Radiotherapy: A Key Treatment for Cancer
Cancer cells are characterized by their uncontrolled growth, that is, much faster than normal cells. Radiation therapy works by damaging the genetic material (DNA) in the tumor cell and preventing it from growing and multiplying
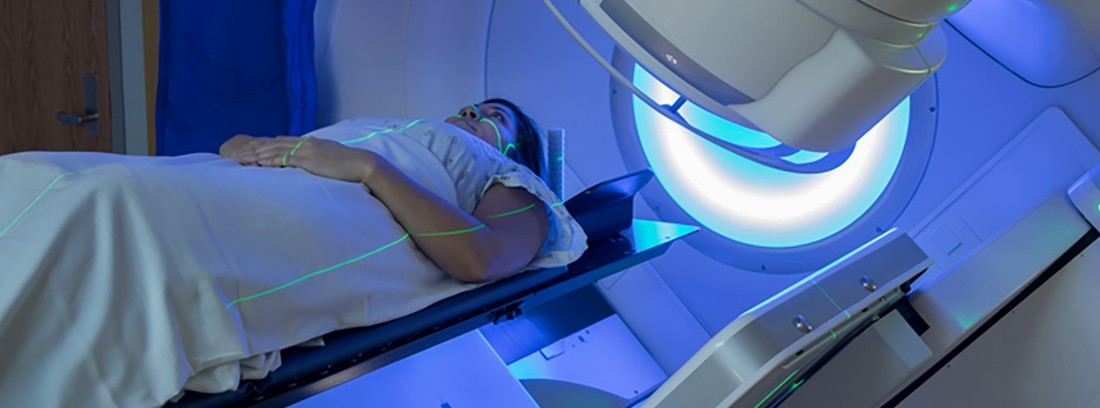
Radiotherapy It is a type of treatment used in oncology to eliminate neoplastic (cancer) cells or decrease the size of tumors and relieve the symptoms they cause. It is based on the use of high doses of ionizing radiation for the elimination of malignant cells from tumor tissues.
Types of radiation therapy
Before carrying out a radiotherapy treatment, a planning is necessary in which the adequate radiation dose, the body area to be irradiated and the number of sessions necessary radiation therapy. Generally, the treatment requires several sessions (called daily treatment or fractions that last a few minutes) over a period of weeks. Basically radiation therapy can be received as:
- External radiation therapy: radiation doses are administered from an external source, that is, a specific machine that emits ionizing rays.
- Internal radiation therapy: a radioactive source that can be implanted (radioactive seeds) is inserted into the area of the body that you want to irradiate, called brachytherapy or it can be administered by vein (radioactive isotope) that attaches to the tumor tissue, destroying it.
Side effects
Although an attempt is made to minimize the damage to the healthy tissues that surround the tumor tissue, there is always an involvement or toxicity on healthy neighboring tissues. This translates into side effects associated with radiation therapy. The most common widespread side effects are:
- Fatigue
- Skin reactions
- nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Inflammation of the (mucositis)
- Alteration of lung tissue
- Cardiac complications
- It is based on the use of high doses of ionizing radiation for the elimination of malignant cells from tumor tissues.
- There is external radiation (radiation is administered from a specific machine) and internal radiation, administering radioactive seeds or radioactive isotopes.
- Most common side effects: tiredness, skin reactions, nausea and vomiting, and diarrhea.
Dra. Eva Ormaechea Alegre Intensive Medicine Specialist
(Updated at Apr 15 / 2024)
Cancer articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.