Cold (nasopharyngitis)
What is it?
Colds (popularly called colds) are the most common childhood infections. Is it so caused by viruses and affect the upper respiratory tract: nose and throat. They are banal processes that heal without any specific treatment.
It is very common that during the winter, and the first years of schooling, the child can suffer several colds in a row that cause parents to have the false feeling that "the cold can never be cured."
It is more frequent consultation with the Pediatrician. In children it is estimated that they can have between 4 or 5 colds a year.
Causes
The cold is a Infective process caused by viruses. There are about 200 viruses that can cause a cold, but the most common are known as rhinoviruses.
The infection is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person by respiratory secretions that are expelled into the air through coughing or sneezing. It is proven that the hands are a very important vehicle of transmission of respiratory infections. In the case of children, this transmission is facilitated by the toys they share and suck.
Babies and children get so much colds because they have someone who infects them: adults with colds and children at school. It is also a way to become immunized to the hundreds of viruses that cause respiratory infections: this is why colds are more frequent in the first years of schooling.
The belief that children will get cold because they "catch cold", is from contact with other infected children or adults.
Symptoms
It is characterized by nasal obstruction (which can make breathing difficult), increased mucus, and coughing. It can be accompanied by fever and general malaise. The presence of fever is more frequent the younger the child is.
In the days before the cold the baby may be upset, eat less or sleep worse (This is what we call the incubation period). It is common for other family members or schoolmates to also have cold symptoms.
When there is a fever, it usually does not last more than three days and the runny and stuffy nose disappear in a week. Coughing is often the most bothersome symptom and may take longer to clear up - two to three weeks.
Nasal mucus also changes with the evolution of the cold. At first it is transparent, like water and, progressively, it thickens and can acquire a yellowish or greenish color. This is not a sign that it has become complicated or that you need antibiotic treatment.
Treatment
Colds do not have any specific treatment. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms: cough, fever, or pain. The cold heals spontaneously in 2 to 10 days.
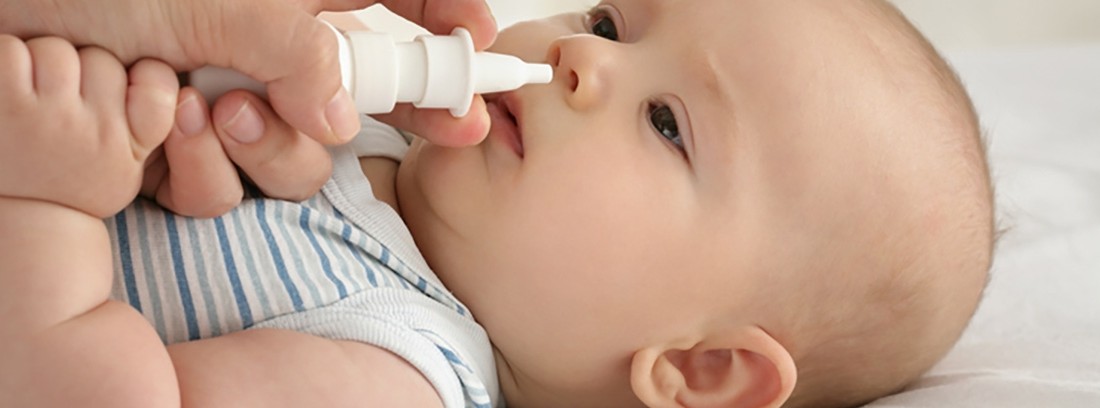
The most effective way to remove mucus and soothe the baby is the nasal wash with physiological saline or sea water. It is advisable to do it before eating and sleeping. If the child has discomfort or fever, the Pediatrician may prescribe paracetamol or ibuprofen.
It is recommended that the child be offered plenty of fluids.
The use of antibiotics is not indicated, it is a viral infection. They do not shorten the duration of the process or avoid complications. It only favors the development of bacterial resistance and the appearance of side effects.
If you are clear if it is, you should know that there are no vaccines for the viruses that cause colds. We only have the flu vaccine that is given each year and that protects against influenza A and B viruses (those that cause the flu) and not against the rest of the possible causes of catarrhal symptoms. Children can be vaccinated from six months.
The best way to prevent contagion is proper hand washing and avoiding contact with sick people.
When to go to the Pediatrician
Colds that do not get complicated heal on their own and do not need drug treatment. You should go to the Pediatrician in the event that the child presents: respiratory distress, conjunctivitis, earache (otitis), high fever of more than three days or poor general condition.
Pediatric Specialist
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)