Congenital chickenpox
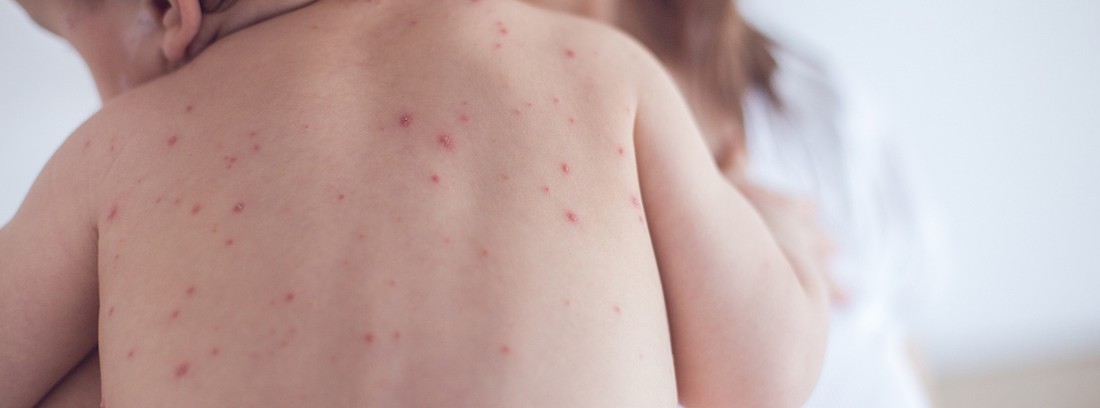
The chickenpox it is caused by a virus, called Varicella-Zoster, from the herpesvirus family; It is also the cause of herpes zoster. In the case of congenital chickenpox It is about when the baby is infected because the mother contracts the disease while she is pregnant or within a few days of delivery.
Symptoms of congenital chickenpox
The severity of symptoms in the newborn depends on when the mother is infected during pregnancy:
- First trimester: about 5% of fetuses are severely affected with significant skin scars and severe neurological and ocular sequelae.
- If the pregnant woman suffers chickenpox Five days before or two days after delivery, it is a very serious situation for the newborn because the baby has not had time to acquire the mother's antibodies against chickenpox. In this case, 25% of newborns are affected by typical chickenpox lesions and can cause death.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by laboratory tests and by the presence of the typical skin lesions of chickenpox in the mother or newborn.
Treatment
In the cases of chickenpox in pregnancyWhen the baby is born, it does not receive any type of treatment because it is not effective, the damage done by the virus is already irreversible.
If the mother develops chickenpox shortly before or shortly after delivery, the newborn needs protection against infection and is given specific immunoglobulin against Varicella-Zoster virus and an antiviral drug called acyclovir.
Prevention
The best prevention against congenital chickenpox is to vaccinate all women of childbearing age who have not had chickenpox and who are planning a pregnancy. The vaccine cannot be given during pregnancy or in the previous three months.
Pediatric Specialist
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)