Scurvy: symptoms, causes and treatment of this disease
This disease appears with a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Let's see how it develops.
Scurvy is a disorder caused by a deficiency of ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which alters the production of collagen.which alters the production of collagen, thus affecting the composition of vital tissues. It is related to low nutrition, as well as to excessive consumption of substances such as alcohol.
In this article we will see what scurvy is and why vitamin C deficiency can cause serious problems in our organism. Subsequently we will see what are the main symptoms and risk factors; and finally its prevention and treatment.
What is scurvy?
Scurvy is a nutritional disorder caused by vitamin C deficiency. As such, it is characterized by a difficulty in synthesizing tissues, especially collagen. Externally it manifests itself on the skin (with spots), mucous membranes, teeth and gums. Internally it manifests as an impoverishment of the blood, and sometimes produces ulcerations.and sometimes produces ulcerations and hemorrhages.
This is because Vitamin C, chemically called ascorbic acid, is an organic compound with antioxidant properties, i.e., it prevents the death of cells and tissues. prevent the death of cells and cellular tissues.. In many species of animals and plants (which have the necessary enzymes to synthesize it) this acid is produced within the organism itself.
However, because humans lack these enzymes (we have 3 of the 4 necessary), we must consume vitamin C externally, and thus, compensate for the nutritional properties that allow the synthesis and functioning of our tissues.
Importance of vitamin C
In addition to being an antioxidant and improving iron absorption in the intestinal tract, ascorbic acid plays a very important role in the hydroxylation of collagen, an indispensable step for the configuration of connective tissues.an indispensable step in the formation of connective tissues. For example, skin, gums, mucous membranes and bones contain a high percentage of collagen.
But not only that, ascorbic acid is also involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Ascorbic acid is also involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and hormones such as dopamine (essential for motor function). (essential for motor function), norepinephrine and adrenaline (the latter important for physiological functions and for the activity of the circulatory system).
Although it has no fixed concentration site, ascorbic acid is usually contained in the adrenal glands, Blood cells and the pituitary gland. It also has a life of approximately 30 minutes once absorbed in the intestinal tract.
Brief history
Scurvy is one of the most studied and described disorders since the early history of medicine. In fact, in the 15th and 16th centuries it was a very frequent disease in seafarers..
In the year 1747, the surgeon of the British naval force, James Lind, performed the first experiment on vitamin C deficiency with sailors. He found that an intake of vitamin C compensated for the early symptoms of scurvy..
Main symptoms
Scurvy usually has an asymptomatic development phase, whereby the first symptoms are visible months after vitamin C reserves have been depleted. This occurs in fats as well as in muscles and other tissues. It usually manifests from the first 8 to 12 weeks after having had an insufficient intake of ascorbic acid..
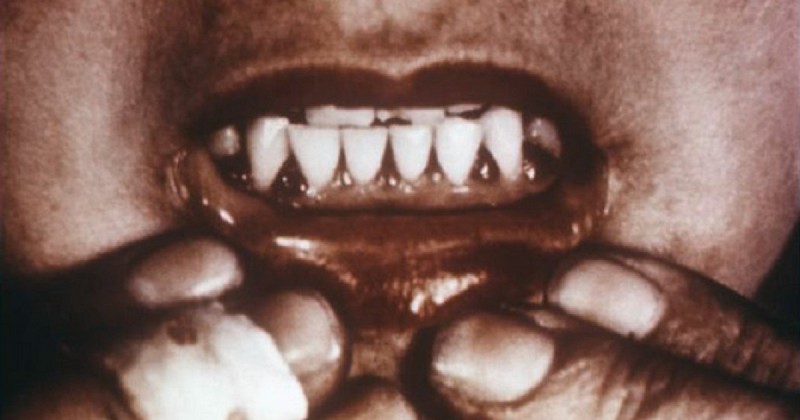
The first symptoms are usually fatigue, pain, stiffness of the joints and lower extremities. Later there is swelling and bleeding of the gums and, later, the teeth may begin to loosen.
Other symptoms, which indicate a high degree of scurvy are bleeding under the skin and from the deep tissues, slow healing, anemia and significant mood disturbances. Finally, if left untreated, it can lead to death (usually as a result of infection from unhealed wounds or as a result of hemorrhage).
Causes and risk factors
Major risk factors for scurvy include low socioeconomic status, alcohol and other drug abuse, and chronic psychiatric disorders that have resulted in low nutrition or excessive use of drugs. low nutrition or excessive consumption of drugs..
Although research on the relationship between substance abuse is recent, the hypothesis is that the prolonged presence of psychotropic substances (including alcohol) accelerates the metabolization and disposal of ascorbic acid. In other words, even if vitamin C is consumed, it does not remain in the body.
Other risk factors related to food intake and the inability to absorb some vitamins are fast diets, anorexia, Crohn's disease, hemodialysis, celiac disease, and numerous food allergies.
Prevention and treatment
As we saw before, human beings do not have the capacity to synthesize vitamin C, so we need to obtain it from external sources, such as from external sources, such as citrus fruits (grapes, limes, lemons, oranges) and vegetables (red peppers, potatoes, potatoes, lemons, oranges). (red bell pepper, potatoes, spinach, broccoli). The latter keep ascorbic acid especially if they are not cooked, since it is easily lost at high temperatures.
The recommended daily doses of vitamin C are between 75 and 90 mg per day, so one of the most commonly used treatments is the prescription of food supplements with high vitamin C content. Depending on the symptoms developed the dosage and time of taking these supplements varies, as well as accompanying this type of treatment with others.
Bibliographic references:
- Agriello, M.F., Buonsante, M.E., Abeldaño, F., Neglia, A., Zylberman, M. and Pellerano, G. (2010). Scurvy: an entity that still exists in modern medicine. Medicina Cutánea Ibero-Latinoamericana, 38(2): 76-80.
- Léger, D. (2008). Scurvy. Reemergence of nutritional deficiencies. Canada Family Physician, 54(10): 1403-1406.
- Scurvy (2018). Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved October 18, 2018. Available at https://www.britannica.com/science/scurvy.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)