Skin diseases – symptoms, types, treatments

The skin is the largest, hardy and at the same time fragile human organ. Like the heart, liver or stomach, it has a complex structure, performs vital functions, and its health is a prerequisite for the well-being of a person as a whole. And just like other organs, the skin is extremely vulnerable to pathological processes.
Short information skin diseases
The peculiarity of skin diseases is that they become evident from the earliest stages. This helps the patient to begin treatment immediately. On the other hand, skin diseases cause severe psychological discomfort to people, especially when it is impossible to quickly eliminate the symptoms. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of any dermatological diseases is a necessary condition for returning to a full life.
Types of skin diseases
There are many reasons why skin diseases occur. These can be both external factors - this includes the traumatic influence of the environment. Internal ones, when the skin is affected by problems of the immune and endocrine systems, the gastrointestinal tract, and so on.
The skin is made up of three layers. The top is called the epidermis. It is constantly renewed (every three to four weeks) and changes color when exposed to ultraviolet rays. Under the epidermis is the dermis - the main layer of the skin, which contains the receptors of nerve cells, glands and hair follicles. When the dermis loses its elasticity, wrinkles appear. Under the dermis is the third layer, the most "heavy" - subcutaneous fat, which helps to keep warm, is a source of fluid and nutrients. Skin weight - 4-6% of the total body weight, and with subcutaneous fat - about 16-17%.

Each layer of the skin is prone to specific diseases. So, the pathologies of the epidermis include scabies and psoriasis, diseases of the dermis - furunculosis and hydradenitis, and the subcutaneous fat can suffer from cellulite and lipoma. Some painful conditions, such as burns, can affect all layers of the skin at once.
Skin pathologies can be divided into infectious and non-infectious, but this division is not always true. For example, seborrheic dermatitis causes a fungus that lives on the surface of the epidermis in absolutely all people, but manifests itself only when immunity is compromised. In addition, infections often join already in the midst of the pathological process: in patients with psoriasis, purulent ulcers often occur, which are the result of bacterial skin lesions.
Chronic skin diseases are of particular importance in dermatology. Unlike acute infectious processes, they accompany a person for extended periods of life and require consistent therapy. Most often they develop under the influence of a variety of external and internal factors: from parasitic invasion to stress.
A predisposition to certain skin conditions can be inherited: many people note that problems like juvenile acne are similar in children and their parents. Statistically, the most common group of skin diseases that become a reason for going to the doctor are dermatoses and dermatitis - diseases of a non-infectious nature, accompanied by itching, peeling and discoloration of the skin. They are observed in both children and adults who suffer from allergies and immunodeficiencies.
Signs of skin diseases: how to tell one from the other
It is easy to suspect a skin disease in yourself or in a child. Normally, the integuments of the body have a uniform color, moderate moisture and a smooth surface, and a violation of any of these criteria or the appearance of unpleasant sensations, itching and pain is already a cause for alarm. Even before visiting a doctor, I want to find out how dangerous this condition is and how to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Dermatitis and dermatoses, as well as psoriasis, are not contagious, but they can significantly worsen the physical and psychological condition of a person, therefore, at the first signs of an illness, you should see a dermatologist.
Dermatitis types
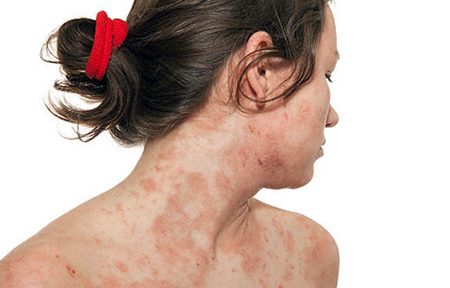
- Atopic dermatitis, or neurodermatitis, is a pathology of an allergic nature, which is manifested by bouts of itching, dryness, peeling, redness and rashes localized on the face and neck, on the scalp and in natural skin folds - in the armpits, in the elbow and knee fossa, in groin, buttocks and so on. The disease is divided into three groups by the age of occurrence. The first type occurs from two months of age. The second type - from two years of age, and the third adolescent or adult atopic dermatitis develops in people older than 13 years. It can be mild or severe, causing severe suffering. In the treatment of atopic dermatitis, an integrated approach is important: cleansing the body, normalizing digestion, diet therapy, excluding provoking factors (from the diet and from the external environment), external therapy to eliminate visible symptoms, and in some cases, systemic pharmacotherapy. If atopic dermatitis cannot be cured in infancy, then it will accompany a person throughout they life in a mild, moderate or severe form with periodic relapses.
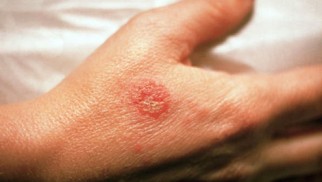
Allergic dermatitis often occurs in both adults and children as a reaction to food or contact irritants. Food allergy manifests itself as itching, swelling, small and large blisters filled with liquid, and occurs within 24 hours from the moment the allergen enters the body. Sometimes the blisters burst, forming extensive weeping foci, which can fester due to the addition of a secondary infection. Localization of an allergic rash can be individual, but usually the rash appears in the same places, with the same intensity and area of the rash.
With contact allergies, a similar inflammatory reaction and changes in the skin are observed only in the part of the body that has been in direct contact with the allergen. For example, if you react to hair dye, redness, itching and swelling will occur on the head, and if you are intolerant of certain metals, on the neck where the person wears the chain, or in the abdomen that was in contact with the belt buckle. Also, an allergen can be drugs, cosmetics and perfumery, soap, plants, rubber products, glue. Some substances cause an increase in the sensitivity of the skin to exposure to sunlight - photosensitization, and thus photodermatitis, which is a type of allergic, occurs. In this case, rashes occur on open areas of the skin that are not protected by clothing from the sun. A key factor in the treatment of allergic dermatitis is the identification and elimination of the allergen, as well as topical therapy to relieve itching, inflammation, infection, and repair of damaged skin.
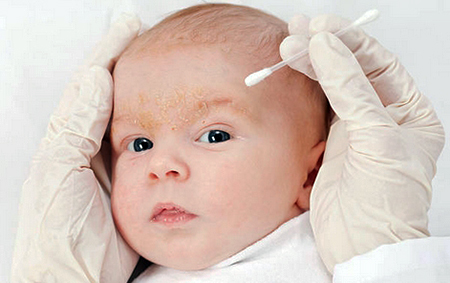
- Seborrheic dermatitis is manifested as a result of excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands, which is accompanied by the release of an increased amount of sebum and active reproduction of the fungus from the genus Malassezia in the epidermis. The disease occurs against the background of psycho-emotional overstrain, stress, hormonal, immune and neuroendocrine disorders, taking certain medications. Seborrheic dermatitis develops on areas of the body rich in sebaceous glands - this is the scalp, face, behind the ear, sternum and navel, the area of the back between the shoulder blades, armpits, and buttocks. Small whitish scales form on the surface of the skin, which easily peel off, exposing a slightly inflamed surface. Therapy for seborrheic dermatitis should be aimed primarily at eliminating the cause (fungus), as well as restoring the damaged structure of the skin - in order to reduce excessive flaking. There are two age peaks in the incidence of seborrheic dermatitis - in the first months of life and after 40 years.
Dermatoses types

- Eczema is an acute or chronic recurrent skin disease accompanied by inflammation, rash and burning sensation in symmetrical areas of the trunk and flexor surfaces of the joints. The disease develops as a result of the complex effects of neuroendocrine, metabolic, infectious-allergic, vegetative-vascular factors. The trigger can be bacterial and fungal infections, chemicals, drugs, food, and more.
Eczema is inherited: with a disease of one of the parents, the probability of developing eczema in a child is about 40%. In the presence of the disease in both parents, the likelihood of the disease development in a child is 50-60%. Distinctive features of eczema are soreness in the affected areas and the inconsistent nature of the rash: first, inflammation appears on the skin, after which it becomes covered with small bubbles, which, bursting, form a moist wound. Over time, erosion on the skin dries up and becomes crusted, after which a period of remission begins. The disease can worsen from year to year, and the final cure, even with proper treatment, may never come.

- Polymorphic photodermatosis is the most common type of photodermatosis, which is characterized by the appearance of itchy spotty, papular, plaque rashes after exposure to the sun (therefore its other name is spring-summer photodermatitis). Lesions appear on the skin after a few hours or days - on the neck, chest, shoulders, forearms, legs, less often on the face and trunk. They do not leave behind scars and disappear within a few days or weeks after stopping exposure to active sun. The pathogenesis of the disease is based on a violation of the immune response, presumably due to exposure to sunlight. Adaptation is characteristic of polymorphic photodermatosis: symptoms decrease after repeated exposure of the patient to the sun for a short period of time, as the skin develops a tolerance to sunlight.
Psoriasis

It is not accidentally singled out as a separate group. This is one of the most severe chronic skin diseases, which is characterized by an unpredictable course and a vague mechanism of occurrence. This disease occurs in 1–2% of the population of developed countries, regardless of age, gender, social status and lifestyle (although it is noted that psoriasis occurs more often against a background of severe stress).
Psoriatic plaques appear almost everywhere - on the elbow and knee bends, scalp, soles and palms, in the region of the sacrum and lower back. The marks range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters and often merge into single spots. Plaques in psoriasis have a scaly structure, when the scales separate, the skin under them shines and sometimes bleeds. In addition to ordinary (vulgar) psoriasis, seborrheic psoriasis is common, in which the scales have a yellowish tint. The disease can affect not only the skin, but also the nails and joints, causing psoriatic arthritis.
Treatment features
There are many skin diseases, but the therapeutic principles for each of them are similar: to defeat the disease, a combination of systemic and local therapy is required. The first involves taking pills and injections aimed at eliminating internal pathological mechanisms: inflammatory and allergic reactions are suppressed, the work of the endocrine and nervous systems is normalized, and so on. Systemic treatment of each of the above diseases has its own characteristics and, as a rule, is prescribed during periods of severe exacerbations.
Local therapy is aimed directly at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, reducing the frequency of relapses and improving the patient's quality of life - eliminating itching, peeling, painful sensations and cosmetic defects. Its advantage lies in the absence of systemic side effects, as well as in targeted action. Topically applied agents are subdivided into medicines and care products.
Topical therapy is used primarily to make the skin more attractive as quickly as possible. Some of the substances used for this purpose are also suitable for people with healthy, but dry and sensitive skin, suffering from cracks and flaking. It could be products with emollients, i.e. the fat-like component of cosmetics, substances that can create a protective lipid layer on the skin's surface.
Acne treatment
Poor ecology, stress, lack of vitamin D, lots of coffee, long conversations on a smartphone and sunscreens are not obvious, but nevertheless, common causes of acne on the face. This skin disease can develop both in children and adults.
First, let's look at the causes of acne:

- Hormonal imbalance. It happens in young adolescent girls, in pregnant women, and in women during PMS. The active release of steroid hormones causes increased secretion of the sebaceous glands.
- Hypersecretion of sebum leads to the fact that the bactericidal properties of the dermis are reduced.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis. The normal process of cell renewal with hair follicles is disrupted and outflow of the sebaceous glands secretion is impaired.
- Increased reproduction of propionic bacteria. Millions of microorganisms on the human body are the norm, they become not the norm when they suddenly begin to riot, developing acute inflammatory reactions. It commonly accompanies the impaired outflow of sebum.
- Zinc deficiency in the body also provokes the active production of sebum and the appearance of acne.
- Improper skin care, low-quality decorative cosmetics lead to the fact that the skin "deteriorates" and acne appears.
- Poor-quality unbalanced nutrition and impaired functioning of the digestive tract can also provoke the appearance of acne.
To treat acne effectively, it is necessary to find out the main cause as you can see, it can be different or maybe it is a combination of different factors.
Dermatologist can help you identify the cause with the help of such tests as general blood test, test of the skin pick to see if there are bacteria, blood test for hormone levels, blood test for vitamins and minerals.
In case of acne of bacterial nature, antibiotics such as Cefaclor (or other based on the sensitive of bacteria) are appointed. They should be applied both topically and orally.
In case of hormonal imbalance, hormonal medicines are used.
We do not advise to take any medicines without first consulting a doctor and finding out the reason for acne.
Post by: Kylie Richardson, General Practitioner, Rotterdam, Netherlands
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)
Ceclor articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.