Mesolimbic pathway (brain): anatomy and functions.
One of the main dopaminergic pathways to the brain. We explain how it works.
The human nervous system is composed of millions of neurons, which are connected to each other forming complex neural networks.
The different networks are usually responsible for transmitting different information, allowing the functioning of various systems with distinctive functions. One of the most important pathways for our survival is the mesolimbic pathway, which we will discuss below.which we will discuss in this article.
The mesolimbic pathway: one of the main dopaminergic pathways
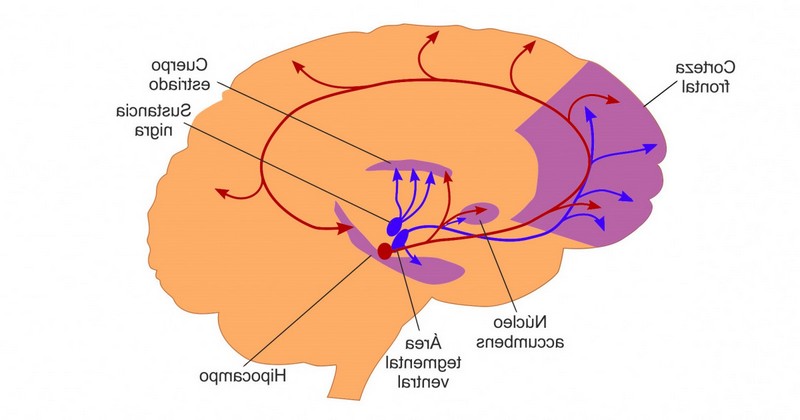
The mesolimbic pathway is one of the main brain dopaminergic circuits, which connects the mesencephalon and the mesencephalon to the mesencephalon.which connects the midbrain with the limbic system going from the ventral tegmental area to the nucleus accumbens, connecting with other structures such as the amygdala and even the prefrontal cortex.
The mesolimbic pathway has been identified with the brain reward mechanism, including most of the structures that are part of it.including most of the structures that are part of it. Thus, it is a circuit of great importance for the development and functioning of the human being, being fundamental in the capture and experience of sensations of pleasure and gratification.
This allows us to approach stimulation, allowing us, for example, to want to eat or maintain relationships due to the experience of satisfaction. In the same way, the correct functioning of this pathway allows us to learn by reinforcing our behavior, seeking to repeat the same actions in those stimulating situations similar to those that provoked the activation of the sensations of gratification. Thus, it allows us to a great extent the learning and conditioning of behavior. It also plays an important role in aspects such as the management of emotions and the physiological reactions derived from them, behavioral control, impulsivity and motivation.
Main structures involved
The mesolimbic pathway is not a structure in itself, but a set of structures that work together to form a network through which information circulates.
Numerous cortical and subcortical structures are part of this pathway, the following being some of the most important ones.
1. Ventral tegmental area
This brain region is the starting point of the mesolimbic pathway, located in the brainstem.. It is one of the areas with the largest number of dopamine receptors, participating in both the mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways. The ventral tegmental area has an important role in the maintenance of motivation, emotion and cognition, as well as in the experience of pleasure. Neurons in this area modulate dopamine release in other areas of the mesolimbic pathway.
2. Nucleus accumbens
Part of the basal ganglia, the nucleus accumbens is one of the most important structures of the brain reward circuit and the mesolimbic pathway. This nucleus largely controls the release of dopamine in the brain. It is in this area that most drugs act, as well as one of the most linked to the processes of habituation and acquisition of addictions. It participates in the integration of emotion and motivation to transform them into actions, as well as contributing to the management of aggression, memory and behavioral planning (through its connection with the prefrontal).
3. Amygdala
The amygdaloid complex is an important part of the mesolimbic pathway, linking emotion with physiological and behavioral responses to its experience. and behavioral responses to its experience. It is the main nucleus responsible for emotional management, especially in the case of fear (which partly explains the feelings of fear generated by the hallucinations of subjects with schizophrenia) and aggression. It also influences sexuality and the feeling of satiation.
4. Hippocampus
The hippocampus is one of the regions of the limbic system most associated with memory and learning, allowing the formation and retrieval of memories and associating them with the emotional evaluation of the experience.
5. Nucleus of the stria terminalis
Part of the limbic system, this nucleus groups the set of fibers connecting the thalamus and amygdala. It is linked to stress management and sexuality (there are differences between sexes and sexual identities in this area).
6. Prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex is one of the areas that governs the cognitive aspects of behavior, allowing the use of skills such as planning and inhibition of behavior.The prefrontal cortex is one of the areas that governs the cognitive aspects of behavior, allowing the use of skills such as planning and impulse inhibition. The mesolimbic pathway also connects to this part of the cerebral cortex.
Role in different disorders
A malfunction of the mesolimbic pathway, either due to hyperfunctioning or hypofunctioning of the mesolimbic pathway, has been frequently linked to the development of a variety of disorders.has been frequently linked to the experience of different mental disorders and behavioral alterations. Specifically some of the disorders to which this pathway has been most often linked are the following.
1. Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
The main disorder with which it is associated, in schizophrenia, it has been observed that the presence of a hyperactivation of the mesolimbic pathway due to an excess of dopamine is linked to the appearance of hallucinations and other positive symptoms, such as restlessness, impulsivity and chaotic and disorganized behavior.
But not only in schizophrenia, this pathway has also been found to be linked to symptoms of other psychotic disorders such as chronic delusional disorder, schizophreniform disorder or acute psychotic disorder, among others. The mesolimbic pathway is in fact the main target of most neuroleptics, and it is essential to work with it in order to solve psychotic problems.
2. Substance addiction and abstinence
As indicated above, the mesolimbic pathway is also part of the brain's reward circuit, and is therefore associated with the experience of pleasurable sensations. In this sense, it highlights its importance in explaining the addictive process of drug addicts, which is due to the facilitation and agonism of dopamine that tend to generate a large number of substances.
In abstinence, the level of dopamine produced by the brain naturally, unlike in schizophrenia, is insufficient to maintain normal functioning.In withdrawal, the level of dopamine produced by the brain naturally, unlike in schizophrenia, is insufficient to maintain normative functioning, resulting in symptoms such as discomfort and craving.
Eating disorders
As a fundamental part of the brain reward circuit, the mesolimbic pathway is also involved in the process of eating and is linked to the sensations of craving. and is linked to the sensations of pleasure we feel when we eat. The activation of this pathway is closely linked to the presence of eating disorders that involve a loss of impulse control, such as binge eating in cases of bulimia and binge eating disorder.
Although obesity is not in itself a mental disorder, excessive food intake despite having had enough or in response to perceived anxiety and stress is also largely due to the pleasure obtained through the activation of this pathway.
4. Other disorders
Dysfunction of the mesolimbic pathway has also been linked to the presence of problems related to aggression and impulse control. and impulse control. In general, it is also linked to compulsive behavior, and this pathway may be affected by other disorders such as OCD or paraphilias.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)