Myelogram: Procedure, Uses, Risks, and Results
Definition
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. It is housed inside the spinal canal, delimited by cervical, dorsal and lumbar vertebrae. Each of these vertebrae are separated from each other by the intervertebral discs. The spinal cord is made up of afferent and efferent pathways. The former conduct the nerve impulse from the brain to the extremities and organs. The efferent pathways pick up the sensitivity and conduct it in the reverse direction to the brain. The medulla, like the brain, is immersed in cerebrospinal fluid, whose function is to cushion and protect.
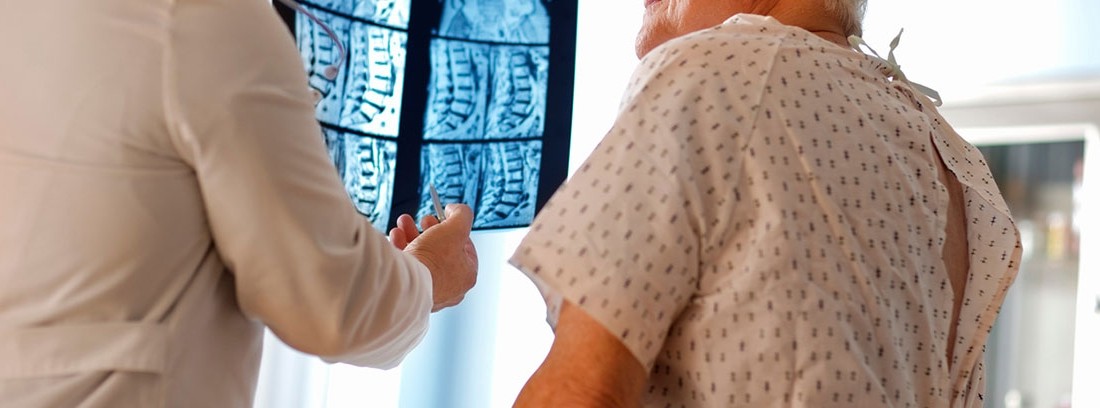
A myelogram is a test that allows the study of the cord and spinal canal. It consists of the injection of a non-ionizing soluble contrast into the spinal canal. Subsequently, radiographs or a computerized axial tomography (CT) are performed in order to assess the correct distribution of contrast in the cerebrospinal fluid and the morphology of the spinal cord and roots.
The myelogram with tomographic study was considered the essential radiological study prior to the intervention of herniated disc. Its use has been displaced in many cases by nuclear magnetic resonance, although it is still very useful in patients with multiple disc lesions, radiculopathies, disc protrusion or previous lumbar intervention.
Alternative names
Myelography.
How is the study done?
The practice of the myelogram is frequent on an outpatient basis, so it does not usually require hospital admission. It must be done under aseptic conditions. The patient must lie face down on a stretcher. The skin on the back is cleansed with antiseptic. A local anesthetic is applied to the puncture site. The puncture site is usually low lumbar, although if it is considered safer or more useful it can be practiced at the cervical level. To do this, the patient will be placed in the lateral decubitus or sitting position. The radiologist inserts a fine needle into the spinal canal, usually guided by the images obtained with a fluoroscope. A small amount of the cerebrospinal fluid is aspirated and the contrast medium is injected. After its application, the needle is withdrawn and the tomographic study begins. During the examination the patient must remain immobile. The duration is usually one to two hours.
Preparation for the study
It is advisable to have a liquid dinner the night before the exploration. Fasting is not required, but a liquid breakfast is also recommended. You should inform your doctor of the treatments you are using, paying special attention to antiplatelet drugs (clopidogrel, acetylsalicylic acid, ticlopidine) and anticoagulants (heparin, acenocoumarol). The physician will assess the indication to withdraw the treatment in the days prior to the examination.
What does it feel like during and after the study?
A brief sting is felt when the local anesthetic is injected and slight pressure is felt in the back when the spinal needle is inserted. Cramps can be felt in both legs at the time of its introduction. Once the examination is completed, the patient will be taken to a resting area for about two hours, where the constants will be controlled. You should always try to keep your head slightly upright, about 35º approximately, and never at a lower level than the rest of the body. It is advisable to drink plenty of water. The incidence of headache, nausea or vomiting is low and is generally not a cause for alarm, but the measures listed are usually sufficient to prevent its occurrence. After this time, and in the absence of complications, he can be sent home. It is important to continue resting 24 hours. The patient can return to normal activity on the second day of the examination.
The responsible physician should be informed if you have persistent high fever, excessive nausea or vomiting, severe headache for more than 24 hours, stiff neck, or numbness in the legs. It should also be reported if you have problems with urination or bowel movements.
Study risks
In general, a myelogram is a safe procedure, but it is not without complications, since it is an invasive examination. Risks may be related to lumbar puncture or contrast infusion.
The risks of lumbar puncture are predominantly infectious (meningitis, cellulitis, spondylodiscitis). They are exceptional if performed under the indicated sterile conditions.
The contrasts used are generally safe and have minimal side effects. The most common are nausea, vomiting, and itching. More infrequent would be dizziness, cough, headache or abdominal pain. In the most serious cases and exceptionally, the patient could present an allergic reaction with respiratory distress, altered heart rhythm, blood pressure, severe allergic reaction or anaphylactic shock. These serious adverse effects are more likely in patients who suffer from some type of allergy and especially in those who have previously suffered an adverse reaction to contrast agents.
For women, if there is any possibility that you are pregnant, it is important that you tell your doctor before the myelogram. The radiological and tomographic study is based on the emission of ionizing radiation that can be detrimental to the correct development of the fetus.
Study contraindications
Contraindications are those that contraindicate the performance of lumbar puncture: psychomotor agitation, coagulation disorders, intracranial hypertension and dermatological infection in the area where the puncture should be performed.
Reasons why the study is carried out
The myelogram is useful in detecting abnormalities that affect the spinal cord, spinal canal, spinal nerve roots, and the blood vessels that nourish the spinal cord. It may be more useful than MRI in patients with previous lumbar surgery, lumbar stenosis, multiple herniated discs, tumors, infections, or spinal abscess. The myelogram is also presented as an alternative in those cases in which the use of nuclear magnetic resonance is contraindicated, such as the case of patients with pacemaker carriers.
Despite this, the invasiveness of the procedure, its use should be limited to specific cases.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)