What is an MRI?
The basis of operation of the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) It consists of the generation of an electromagnetic field through the use of a large magnet and the emission of radio waves by a scanner; radio waves and the electromagnetic field excite protons (nuclei of hydrogen atoms) found in tissues that want to be studied causing them to align with each other.
When the electromagnetic radiation stops being emitted, the protons are released and return to their initial position releasing energy in the form of radio waves that will be collected by the scanner and sent to a computer for processing as a radiological image that will later be studied by the
Magnetic resonance imaging does not use ionizing radiation (X-rays) or radiopharmaceuticals.
How is the study done?
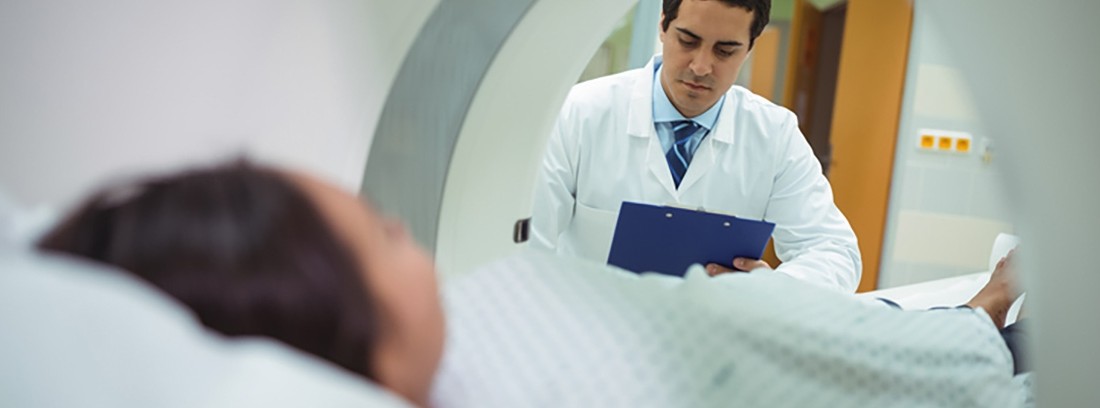
The MRI is performed in the radiology room of the medical center or hospital by a radiology technician. The patient must undress the anatomical area under study and, in necessary cases, they will be provided with a gown to cover themselves; at the same time you should remove your personal items, especially jewelry and metal objects that can interfere with radiological images.
Some studies require the use of a contrast for a better definition of the radiological image.
Once the contrast has been administered (in those studies that require it), we will proceed to take the radiological images for which, the patient will lie on a table that will slowly move into the scanner (tube-shaped). Once inside the scanner, the patient must stand still until the end of the study.
The magnet located around the scanner tube will begin to rotate around it to generate the electromagnetic field necessary for the study. Inside the scanner, radiological images of the anatomical area to be studied will be obtained and sent to a computer for processing and further study.
The duration of the examination will depend on the anatomical area to be studied and the amount of radiological images necessary to complete the study, generally it usually takes between 30 and 60 minutes.
Preparing for an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging does not require prior preparation, but an informed consent will be requested by the patient. The patient must undress the anatomical area under study and remove their personal belongings, especially jewelry and metal objects and certain prostheses.
Some studies may require some type of simple preparation such as avoiding the ingestion of certain foods hours before the study. The doctor or radiology technician should inform the patient of these conditions prior to the study.
What does it feel like during and after the study?
MRI is painless for the patient Except for the inconvenience of administering contrast in studies where its use is necessary. The patient should stand still while the study is in progress. Sequences of images are made of several seconds or minutes each, with a few seconds of rest between each sequence in which the patient can relax. Scanner rooms are usually air-conditioned. Some centers offer open scanners for people who suffer from claustrophobia and obesity. The patient can lead a normal life once the study is finished, except for specific indications from the doctor or technician.
Study risks
Magnetic resonance imaging does not imply a health risk by not using ionizing radiation or radiopharmaceuticals. In some cases an allergic reaction to the contrast may occur; In the case of presenting a skin rash, or respiratory distress during the study, it should be indicated to the radiology technician immediately. Severe anaphylactic reaction is rare.
The possible effects of electromagnetic fields on the embryo or fetus are not known, so the pregnant woman or one who suspects that she may be pregnant (including those who carry one should avoid the study as far as possible and should indicate to the technician in radiology that you are pregnant before having an MRI.
Contraindications of MRI
The patient should consult with his doctor before carrying out the study in case of:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- in contrast studies)
- Perform some type of treatment
- allergy to contrast in previous studies.
- Prosthesis and in general any implanted metallic device.
Some devices can be altered due to the magnetic field, in these cases, the use of resonance is totally contraindicated, among them:
- Internal defibrillator (implanted)
- Cochlear (ear) implant
- Clips used in brain aneurysms
What is the study done for?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a simple and safe test, widely used in recent decades in the field of Medicine as it provides very valuable information for the doctor. Since radio and electromagnetic waves have a special affinity for hydrogen atoms found in high concentration of organs and soft tissues, this is an especially useful test to assess the brain, lungs, liver, heart, reproductive organs, large bones ... allowing the study and monitoring of multiple conditions (inflammations, infections, injuries tumor) with great diagnostic sensitivity.
If you need to get an MRI and you don't want to wait, you may be interested in one of the closest centers where you can use the platform of services ofMAPFRE digital health
SIGN UP FREE
Family and Community Medicine Specialist
(Updated at Apr 15 / 2024)