Differences between white fat and brown fat
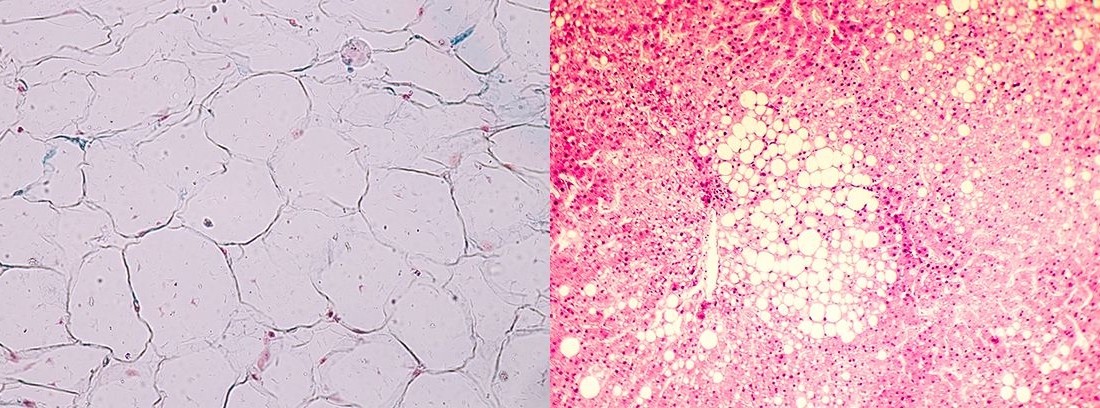
The white fat it accounts for 20-25% of the body's weight and is a reservoir of energy. The brown fat Its main function is thermoregulation, that is, to generate heat in response to the cold outside.
What is white fat?
The white fat it is the majority, represents 20-25% of the body's weight and is an energy reservoir, an accumulation of fatty acids that, if necessary, are metabolized to obtain food in the form of glucose for the cells. White fat accumulates mainly at the level of the abdominal wall in men and in the area of the hips and buttocks in women. An inadequate diet rich in fatty acids and excessive carbohydrates causes white fat to increase and occur, with the consequent health risks that this entails, especially at the vascular level.
What is brown fat?
For its part, brown fat it is more present in newborns, where it accounts for 5% of total body fat, and its percentage decreases as we grow older. The brown fat is located mainly around the renal arteries, the mediastinum, the carotid arteries, the thyroid and in the axillary area.
Unlike white fat, brown fat has thermogenesis as its main function, that is, to generate heat in response to the cold outside. This is especially important in newborns, by use their proportion is higher at birth. It is called brown or brown fat because of its coloration, as opposed to the pale yellowish color of white fat.
It is easy to understand that this type of fat is very abundant in those animals that hibernate, providing heat, while white fat get nutrients.
Studies on white fat and brown fat to help the body
Due to the characteristics of brown fat, its ability to generate heat and the lower risk to the heart and brain that it entails, several studies are currently being carried out on it and on how it could be benefited . In the cervical region of children there are, on average, about 50 grams of brown fat, which is activated and deactivated throughout the day to generate heat based on external thermal stimuli, or when eating or doing physical activity.
The lines of research are aimed at discovering the mechanisms by which brown fat is activated, in this way one could try to activate said fat to help burn white fat. Another avenue of research is to convert white fat into brown fat so that it can be regulated and "burned" through thermal stimuli or physical activity more easily; Studies on two hormones, irisin and FGF21, have shown promising results on the conversion of white fat to brown fat. While 50 grams of white fat accumulate 300 Kcal of energy, the same amount of brown adipose tissue is capable of burning the same amount of kilocalories in 24 hours.
Can you lose weight by eating more fat?
Scientists who study brown fat believe that if brown fat could be activated at will, it would mean that more fat could be ingested without fear of gaining weight. However, this could lead to excessive energy consumption, heat would be generated and body temperature would increase, with which the body would seek to compensate. How? Sweating non-stop to remove heat with perspiration from the skin, which can be a significant inconvenience. Likewise, although burning unnecessary calories and not accumulating in the form of fat is a priori a good idea, the pharmacological agents that are studied and that can induce this effect are not without risks and side effects are one of the main pitfalls of research, as well as the low amount of brown fat in adults, where there is one brown adipocyte for every 200 of white fat.
More research is needed ...
The mechanisms that make the calories we eat turn into brown or white fat are not clear, we have no control mechanism in this regard. For this reason, other lines of research focus on what we can control, such as nutrition, physical activity or environmental or therapeutic interventions and how these modify the presence and activity of brown fat.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)