Symptoms and treatment of ovarian cancer

Ovarian cancer is a type of malignant neoplasm that primarily develops from ovarian tissue. Causes of ovarian cancer
The reliable reasons for the formation of a tumor are unknown, therefore, when discussing the causes of ovarian malignant neoplasms, doctors talk about risk factors.
Short information about ovarian cancer
These include the following conditions:
- Hyperestrogenism - excess production of female sex hormones (estrogens) in the first phase of the menstrual cycle. Since the ovarian tissue is sensitive to their action, hormonal stimulation can lead to active cell division and their malignant transformation. Hyperestrogenism is also observed when superovulation is stimulated during IVF or egg donation, during hormone therapy during for the treatment of menopause pathology, as well as in obesity, since adipose tissue has its own hormonal activity;
- Long reproductive period with constant ovulation - early onset of puberty, late menopause, absence of pregnancy, refusal to breastfeed;
- Heredity and genetic predisposition. About 10% of cases of these neoplasms are due to genetic causes. First of all, we are talking about mutations in genes. There is an increased risk in the history of hormone-dependent cancer in female relatives.
Stages of ovarian cancer
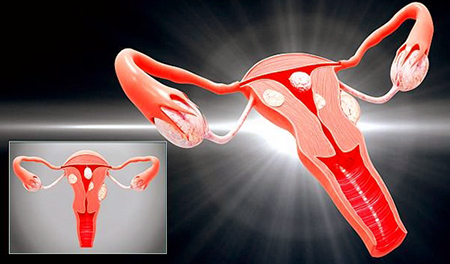
- Stage I - cancer spreads only to the ovaries and does not go beyond them;
- Stage II - the pelvic organs are affected;
- Stage III - the abdominal organs are affected;
- Stage IV - cancer extends beyond the abdominal cavity, for instance, into the lungs or pleura.
Symptoms
At an early stage, symptoms are either absent or nonspecific; therefore, based on complaints, it is difficult to suspect the presence of such pathology. More specific symptoms appear in the later stages.
The first symptoms may include:
- Stretching in the lower abdomen;
- Abdominal pain of unclear localization. First, they appear suddenly and just as suddenly disappear, and for a long time;
- Bloating.
Symptoms in late stages
- Disorder in stool and urination - develop due to the fact that the tumor displaces the uterus, and that, in turn, presses on the intestines and bladder;
- An increase in the volume of the abdomen. As a rule, it develops due to ascites - the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal. Hard palpable formations in the abdomen;
- Pain can be a sign of torsion of the tumor stem and its ischemia. It is rare as the first sign.
Common manifestations of ovarian cancer:
- Weight loss for no apparent reason;
- Loss of appetite and feeling of fullness from a small amount of food;
- Fast fatiguability.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is made in 2 stages - detection of neoplasm, its verification and stage determination. As a rule, a tumor is detected using radiation diagnostic methods - ultrasound, CT, MRI. For example, ovarian cancer on ultrasound looks like an irregularly shaped formation with fuzzy, blurred boundaries. Also, using these methods, a preliminary assessment of the spread of the process is made, for example, the germination of cancer in the pelvic organs or organs of the abdomen.
If a neoplasm is detected according to the data of radiation research methods, the patient is offered to give blood for ovarian cancer (for the determination of CA 125 and HE 4 tumor markers with the calculation of the ROMA index), this study will make it possible, with a certain degree of probability, to differentiate ovarian carcinoma. If germ cell tumors are suspected, the doctor may suggest tests for AFP and hCG.
The final diagnosis and determination of the stage is mainly carried out after the operation, during which material is taken for histological study and the abdominal cavity is revised for carcinomatosis and metastases.
How is ovarian cancer treated?
Usually, a combination of surgery and chemotherapy are appointed. The goal of the surgery is to remove the tumor mass as completely as possible, and chemotherapy destroys the remaining malignant cells and diminishes the risk of recurrence or progression of the pathology. For the diminishing of the tumor growth and size cytostatics such as Hydroxyurea are used.
Surgery
The amount of intervention depends on the stage. Stage I allows the removal of the affected organ and fallopian tube. This allows to temporarily save the second ovary and, if desired, the woman to have a child. After this, an ovariohysterectomy is performed. The indications for such treatment are very limited. Basically, the standard of operation involves the removal of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, lymph nodes, and resection of the greater omentum (this helps to prevent peritoneal carcinomatosis and its spread throughout the abdomen). Besides, resection of the organs involved, such as the bladder or intestines, may be necessary.
In many patients, the disease is found at late stages, when the abdominal organs, distant lymph nodes are involved in the process, or there are metastases outside the abdominal cavity. Then treatment begins with several rounds of chemotherapy, and the surgery is conducted after diminishing the volume of the tumor mass.
Chemotherapy
As a rule, chemotherapy for ovarian cancer is conducted after surgery, which will not only reduce the volume of the tumor mass but also synchronize the life cycle of malignant cells, which will make the treatment more effective.
The selection of medicines is made on the basis of the histological type of neoplasm. For example, a combination of platinum and taxanes is the first-line treatment choice for adenocarcinoma. After the patient receives the required number of rounds of chemotherapy, therapy is stopped and active observation is switched on for the timely detection of relapse. Targeted therapy with bevacizumab may be prescribed for some women when indicated.
Evidence of the progression of the disease is the emergence of new tumor foci according to ultrasound, CT or MRI, and/or the growth of CA125. The type of relapse matters here:
- Platinum-sensitive - tumor progression began no earlier than 6 months after stopping the chemotherapy. In this case, you can continue treatment with platinum drugs, but in combination with other, previously unused drugs. If more than a year has passed since the end of treatment, 1-line chemotherapy can be used;
- Platinum-resistant - the tumor began to progress earlier than six months after stopping treatment;
- Platinum-refractory relapse - the tumor progresses already during chemotherapy of the 1st line.
In the latter two cases, schemes that do not contain platinum preparations are used for further treatment. If it does not help, then they are limited to supportive therapy.
Ovarian cancer prophylaxis
There is scientific evidence that the continuous use of oral birth control for 5 years lowers the risk of ovarian cancer by 2 times. But it is not recommended to take these drugs solely for this purpose. Pregnancy and breastfeeding also lower the risk of malignant tumors of this localization.
Separately, it is worth noting the history of the disease in the family. Women at risk are advised to have an annual examination, including pelvic ultrasound and determination of CA 125. In addition, when they reach a certain age, they may be offered preventive oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries).
Post by: Katherine Christensen, gynecologist, sexologist, Copenhagen, Denmark
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)
Hydrea Hydroxyurea articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.

