What is hemiplegia and how is it treated?

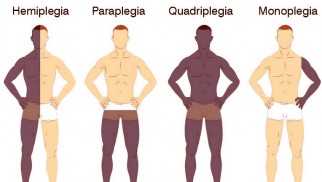
Many have not even heard of such a disease also known as hemiparesis, or one-sided paralysis. Hemiplegia is a rare and serious illness that manifests itself in the form of paralysis of one side of the body. This occurs as a result of damage to areas of the central nervous system.
Short information about hemiplegia
Main types
Often the disease can be found among children, as a consequence of cerebral palsy. In general, there are different types of the disease that occur in both children and adults. Spastic hemiplegia is more common in pediatric patients. Adults are characterized by contralateral hemiplegia and alternating hemiplegia.
Depending on the type, it can be organic and functional. The organic form is characteristic when the blood circulation in the brain is disturbed. Usually it is observed with thrombosis, cerebral hemorrhage, sometimes it is observed as a result of inflammatory diseases of the brain.
The organic form develops in connection with disturbances in the work of the central nervous system as a result of pathologies. In this case, there is a strong tension of muscle fibers, tendons in the limbs affected by paralysis. The disease is commonly either right or left-sided, but sometimes double hemiplegia also occurs, when a violation of the motor function is observed on both sides. Sometimes the disease can manifest itself in the form of deterioration in the work of the facial muscles.
When the functional form of the disease manifests itself, it is similar to the organic one in only one sign - paralysis of the limbs on the one hand, the other symptoms are completely different. Often this form goes unnoticed.
There is another form of the disease when the paralysis is crosswise, for example, paralysis of the left hand, when a lesion occurs, develops on the opposite side. This form is called contralateral, and it is caused by multiple negative effects on the brain.
Alternating hemiplegia is rare, more common among pediatric patients. It manifests itself spontaneously by random attacks of paralysis of the limbs. This condition can last from a few minutes to several days. With this form, complications such as impaired motor functions of the eyeballs, the occurrence of dystonia (reflex motor contractions of certain muscle groups in any part of the body), and impaired functioning of the systems responsible for the perception of information are possible.
Causes of occurrence
There is a wide range of causes for this ailment:
- Head and upper back injuries;
- Infections and inflammatory processes in the central nervous system;
- Ischemic diseases;
- Neoplasms, tumors developing in the brain region;
- Hysterical neurosis and other psycho-emotional disorders.
However, these reasons are not common among pediatric patients. Childhood hemiplegia is often a congenital malformation. Some babies are already born with similar disabilities.
The development of capsular hemiplegia or other forms occurs during the embryonic period. This happens when, during the formation of the fetus, central neurons develop incorrectly or a violation of spinal and cerebral functions is observed.
The frequency of hemiplegia is significantly higher in prematurely delivered than in full-term infants. There is also a high frequency of the disease development during pregnancy, and experts say that this could be due to traumatic delivery, the use of forceps, or some event that causes brain damage.
Other causes of disease development in adults are brain injury, hemorrhage, infections, and tumors. People with uncontrolled diabetes, high arterial pressure, and tobacco smokers have a higher risk of a stroke leading to partial paralysis.
General
- Vascular: brain hemorrhage, stroke;
- Infectious: encephalitis, meningitis, brain purulent inflammation, spinal epidural purulent inflammation;
- Neoplastic: gliomas, meningiomas, brain tumors, spinal cord tumors;
- Demyelination: multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optic;
- Traumatic: cerebral laceration, subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma, compression or fracture of vertebra;
- Iatrogenic: local anesthetic injections given intra-arterially quickly, instead of given in the nerve branch;
- Congenital: Cerebral Palsy, and others;
- Degenerative: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, corticobasal degeneration.
- Parasomnia: sleep paralysis.
Manifestation of the problem and symptoms

Outwardly, capsular hemiplegia looks like paralysis of the limbs. That is, at the same time, there is a lack of response of nerves to stimuli, reflexes, lack of ability to move in the limbs either on the side that was damaged or on the opposite, depending on the type of ailment.
As mentioned above, the disease manifests itself in different ways. Doctors outline 3 cases of manifestation: right-sided, left-sided and double hemiplegia. When a person has a hemiplegic form of cerebral palsy, it is usually associated with double hemiplegia.
Usually, the disease is characterized by a lack of movement in the limbs, an increase in muscle tone, and manifestations of pathological reflexes.
The pathological reaction is characterized by some signs. It is possible to observe changes in flexion and extension of the foot functions, changes in the reaction and behavior of the upper limb. In the case of peripheral plegia, a noticeable decrease in muscle tone, atrophy of some muscles, and the extinction of reflexes can be observed.
Sometimes there is such a phenomenon as a hemiplegic gait. This is a condition when the patient can notice a certain change in the position of the arms and legs in motion. Usually the shoulder is turned inward, the arms are bent at the joints at the same time, and the fingers are tense and clenched. One of the lower limbs is extended in the area of the hip, ankle and knee joints. Usually, if the gait starts from the affected limb, then it looks like walking in a circle, since the step is taken with the hip abducted to the side, and the body moves in a different direction. This is most often caused by spastic hemiparesis. A similar condition occurs in patients after a stroke.
Diagnostics
To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to pass a number of tests and undergo physical examination. Among the first, the doctor determines the signs of the disease through the Barre test. To do this, the paralyzed leg is lifted and then allowed to gradually lower, the second is held in its original state.
The Mingazzini test is performed by stretching the paralyzed arm forward. A healthy limb remains in place along the body. Another test implies bending the forearm and raising the hand vertically, while fingers are spread as wide as possible from each other. The fingers on the injured limb slightly move and are slightly squeezing.
Treatment of the disease
Many people believe that this complex and unpleasant disease is practically incurable. Today, treatment involves a whole range of measures. These measures include inpatient, outpatient and home treatments. Usually, treatment begins with early rehabilitation, which is carried out in a hospital, but it does not end there. After hospitalization, treatment should continue at home.
Hemiplegia is just another ailment syndrome. Therefore, in order to finally understand how to get rid of the problem, you need to find out what was the main reason for the development of such a symptom. Most often, with such disorders of the nervous system, medications are prescribed that affect the nervous tissue. They help to improve its trophism and the conduction of nerve impulses, restore and improve the pathways and reduce muscle spasticity.
The main medications that are most often prescribed by doctors in this case:

- Neutrotrophic medications that affect the neurotrophic system;
- Neuroprotectors - substances used for prophylaxis of cerebral neurons condion;
- Vasoactive drugs promote active blood supply to the nervous tissue, are able to influence the regulation of metabolic processes for rapid resuscitation of the lost function of neurons;
- Antioxidants;
- Vitamins of group B;
- Cholinesterase inhibitors - drugs that act on the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, slowing down its activity. This increases the level of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the body;
- Muscle relaxants - drugs that reduce the tone of skeletal muscles (for instance, Tizanidine).
The most commonly prescribed drugs are proserin, nivalin, glutamic acid and others. Sometimes, with spasticity of muscle fibers, drugs such as melliktin, tropacin, tizanidine and others are prescribed. The speed and intensity of recovery depend on the number of affected areas, the area of their spread, the size and nature of pathological processes. All patients are advised to have hot drink regularly.
The list of drugs presented above is aimed only at improving the functioning of the nervous system. Other measures are necessary to improve the performance of paralyzed limbs. Physical rehabilitation methods are usually used. This includes massage, kinesitherapy and remedial gymnastics. Some may wonder what kinesitherapy is. It is a special therapy aimed at restoring human motor functions.
These methods are based on regular, passive movements while lying on the bed. Such movements can improve blood circulation in the body and limbs. Sometimes some special devices are used to help the patient get upright.
Some exercises required for such violations:

- One of the best exercises is going up and down stairs.
- Lying on the couch with your stomach up, it is necessary to bend your knees, and then slide your heels along the surface of the couch until the sole of the foot fully touches the surface at the moment of full bending of the leg.
- Raising straight legs at an angle of 45 degrees from the bench surface.
- Lying on your back try to turn your straight leg inward so that it remains straight without bending your feet and toes.
- Separate flexion of one leg at the knees.
- Rotation of the hand in the wrist, contrasting the thumb with the rest of the others.
- Raising the arms in front of the body. They should be straight and parallel to the floor, palms facing forward, fingers extended apart, thumb to the side.
- Abduction of straight arms from each other. Starting position - hands in front, palms facing up, fingers extended from each other, thumb opposed to the rest.
- Changing the position of the arm, by bending at the elbow. In this case, the hand should remain close to the body, and the elbow should not be retracted.
In addition to gymnastics, physiotherapy procedures have proven themselves well:
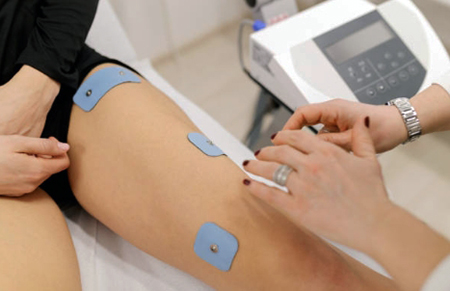 - Muscle electrical stimulation. What is it and how does it work? This is a procedure that uses pulsed currents to repair tissues and organs, and is especially effective in treating nerves and muscles. - Exposure to a magnetic field on the body.
- Muscle electrical stimulation. What is it and how does it work? This is a procedure that uses pulsed currents to repair tissues and organs, and is especially effective in treating nerves and muscles. - Exposure to a magnetic field on the body.
- Barotherapy - a physiotherapy procedure in which the body is exposed to small portions of low or high pressure.
- Laser therapy - a procedure performed using a light source that has a therapeutic effect.
Sometimes wrapping or applying compresses is used. Patients with similar disorders also need social and household rehabilitation. Still, patients faced with such a problem need to adapt to the social environment. Therapy includes teaching patients how to use objects of daily life, redesigning living spaces to meet the needs of the patient. Sometimes, prosthetic and orthopedic equipment is required, especially for patients who have a hemiplegic gait.
For people who are already able to work, sometimes a professional retraining is advisable. For social adaptation, special psychological therapy and trainings are carried out.
Post by: John Johansson, M.D., Amsterdam, Netherlands
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)
Zanaflex articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.