Nosebleed
Nosebleeds are bleeding from the lining of the nose. Nosebleed is also called epistaxis. It is a very common phenomenon among children from 2 to 10 years old. Most often, the bleeding is unilateral: only from one nostril.
Causes
The nasal septum is made up of a very thin mucosa that has many blood vessels. Little ones bumps or wounds, environmental dryness or a simple cold, they can make it bleed easily. Sometimes it can happen while the child is sleeping. Bleeding occurs most frequently in the anterior and inferior area of the nasal septum (Kiesselbach's area).
Other less common causes of nosebleeds They are: the use of drugs and nasal decongestants, blood clotting disorders or high blood pressure. When the bleeding is very abundant and frequent, the existence of a nasal angiofibroma (benign tumor of vascular origin that is frequent in adolescent males) must be ruled out. Obviously a trauma to the face or directly to the nose can also cause a nosebleed.
Symptoms
The emission of blood through a nostril occurs with more or less intensity. It can happen while the child is asleep.
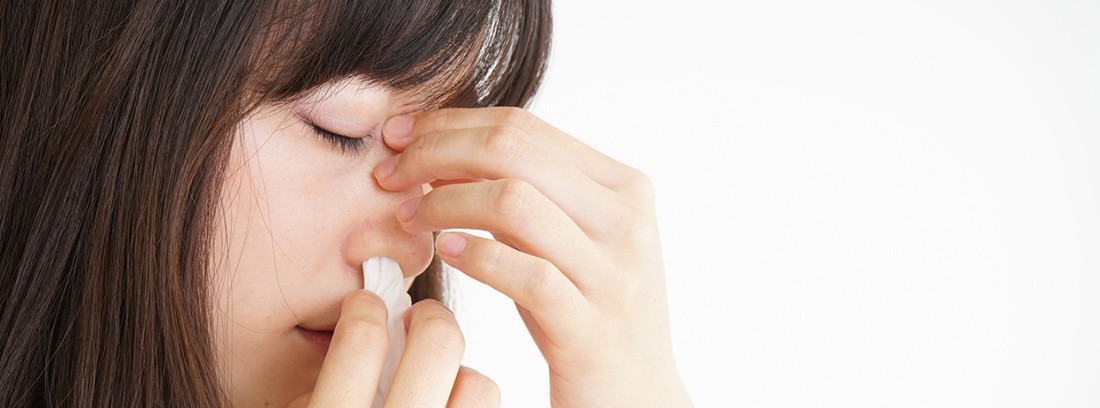
Treatment
You must remain calm. If we are calm, we will not scare the child who, in most cases, does not have any discomfort. In most cases, epistaxis in children is usually mild and resolves easily. The bleeding is usually in the form of a drip and can yield on its own in a few minutes.
We can perform some maneuvers to stop the bleeding more quickly. The simplest and most effective way is squeeze the bleeding nostril with your fingersand with the child's head in a normal position. Pulling it back is not recommended because blood from the nose could be swallowed by the child and cause gastrointestinal upset. The nose is held tight during 5-20 minutes until the bleeding stops. If after 20 minutes the bleeding has not subsided, go to a medical center. In the case of needing medical attention, the Pediatrician will perform a nasal packing or he will put some medicine that causes vasoconstriction and makes the bleeding stop. If the bleeding is repeated or is very bothersome for the child, the bleeding area may be burned (cauterization).
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)