Allergic angioedema - causes, symptoms, treatment
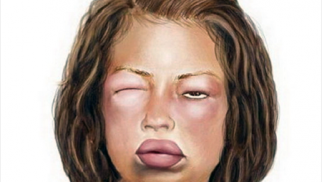

Angioedema or Quincke's edema is a condition that often requires urgent help, so it's best to know its symptoms, possible causes, emergency measures and treatment approaches so as not to panic and take the right steps.
Short information about allergic angioedema
What is angioedema?
In most cases, the disease has a mechanism of occurrence similar to allergic reactions. Unlike urticaria, when the reaction occurs on the skin in the form of a rash, with angioedema, the edema spreads to areas with loose subcutaneous fat - the neck, lower face, eyelids. Less commonly, there is swelling of the hands, feet, genitals and internal organs.
Approximately one in ten people in life has suffered this condition at least once. But women of young and middle age are more susceptible to this disease. Allergic edema can be caused by a chemical agent, medications, food, contact with plants, an insect bite, or be caused by a pseudo-allergic reaction to cold or heat, sun light, and stress.
Angioedema symptoms

It manifests in an increase in a separate part of the face or body or whole face. The swelling has smooth contours without any significant changes in the skin. The edema is dense, it cannot be squeezed by pressing on it. It feels like "tension" in the tissue, a patient can distinguish pain and internal itching. Swelling in the mouth and neck can spread deep into the larynx and cause difficulty breathing and suffocation, which occurs in every third case. The patient has voice and has an urge to cough. Angioedema can cost your life if you are late with help. In some cases, the attack can go away on its own or after using over-the-counter antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil, Claritin, Cyproheptadine, etc.). If angioedema occurs and you have allergy pills at hand, take them but make sure to seek urgent medical help. People prone to allergies are advised to always have allergy pills at hand to quickly stop an unexpected severe allergic reaction.
What to do before the doctor arrives?
- Try to calm the patient down,
- Remove the allergen that caused the attack,
- Put a cold compress in place of the swelling, you can use a strong solution of soda or salt;
- Provide access to fresh air,
- Give the patient an antihistamine (allergy drug, such as Cyproheptadine or Allegra),
- Give them nasal spray and help them use it to facilitate breathing (vasoconstrictor spray, for example, Otrivin or other than you have at hand).
Angioedema treatment
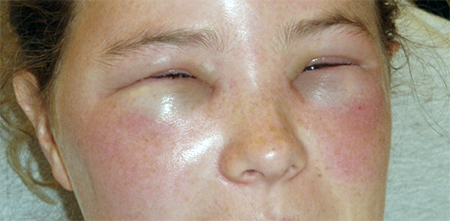
Hospitalization in an ENT, allergy or therapeutic department is usually indicated. In a threatening situation, resuscitation measures can be carried out. Antihistamines are prescribed in the form of injections, since the possible edema of the internal organs will reduce absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Besides, drugs for narrowing of peripheral vessels (ephedrine, caffeine), ascorbic acid, B vitamins, calcium preparations and also administered intravenously.
Those who have suffered from angioedema should follow a hypoallergenic diet that excludes chocolate, eggs, fish, citrus fruits, wheat, milk and some other foods. Recovery lasts up to several weeks, depending on the severity of the attack. For prevention, it is necessary to identify the provoking agent and try to avoid it in the future. Also, such patients should have antihistamines and sorbents (to wash out the allergen quickly) at hand.
Remember, angioedema is a strong manifestation of an allergic reaction that requires immediate assistance from specialists. Untimely treatment can be fatal, since the allergen is like a poison for the body, which reacts so strongly to certain foods, an insect bite, cosmetics, or medication.
Post by: John Johansson, M.D., Amsterdam, Netherlands
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)
Periactin articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.