Physiotherapy and its intervention in esports
Is it funny or it may sound strange that a physiotherapist can be considered a part essential for an eSports team. To play at these levels, physical and mental preparation is required to match, so, like a traditional athlete, they need a team made up of a coach, physical trainer, psychologist and physiotherapist to help the player's performance be optimal.
How can physical therapy help the gamer?
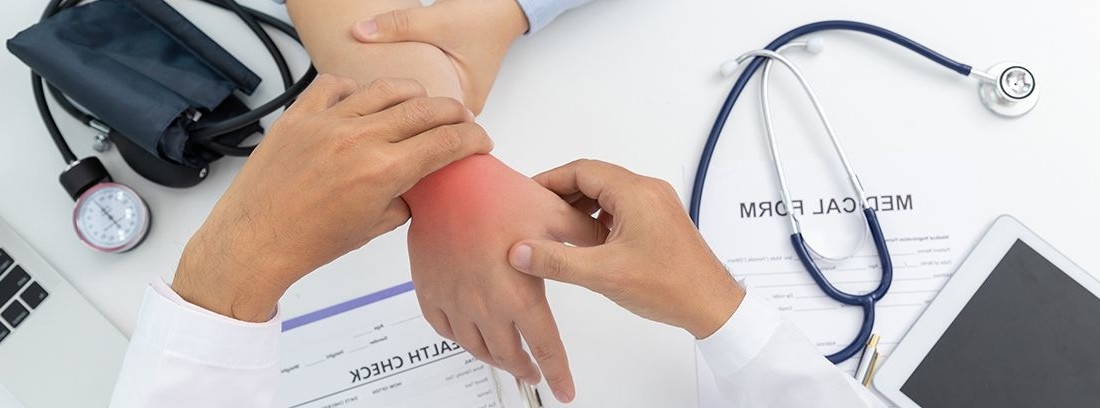
Gamers can spend many hours training or competing, and although it seems like a sport with little physical exhaustion, it is not like that. We agree that it is not an impact sport, where the body is exposed to blows or falls, such as rugby, football or basketball. But the fact of spending many hours sitting in front of a screen and using a keyboard, mouse or a console predisposes the body to suffer injuries such as inflammation of the tendons, bursae, fibrillar tears or muscle contractures. Next, we will detail which are the most common in this type of activity.
Most frequent injuries in eSports
By discard, the tendinopathies are the most frequent injuries in this collective. They usually appear on the wrists, elbows or the phalanges of the hand. The different ways of appearance in relation to the activity are:
- Epicondylitis: it is located in the elbow and it is due to the overload of the forearm and wrist muscles that insert into the epicondyles of the humerus. The continuous tension of the musculature due to the prolonged use of the keyboard or game controllers They end up overloading the muscles and inflaming the insertion tendons. The injury is characterized by weakness in the forearms and pain that can be disabling.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: it is the compression or entrapment of the median nerve at the wrist level, just below the flexor retinaculum, through which nerve and tendon structures pass. Inflammation of this area due to its overuse during play can cause a compression of the median nerve which gives symptoms of tingling, stabbing pain and weakness in the hand and forearm.
- Quervain's syndrome: it is located in the thumb area, is an inflammation of the abductor longus tendon sheath and the extensor brevis due to overuse. In video games, control knobs are also used that require very fast and repetitive movements of the thumb to press the buttons. In these cases, the tendons of the thumb and its tendon sheath can be damaged, giving rise to the appearance of this tendinopathy that causes pain and difficulty moving the phalanges and the trapezius-metacarpal joint (the one that allows the opposition movement of the thumb).
- Bursitis: It's about the bursa inflammation that avoid friction between some bone structures, as in the shoulder or elbow. Repetitive and continuous movements can inflame these structures creating pain and functional impotence, such as the use of the mouse or more complex control commands.
- Eye fatigue- The musculature of the eye has to do work to focus closely or when there is much or little light, so it can cause itchy eyes, redness and even a headache.
Some recommendations if you are a gamer ...
- Take breaks and stretches every 60 minutes. They will help prevent fluid retention in the lower limb and the muscles from seizing due to static positions conditioned by activity.
- Maintain a good physical condition. Maintain well-toned postural muscles to avoid muscle overloads and perform cardiovascular exercise such as cycling, running, swimming, etc ...
- . Ergonomics is important, but it must be taken into account that injuries in gamers appear sooner or later, simply due to the fact that during training and competitions they can spend many hours playing and thus harm their health. Which is why it is really necessary to have a physical therapist nearby who provides follow-up and physical maintenance for prevent injuries and improve performance during play.
By way of prevention ...
What stretches can I do to avoid tendon inflammation and muscle contractures? Stretches should be done two to three times and each lasts 15 seconds. Next, we will detail the muscles that you should stretch if you spend many hours in front of a screen practicing electronic sports:
-
Stretching of the cervical region:
- Upper trapezius: tilts to the sides. Bring the ear towards the shoulder on the same side and use the ipsilateral hand to finish tilting the head.
- Lower trapezius: bring the nose towards both shoulders, help with the hand on the same side to finish tilting the head.
-
Forearm Stretch:
- Flexors and extensors of the wrist: with the elbow straight and the palm of the hand facing up, take the fingers of the hand and bring them towards the ground to stretch the flexors. The same movement is performed, but with the palm facing the ground to stretch the extensors.
-
Arm and shoulder stretches.
- Triceps: with the elbow bent to the maximum, we bring it up with the help of our contralateral hand until we feel the tension of the back muscles of the arm.
- Pectoral: raise the arm with a slight elbow flexion (the hand should be at a height above our head), rest the palm of the hand on the frame of a door or a column and take a step forward maintaining the support About this.
- Infraspinatus: raise the shoulder in flexion and with the elbow bent, bring it with our other hand towards the contralateral shoulder until tension is felt in the posterior muscles of the arm and shoulder blade.
- Spinal self-stretching: hanging from a bar without the feet touching the ground (on a trellis, for example) to stretch all the muscles and self-traction the lumbar vertebrae that can be compressed by prolonged sitting position.
- The fact of spending many hours sitting in front of a screen and using a keyboard, mouse or a console predisposes the body to suffer inflammation of the tendons, bursae, fibrillar ruptures or muscle contractures
- It is convenient to carry out the stretches (such as those proposed) two to three times and with a duration of 15 seconds each.
yasmina Santiago
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)