What is osteoarthritis?
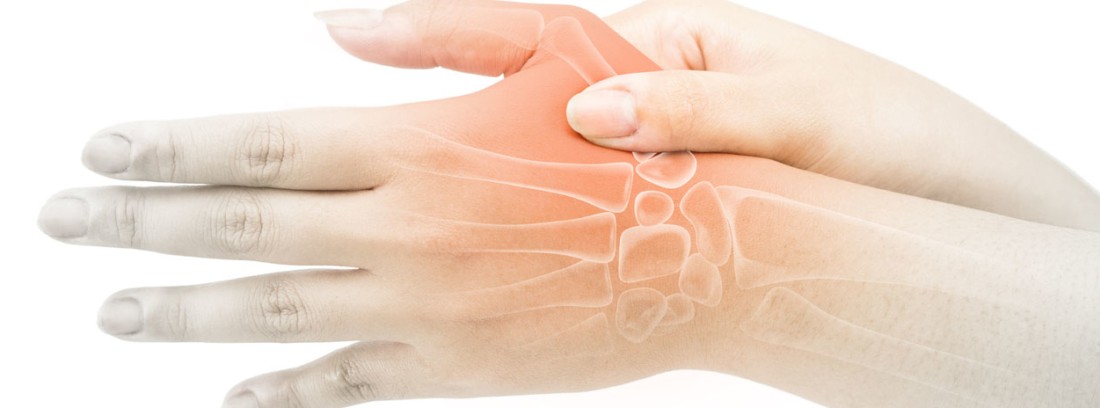
Osteoarthritis it is a non-inflammatory disease characterized by the. It is the second leading cause of permanent disability after cardiovascular diseases. Its incidence increases with age, and from the age of 50 it predominates in women. Approximately 85% of the.
How it is produced
Osteoarthritis is the result of biomechanical, metabolic disturbances and related to cellular characteristics cartilage and adjacent bone. Initially, an aggression, whether mechanical, genetic, hormonal or otherwise, increases the release of enzymes that begin to degrade cartilage. Later, an attempt is made to repair with proliferation of cartilage cells, but these are of a defective quality. Even if there is an increase in the activity of the arthritic cartilage, its degradation prevails, in which other elements intervene. The adjacent bone responds with proliferation of the edges of the joint, a lesion that can already be seen in imaging tests such as radiography.
Osteoarthritis is classified as:
-
Primary: unknown cause (most common)
-
Secondary: injuries, infections, hereditary diseases ...
Are considered risk factor's for osteoarthritis, age, female sex, mechanical factors, constitutional factors, and genetic factors.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
- The pain is the main symptom of osteoarthritis; is an insidious and mechanical onset pain, which worsens with activity and improves with rest. Initially it may improve after some activity, but later the pain increases the more the joint affected by osteoarthritis is used. In advanced cases, the pain can be nocturnal and at rest.
- The joint stiffness It appears after hours of inactivity, lasts a few minutes and disappears with joint mobilization.
- They can also refer joint crunches.
- As the disease progresses, joint deformities, joint instability, abnormal joint mobility and / or joint effusion. Consequently, there is an important functional limitation.
Diagnosis
It should be based on the symptoms, physical examination and radiological signs, previously ruling out other rheumatic diseases.
- In the physical exploration Joint crackles, local pain, joint heat, bone deformity, joint effusion, and Heberden and Bouchard nodules are examined, among the most frequent.
- The bone scan It is the first test to request of the joints that present symptoms or signs of osteoarthritis. It is important to take an X-ray of the contralateral joint. Radiographic signs include joint space narrowing, subchondral bone sclerosis, formation of marginal osteophytes (bony prominences), and bone contour alterations.
- The Lab tests They do not usually show any specific alteration unless there is an associated disease.
Treatment for osteoarthritis
It is a symptomatic treatment that must be accompanied by information to the patient about the nature of the disease, teaching the patient to avoid overloads, avoid incorrect postures and carry out adequate exercise.
- The repose It is indicated in phases of acute pain.
- The use of drugs such as paracetamol. If it does not improve, it is advisable to add a drug nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) for a period of approximately 15 days.
- The NSAIDs Topical (in the form of gel, spray, cream) have not been shown to increase the effectiveness over the oral route.
- Other drugs Newer ones such as sulfate are substances that have been shown in an experimental way to prevent the development of osteoarthritis or slow down the damage in joints already affected, but until obtaining future studies that support their effectiveness, their use is not recommended.
- The surgery It should be evaluated in those patients who present intense pain resistant to treatment, a deformity that hinders mobility and a significant functional limitation. The hip and knee are the joints that benefit the most from surgery in the form of prosthetics mainly.
- Age is the main risk factor (85% of the elderly population suffer from osteoarthritis).
- pain is the most common symptom: it gets worse with activity and improves with rest.
- Treatment is symptomatic: rest in the acute phase with drugs such as paracetamol. If it does not improve, it is advisable to add a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)