Transcranial magnetic stimulation: types and uses in therapy
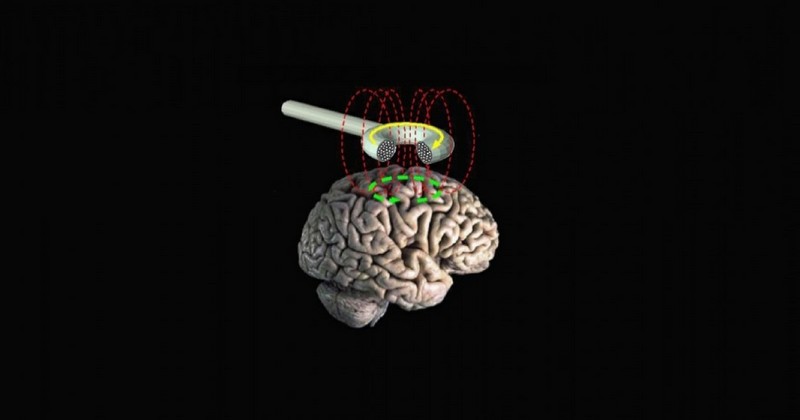
A tool that can be helpful in the treatment of various neurological pathologies.
There are a large number of disorders and diseases that affect the brain and its functioning. These disorders can cause or be caused by the fact that sometimes different areas of the brain are not sufficiently activated or function in an altered way. In order to solve them, different mechanisms and treatments have been developed or tried to be developed with greater or lesser effectiveness.
One of them, not very well known but which has shown some usefulness, is transcranial magnetic stimulation.
What is transcranial magnetic stimulation?
The technique known as transcranial magnetic stimulation is a non-invasive a method or type of non-invasive intervention based on the application of magnetic fields to the brain. controlled to stimulate nerve cell activity. Such stimulation does not generate Pain and allows a control of the activity of the targeted brain areas.
The principle by which it works is the application of electromagnetic induction, applying electric current to an electromagnet that will be placed on the scalp in such a way as to generate the aforementioned magnetic fields (sufficiently attenuated so as not to generate damage).
Thus, these fields influence the transmission of information, facilitating the brain activity (although it is not completely (although it is not fully understood how it works) and the generation of action potentials through neuronal depolarization. The normal rhythm of activation of these neurons is interrupted, which in turn can generate delayed effects in those neurons with which those affected by the stimulation are connected. It has been associated with depression and long-term potentiation.
The studies carried out so far seem to indicate that it is a methodology that presents a certain effectiveness and that has few risks, although it is often used as an alternative method or as a support to the treatment carried out in the long term. as an alternative method or as a support to the treatment carried out and not as a first option and not as a first option (other types of treatment that have demonstrated greater consistency and effectiveness are usually preferred).
Basic procedure
The basic procedure usually followed in the application of transcranial magnetic stimulation is roughly as follows. Prior to the treatment, a visit to the doctor should be made to check that the patient does not have any type of pathology or element for which this technique is contraindicated.
As for the application itself, first of all, after bringing the patient into the room, some kind of barrier element such as earplugs will be provided so that the patient can protect his or her ears. Beforehand, it would be advisable to explain to the patient what is going to happen during the session, and it may be necessary to reassure the patient.It may be necessary to reassure the patient (without using anesthesia or sedatives).
Then proceed to place a coil with an electromagnet on the scalp, placing it in the area to be stimulated. It is possible that instead of one there are two or several elements to be placed, depending on how the stimulation is carried out. The brain mapping will be performed, introducing brief pulses to observe and locate the brain areas and their bioelectrical functioning. It is likely to notice some sensations and sounds at this stage.
After that, the doctor will proceed to turn on the coil and regulate the intensity of the stimulation, increasing it up to the motor threshold (generally until the fingers contract).increasing it up to the motor threshold (generally up to the point of generating finger contraction). After reaching the threshold, finally, the magnetic field is allowed to pass for a variable period of time depending on each case. These sessions can vary in number and timing, being usual the realization of about ten sessions.
Types of transcranial magnetic stimulation
There are different ways of applying transcranial magnetic stimulation.. Some of the main types are the following.
1. Transcranial magnetic stimulation with single pulses.
One of the ways to apply this technique is with single pulses, through the application of a stimulus every three or more seconds, or with a train of stimuli of varying frequency over the same area. a train of stimuli of variable frequency over the same area for several seconds. for several seconds. Used in research or in the treatment of a specific problem.
2. Transcranial magnetic stimulation with paired pulses
In this case, two stimuli whose intensity can be equal or different from each other are applied through the same coil and in the same brain region or with two different coils. Typical of the study of corticocortical connectivity..
3. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
This application is one of the best known. It is based on the emission of repetitive pulsesIt is based on the emission of repeated pulses, applying one stimulus (of low frequency) or more (reaching up to twenty in fast or high frequency rTMS) per second or less time. It is often used in the treatment of neuropsychiatric problems.
In what diseases is it used?
Although it is not especially recognized, the transcranial magnetic stimulation has been applied to different cerebral and psychiatric afflictions. Some of the best known are the following.
Parkinson's and motor syndromes
One of the most frequent disorders in which this technique is used is Parkinson's disease or problems related to its symptoms, causing functional improvements and reduction of motor problems..
2. Mood disorders
Perhaps the best known psychiatric application of this technique is in major depression. Functioning in part similar in part to electroconvulsive therapy but without the side effects of the latter, this treatment has been found to beIt has been observed that this treatment contributes to reduce depressive symptomatology when applied to the left dorsolateral prefrontal area, although further research is needed.
It has also been applied in the treatment of bipolar disorder, although in this case there is a risk of inducing manic episodes. This is why special caution is necessary in this disorder.
3. Neurorehabilitation
Another area of application is neurorehabilitation, using stimulation as a way to generate neuronal activation. as a way of generating neuronal activation and to try to improve functionality after a brain injury. It is applied among others in trauma, infarcts, spinal cord injuries, neglect syndromes, hemiparesis or cognitive difficulties.
4. Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a disorder in which this type of treatment has sometimes been used. It can allow the stimulation of some relevant brain areas in order to palliate the palliate impairments generated by this conditionIt can even facilitate the appearance of epileptic seizures in order to localize the area that generates the seizures and to evaluate the possibility of other therapeutic options.
5. Pain disorders
The use of transcranial magnetic stimulation has been proposed for the treatment of pain disorders, such as neuropathies and neuralgias, or phantom hand pain (in amputees), fibromyalgiaThe use of transcranial magnetic stimulation has been proposed in the treatment of problems involving pain, such as neuropathies and neuralgias, or phantom hand pain (in amputees), fibromyalgia or even migraine.
6. Neurodevelopmental disorders
There are researches that propose the use of this therapy in autism and ADHD, using stimulation on the neurodevelopmental muscles.using stimulation on the nuclei that govern attention to cause improvements in the symptoms of these neurodevelopmental disorders and stimulating their attentional capacity. However, much more research is still needed in this area.
7. Schizophrenia and psychotic problems
Depending on the use and the stimulated areas, it is possible to find a utility of this technique in the case of schizophrenia and psychotic disorders. This is especially useful in the stimulation of mesocortical pathways, so that negative symptoms are reduced. Also in some cases it can be used in the treatment of positive symptoms by altering the cerebral mechanism that produces them (although it can run the risk of generating psychotic outbreaks).
Contraindications and side effects
As we have said, transcranial magnetic stimulation is generally considered a non-invasive and low-risk therapeutic option, with no major complications in most cases. However, this does not mean that it cannot have bothersome side effects or even be contraindicated in specific cases.
As far as side effects are concerned, generally patients undergoing this treatment may experience headaches and dizziness. may experience headaches and dizziness, tingling and paresthesia of the face and scalp. or even some small involuntary spasms. Occasionally, however, more serious alterations may occur, such as hearing loss, convulsions and manic episodes. Therefore, although apparently low risk, caution should be exercised in its use.
With regard to people who are contraindicated for transcranial magnetic stimulation or who are required to consult or inform their physician of the presence of specific characteristics before undergoing it, those who carry implants or have any metallic element in their organism that could be altered by magnetic stimulation are particularly relevant. Particularly relevant is the case of pacemakers (which could be altered by magnetic stimulation). (which the stimulation could alter to the point of causing death), infusion pumps, elements and valves implanted in the nervous system or cochlear implants. Something as simple as dental implants can also pose some danger, as well as shrapnel or metallic elements present in the body due to some type of accident or trauma.
Special caution is also required for people suffering from brain injuries such as recent strokes (although it is sometimes used as a rehabilitation of its effects, it is not recommended to be applied in subjects who have suffered a stroke). Although it is used as therapy in some cases of bipolar or schizophrenia, special caution should be taken in these cases because if the subject's state is not controlled the appearance of psychotic outbreaks or manic episodes may be favored.. The same applies to epilepsy. Those who take any type of medication (whether or not it is a psychopharmaceutical) should consult their doctor first. Finally, pregnant women are also contraindicated for this treatment.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)