What is 5D ultrasound and how is it performed?
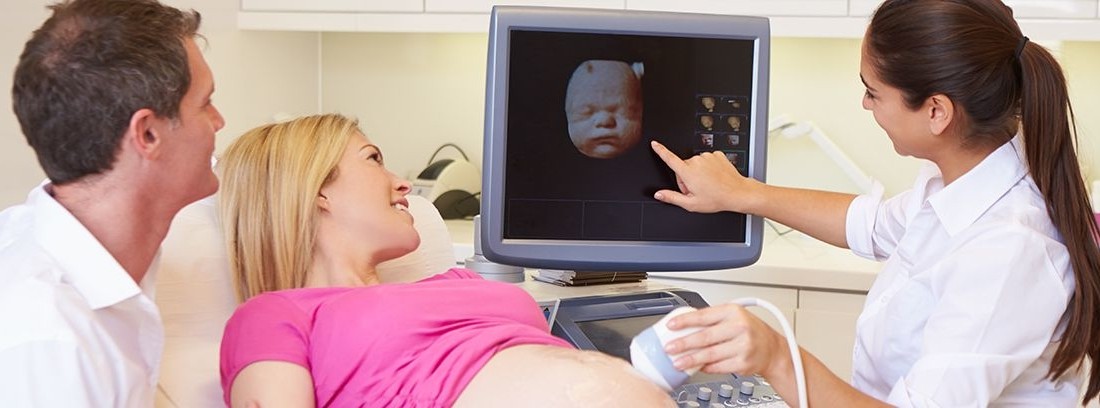
5D ultrasound is an image in three dimensions and in real time, like 4D, but in which the treatment of the images in the computer allows to soften the textures, modify the color of the image and apply a light source from different angles so that lights and shadows are created and this gives a more real picture. However, 5D ultrasound does not allow the detection of more malformations than the other ultrasounds .
What is an ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic test using ultrasound, similar to ship sonar. The machine has a transducer that is placed on the patient and that emits ultrasounds (high frequency sounds) that are reflected differently in each tissue of the body.
The transducer receives these reflected ultrasounds and the machine's computer processes them so that an image is projected on the screen. Hence the name of ultrasound, because it collects the echo of the sounds emitted.
Different probes or transducers can be used, which in pregnancy controls can be abdominal to explore the fetus in gestations between 12 and 42 weeks and the vaginal one, for incipient pregnancies.
What is seen in each ultrasound?
Depending on the weeks of gestation at which the ultrasound is performed, what we can expect to see is different:
- Between 8 and 20 weeks The fetus can be seen in its entire body, as it is being formed, the beginning of the extremities, the sex from approximately 14 weeks, but it is still difficult to see the features of the face.
- Between 20 and 26 weeks images of specific planes of the fetus, face, hands, feet, genitals… are obtained.
- Between 26 and 30 weeks you can better appreciate the gestures, movements, how they yawn, how they suck their thumb ... and the face already has more of a baby image than before.
- From 30-32 weeks Good images are more difficult to obtain because of the position of the baby and the decreased proportion of normal amniotic fluid in late pregnancy.
Is it a safe test?
It is important to know that when it comes to ultrasounds has no harmful radiation, neither for the pregnant woman nor for the fetus, unlike the It is necessary to place a transmitter gel so that the ultrasounds propagate correctly since they have very poor transmission through the air.
Another big difference with X-rays is that it is a real-time image, that is, it is a dynamic test and not a static image like a photograph. You can freeze the image on your screen for study, as well as print this image on your printer.
What's new in 5D technology
Recently, the software that allows image composition and treatment has been improved, modifying the sepia tone of 3 and 4D ultrasounds by a rosier hue with more shadows and a textured feel, as if we could see a real image of the illuminated fetus. And it is what has been called 5D.
Currently, the realization of a 5D ultrasound Rather, it responds to a desire for get pretty pictures of the fetus in motion, of its features and evolution, so we are not facing a medical test for diagnostic purposes. In fact, there are many centers that perform them. Yes indeed, for eye-catching images we depend on:
- Fetal collaboration, it must be in a good position.
- That the placenta does not obstruct vision. yes as if the placenta does not obstruct vision.
- That there is abundant liquid.
- If the pregnant woman is thin, much better.
Despite the qualification of the technician or doctor and his best intention, a good result is not always achieved. In this, 5D technology has also been an advance as it better solves the problem of interference from organs or tissues that get in the way of the image.
After the ultrasound is done, expectant dads take home 20-30 minutes of pictures recorded on digital media such as CD / DVD or storage pencils, photos, even projections on the mother's womb at the same time as the ultrasound is performed.
Differences between 5D ultrasound and other ultrasound scans
The medical utility is limited, for example, it is not possible to diagnose a fetus with only by ultrasound neither 2D nor 3D nor 4D.
2D ultrasound
Traditional or 2D ultrasounds are the most widely used, in addition, many of the malformations are suspected or diagnosed on 2D ultrasound.
The image we visualize is seen in different shades of gray, white or black and it is an image like a slice, it makes a cut of a tissue, organ, etc. By moving the transducer we can go more or less into the fabric and make different cuts. In addition, by moving the transducer in the different axes of space we will achieve different viewing angles and make cuts in the three axes of space.
In an ultrasound of a patient, both adult and child, we can place the transducer in a certain position to have the expected cut of the different organs, but in fetuses, since they are not positioned as we want and we cannot move them at will in occasions it is difficult to see all the structures we want to see. For this reason, it is often said that the patient eat something before the examinations, so the fetuses tend to move more and we can achieve the desired cuts.
3D ultrasound
3D ultrasound is a three-dimensional picture. The ultrasound computer achieves different parallel sections of the fetus (or the organ to study) and performs a reconstruction in three dimensions. That is why 3D ultrasound achieves only motionless photographs.
Generally photographs of the face are taken, but sometimes also of the extremities and genitals since they are usually the ones that future parents like the most. Only on some occasions is 3D ultrasound used to detect facial defects such as cleft lip, neural tube defects such as or some limb malformations.
4D ultrasound
4D ultrasound introduces time, that is, they are moving images like conventional 2D ultrasound but in three dimensions. For some heart diseases, 3-4D ultrasound is also helpful since it allows delayed work with volumes and functional studies.
What does the future hold?
Although at the moment the objective of the 5D ultrasound It is rather playful, there is a very important medical indication of this technology that is in its infancy but which already promises a great future, since allows better visualization of possible external anatomical alterations of the fetus (cleft lip, genital malformations,, limb malformations). And the acquisition of volumes of images that, once the examination is finished, when the patient is already at home, allows the doctor to examine her from different angles to those who looked at her live and take different measurements. This is one different conception of what was known until now of an ultrasound, which was a test that was interpreted as it was performed.
You have doubts? Sign up for Savia, the service platform of MAPFRE digital health that allows you to speak for free by chat or video consultation with a doctor to solve all your medical doubts.
SIGN UP FREE
What you should know:
- It allows to obtain an image of the fetus that to many seems more real, but it does not allow to detect more malformations than in previous ultrasounds.
- As it is ultrasound, it does not have harmful radiation, neither for the pregnant woman nor for the fetus, unlike X-rays.
- Traditional or 2D ultrasounds remain, for now, the most widely used.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)