
Lesions or alterations in the mesocortical pathway are common in certain psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia such as schizophrenia, which is hypothesized to be the cause of the cognitive and negative symptomatology of this disorder.
Within the dopaminergic system, we also find other pathways whose main task is to transporting dopamine from one part of the brain to another.. The neurons that make up these pathways are formed by somas that synthesize dopamine, while the axons are responsible for transmitting it along the entire pathway.
These pathways that accompany the mesocortical pathway and form the dopaminergic system are:
- Mesolimbic pathway.
- Mesocortical pathway.
- Nigrostriatal pathway.
- Tuberoinfundibular pathway.
Parts and structures
As mentioned above, the mesocortical pathway mainly involves the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and the cerebral cortex. In addition, this connection is made at the level of the frontal lobe, this connection is made at the level of the frontal lobe..
1. Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is an area of the cerebral cortex located in the anterior area of the brain, its main characteristic being that it is only fully developed in the most complex animals such as vertebrates, mainly hominids.
Among the functions of the frontal lobe are linguistic and oral production, as well as phonoarticulatory movements. In addition, the frontal lobes have the very important mission of coordinating the executive functions. These functions are the ones that provide the capacity to direct behavior, attention, planning, sequencing and sequencingsequencing and reorientation of behavior.
- Related article, "What is the frontal lobe and how does it work?"
2. Ventral tegmental area
This area also known as ventral tegmentum is formed by a group of neurons located in the midline of the floor of the midbrain.
This area is the origin of the mesocortical dopaminergic pathway and its function is to regulate the brain's natural reward system. Therefore, it has a fundamental role in motivation, pleasure and orgasm, addictions, amorous feelings and in some psychiatric disorders.
3. Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral cortex, is formed by the network of neurons that form the tissue covering the extension of both cerebral hemispheres.
Its functions are focused on governing perception, imagination, thought and reason..
Its involvement in brain functions
Like the other dopaminergic pathways, the mesocortical pathway plays an important role in a number of essential brain functions. has a very important role in a series of brain functions essential for the mental health of the person. for the mental health of the person.
These functions are, on the one hand, cognition as an executive function, and emotions and affectivity on the other.
Cognition
By cognition we mean the capacity of people to process the information they receive from the environment through perception, as well as the interpretation and meaning they give it.
Cognition is used in a large number of processes such as learning, reasoning, attention, memory or problem solving..
2. Emotions and affectivity
An emotion is a psychophysiological response to a certain stimulus; whether it is a person, a place or situation, an event or the person's own memories.
At the psychological level, emotions generate changes in attention and activate or inhibit certain behaviors. It also has the ability to strengthen associations, it also has the capacity to strengthen important associations in the memory..
As far as affectivity is concerned, while emotions are associated with a series of bodily reactions, affectivity and feelings are related to the mind. Also, unlike emotion, affectivity involves a process of interaction between two or more people.
Implication in psychotic disorders
Once the areas of action and functions of the mesocortical pathway are known, it is easier to understand why a decrease in its activity can lead to numerous symptoms characteristic of psychotic disorders.
Specifically, in schizophrenia, hypofunction of the mesocortical pathway gives rise to the cognitive and negative symptoms of this disorder. symptoms of this disorder.
Negative symptomatology
The negative symptomatology characteristic of schizophrenia is that which manifests itself through an impoverishment of the personality and relationships and a deterioration of the state of mind..
Within this symptomatology we can find three different subtypes: language disturbances, mood disturbances and a third subgroup with other symptoms that do not fit into the previous ones.
Language disturbances
Among these symptoms are laconic speech, poor language and short responsesThe lack of language content and empty responses, blocking, and increased response latency.
Alterations in mood
It is mainly manifested with affective dullness or flattening, facial inexpressiveness or less spontaneous movements.
Likewise, patients with negative symptomatology show great incongruence show great incongruence between the feelings manifested and the situation that surrounds them.. An example could be laughing at a funeral or crying at a joke.
Finally, other mood-related symptoms include inappropriate affect or ambivalence, feelings of emptiness and the feeling of deep distress.
Other symptoms
Among the rest of the negative symptoms in which the mesocortical pathway is involved, we find abulia and apathy, anhedonia and unsociability, social maladjustment.
Cognitive symptoms
The cognitive symptomatology characteristic of schizophrenia refers to concentration and memory problems, which are reflected in a lack of attention, slow thinking and lack of awareness of the disease, or anosognosia.or anosognosia.
(Updated at Apr 15 / 2024)