Laparoscopy
Definition
Surgical intervention for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes that is performed through the use of a laparoscope. It is an invasive procedure but less aggressive than conventional open surgery or laparotomy.
The laparoscope is an instrument in the form of a flexible tube that has an optical system inserted that, connected to a video monitor, allows the interior of the anatomical area to be studied to be visualized.
The most commonly used forms are abdominal laparoscopy (for the study and / or treatment of the viscera contained within the abdomen) and pelvic laparoscopy (for the study and / or treatment of the viscera contained within the pelvis).
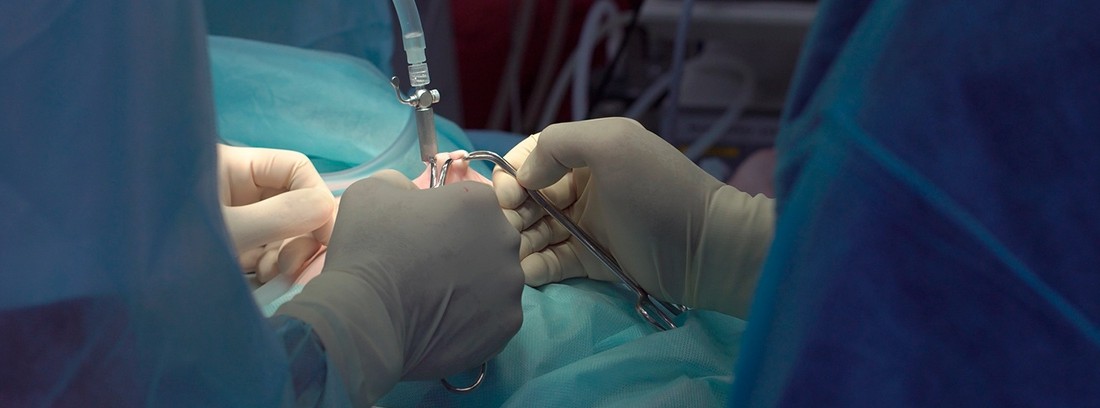
How is the study done?
Laparoscopy is performed in wards operating room at the medical center or hospital by specialized personnel generally on an outpatient basis.
The patient lies on a stretcher throughout the study in aseptic conditions. The doctor proceeds to disinfect the anatomical area to be studied or treated, makes a small incision with a scalpel and inserts the laparoscope. Subsequently, a small amount of air is blown into the studied area to allow correct mobilization of the laparoscope and visualizes the area with the help of a monitor on which the images captured by the laparoscope are projected. Once the visualization is finished, the laparoscope is removed and the incisions are closed.
When laparoscopy is performed for therapeutic purposes, it may be necessary to make other small incisions for the introduction of surgical instruments.
Laparoscopy can be performed with sedation and local anesthesia or in some cases with general anesthesia.
The duration of the study varies depending on the reason for which it is carried out and whether it is for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Preparation for the study
Laparoscopy does not require prior preparation by the patient, except to avoid the intake of liquids and solids between 6-8 hours prior to the study.
If laparoscopy requires the use of general anesthesia, the patient should undergo a pre-anesthetic study (with chest X-ray, blood tests and electrocardiogram).
Some drugs will need to be withdrawn before the study.
What does it feel like during and after the study?
Laparoscopy is an invasive and painless surgical technique for the patient thanks to the use of anesthesia.
The patient may feel a small sting or burning at the time of administration of anesthesia. If general anesthesia is used, drowsiness, nausea or vomiting, dizziness or general malaise may appear upon waking up.
After surgery, the patient may have pain in the incision area that generally subsides with commonly used analgesics and generally be careful with it.
Nonspecific discomfort may appear in the proximity or distance of the studied area as a consequence of the air blown during the study, which will disappear once the gas is reabsorbed.
Study risks
Laparoscopy, like any surgical procedure, has the following risks:
- Infection of the surgical incision or internal organs.
- Bleeding from the surgical incision or internal organs.
- Poor wound healing.
- Surgical damage to internal organs.
- allergy to drugs used during the study (sedative, anesthetic)
- Anaphylactic shock (rare)
The patient should urgently consult with his doctor if hours or days after the study he presents high fever or chills, severe abdominal or pelvic pain, inability to urinate or defecate, presence of blood in stool or urine.
Contraindications
The patient should consult with his doctor before carrying out the study in case of:
- allergy to drugs used during the study (sedatives, anesthetics)
- Coagulation disorders
- Take some type of medication, especially blood thinners or aspirin.
Reasons why the study is carried out
Laparoscopy is a widely known and widely used surgical technique in the field of Medicine.
It can be done for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Laparoscopy performed for diagnostic purposes allows the identification of possible causes of severe abdominal or pelvic pain, the presence of foci of infection or ischemia, benign tumors or malignant tumors, scars or adhesions, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis, and so on. At the same time, it allows the taking of biopsies or tissue samples for later study.
- Laparoscopy performed for therapeutic purposes allows for invasive surgical interventions such as removal of the gallbladder or spleen, removal of small tumors or cysts, adhesions (scars), etc.
Do you know the new insurance Sap? If you are concerned about the economic impact that your admission or that of a family member may have for you, the new hospitalization indemnity insurance MAPFRE can give you peace of mind.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)