Coenzyme Q10: Energy and cardiovascular health
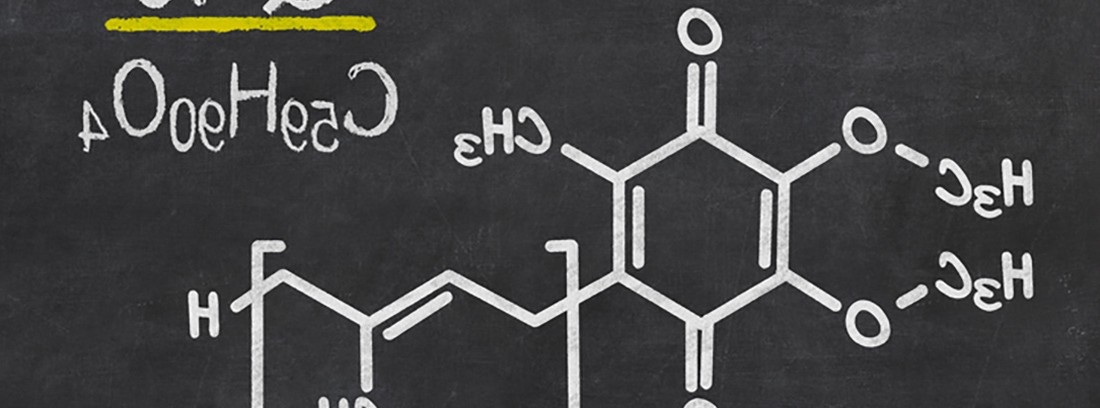
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance similar to a fat-soluble vitamin, which exists naturally in all cells of the body and is essential for the production of energy in cells. It belongs to the family of ubiquinones, substances whose name refers to the fact that they are practically present in all living organisms. It is part of the membranes of the mitochondria, which are the organelles of cells responsible for the production of most of the energy that our body requires. The highest concentrations of coenzyme Q10 are found in the heart, kidneys, liver, and muscles because they are the organs that require the most energy.
What is it for
The main functions of Coenzyme Q10 are convert energy from carbohydrates and lipids in the form of energy usable by cells, and protect cells, tissues and organs from the oxidative and damaging action of those involved in the aging processes and in the development of health problems such as cancer.
Coenzyme Q10 content decreases in the human body with age, but it can also decrease by stress, by certain diseases or by taking some medications such as statins to lower the. Also the practice of exercise or physical overexertion consume energy and therefore increase the requirement of CoQ10.
Power source
The practice of exercise generates an overload of work of the heart and the muscles that are the organs that consume the most energy, which causes the release of free radicals that are produced in the process of obtaining the necessary energy to perform these tasks. This increase in free radicals produces oxidation reactions that can translate into cell damage, muscle overload and fatigue, with decreased physical performance.
Various scientific studies have been carried out in which it has been proven that when sports or any kind of physical exercise is performed, supplementation with coenzyme Q10 may protect against cellular depletion and therefore increase resistance to fatigue, or the delay in its onset, by maintaining the energy of the mitochondria. As already mentioned, coenzyme Q10, in addition to being essential for the transformation and contribution of energy to every living cell, has a powerful antioxidant action. It has also been observed that in combination with coenzyme Q10 it can increase the brain energy.
cardiovascular health
As, coenzyme Q10 can potentially inhibit the harmful effects that contribute to the formation of atherosclerosis by inhibiting the oxidation of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol), which is one of the causes of atheroma formation and because it is also one of the main nutrients in the heart tissue, promotes oxygenation and fights free radicals, so it can contribute to the treatment and prevention of heart problems (angina pectoris, heart attacks, etc.). Research suggests that the beneficial effect of coenzyme Q10 in preventing cardiovascular disease is primarily due to its ability to act as an antioxidant. Studies have shown that coenzyme Q10 supplements administered within the first three days after a heart attack they could reduce the possibility of suffering new heart attacks.
In addition, it has been seen that coenzyme Q10 levels tend to be lower in people with high cholesterol, compared to healthy people of the same age. On the other hand, it has been observed that some cholesterol-lowering drugs, statins, seem to decrease the natural levels of coenzyme Q10 in the body, so it seems that supplementation with coenzyme Q10 could be beneficial for patients taking statins, both at the cardiovascular level and to help them conserve energy. In studies carried out, the consumption of coenzyme Q10 supplements has been shown to correct the decrease in CoQ10 levels produced by statins without affecting their efficacy in reducing cholesterol levels.
But nevertheless, in case of cardiovascular problems The advisability of taking CoQ10 as a supplement should be consulted with the doctor since it can interfere with some treatments with anticoagulant effect. Due to lack of safety studies, it should not be consumed without medical supervision during pregnancy and lactation.Coenzyme Q10 sources
Coenzyme Q10 found naturally in food, which contain varying amounts from one food to another. The amount of CoQ10 that a person usually incorporates daily through the diet is around 10 mg (average in Europe). When there are situations of increased requirements, such as any of those already mentioned, in order to absorb the amount that the body needs, much higher amounts have to be ingested.
The doses of CoQ10 that appear to be effective according to the studies, would be between 50 and 100 mg. However, it is difficult to reach these amounts through food, since we would need to eat, for example, 800 g of or 1.5 kg of meat to ingest 50 mg of CoQ10. For this reason, when it is necessary to supplement, it is possible to resort to food supplements that in dosed form (generally soft gelatin capsules) contain CoQ10 in concentrated form in amounts that allow 50, 100 mg or more to be dosed, to suit individual needs.
- It is responsible for converting the energy of the lipids into usable energy by the cells.
- It is found mainly in the heart, kidneys, liver and muscles, the organs that require the most energy.
- Age, stress, certain diseases and medications, physical overexertion increase the requirement of this coenzyme.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)