What is pollinosis (hay fever) and how can it be treated?


Pollinosis or "hay fever" is an allergic disease that is the number one cause why people seek help from an allergist. Pollinosis occurs in humans from contact with pollen from various plants and mainly affects the eye mucosa and respiratory tract. In nature, very many types of plant or flower pollen have pronounced allergic activity, which in highly sensitive people, after contact with pollen, causes a seasonal disease with a whole range of allergic reactions. But a huge number of people may not experience any discomfort from contact with dusty plants. They can sneeze a couple of times due to a pungent smell of a flowering plant but that is all. But for people suffering from hay fever, the joy of the spring nature awakening is clouded by the development of allergies. Many patients with symptoms of this seasonal illness completely disrupt the usual rhythm of life - they are unable to work, study, or even do their daily activities. Why is this happening?
Short information about pollinosis (hay fever)
The reasons for the development of hay fever
An allergic reaction is, first of all, the response of the immune system to the ingress into the body of a certain foreign substance (allergen) from the environment. With hay fever, pollen of plants is this foreign body. An ordinary person who is not exposed to its dangerous effects does not observe any immune reaction when inhaling and exhaling pollen. But the immune system of an individual with hay fever, after getting the smallest pollen, even 10 microns, into the respiratory tract or on the mucosa of the eyes or on the skin, turns on the system for recognizing an allergen as some kind of pathogenic virus or bacteria. This triggers the defense mechanism manifested in inflammation and accompanying symptoms – itching, reddening, mucus secretion.
Incidence and risks of pollinosis or hay fever
Depending on the climatic zone and regional characteristics, from 1 to 15-20% of the population can be sensitive to pollen. Naturally, in the north people are less likely to have this type of allergy and southerners are more likely to have it. The periods of pollinosis flare-ups are directly related to the periods of the flowering of certain plants.
The plants that have a high likelihood of causing pollinosis when flowering:

- Alder,
- Birch,
- Hazel,
- Oak,
- Various cereals,
- Wormwood,
- Ragweed and many other plants.
The intensity of hay fever increases in windy and dry weather due to an elevation in the concentration of pollen in the air. With the onset of wet and rainy weather, the amount of pollen decreases and the severity of allergy decreases.
A significant role in the development of hay fever is played by a hereditary predisposition. It is clinically proven that if both parents of a child are susceptible to allergic diseases, then the probability of an allergy in a child can reach 80%, if only one of the parents is allergic - 25-40%. In cases where parents are not allergic, the risk of developing allergic diseases is only 10%.
Symptoms and manifestations of pollinosis
The most frequent manifestations are those of allergic rhinitis, which are characterized by:

- Prolonged sneezing;
- Profuse mucous discharge from the nose;
- Itching in the nose;
- Perspiration in the oropharynx;
- Runoff of mucus along the back of the pharynx;
- Nasal congestion;
In most patients, rhinitis is combined with allergic conjunctivitis:
- Redness and swelling of the eye mucosa;
- Itching of the eyelids;
- Photophobia;
- Lacrimation;
- Sensation of "sand in the eyes".
Another manifestation of hay fever can be pollen bronchial asthma:
- Cough,
- Labored breathing,
- "Wheezing" and/or "whistling" in the chest,
- Choking.
Somewhat less often, with pollinosis, there are itchy rashes on the skin (urticaria) or local edema (Quincke's edema or angioedema), separate manifestations of atopic dermatitis.
The severity of hay fever

Pollinosis can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on the intensity of symptoms.
With moderate to severe and severe course, symptoms of pollen intoxication can be observed in the form of general weakness, malaise, headache, loss of appetite. In the case of inadequate treatment or with its severe course, complications as a result of the addition of secondary infection such as purulent conjunctivitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, or even pneumonia can develop.
In some patients, a reaction to plant pollen may be accompanied by symptoms of the development of food allergies, and its manifestations will be year-round. For instance, if a patient is allergic to tree pollen, then he or she may develop a reaction to the fruits of trees (apples, pears, peaches, apricots, plums, nuts, etc.), as well as to raw carrots and some other types of products. This is manifested by the development of sore throat, discomfort in the throat, itching, swelling in the mouth and throat.
Worth noting, manifestations of seasonal allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma are observed not only with allergies to pollen but also to molds. A huge number of microscopic mold spores appear in the air from the start of sporulation - from March to mid-autumn.
Thus, hay fever can also occur in the context of year-round allergic rhinitis, when an allergy to pollen is combined with an allergy to non-seasonal allergens.
Very often, hay fever can be hidden under the diagnoses of "chronic rhinitis" or "vasomotor rhinitis", which leads away from choosing the right treatment tactics.
Pollinosis diagnostics
If you suspect the development of hay fever, you must, first of all, seek qualified help from a therapist or allergist. It is very important to exclude the presence of diseases with a similar course. First of all, it is ARVI, acute tracheitis, or bronchitis. It is important to remember that only an experienced allergist-immunologist with the help of modern diagnostic equipment can accurately diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
First of all, for the diagnosis of hay fever, the allergist-immunologist conducts a thorough collection and analysis of the patient's history, a thorough examination. If necessary, the otorhinolaryngologist performs a rhinoscopy to determine the condition of the nasal cavity, its swelling, and the narrowing of the nasal passages.
Skin allergy testing has also proven itself well for diagnosing household allergies (house dust allergies, microscopic mites, library or book dust), pet allergies (epidermal allergies), and food allergies.
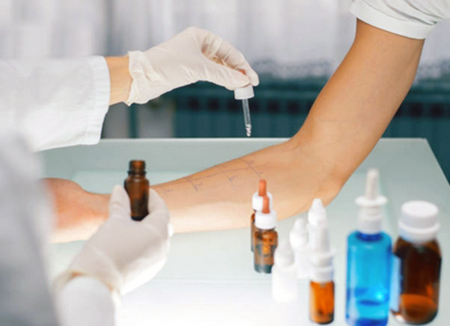
Skin tests, called "prick testing" are a safe and highly informative examination method. It is advisable to carry out such tests without exacerbation of the allergic disease. The advantage of "prick testing" in comparison with classical scarification tests is less trauma to the skin with a higher specificity of the reaction (i.e., the nonspecific reaction of the skin to the scarification effect is excluded, the probability of a "false positive" result is reduced).
The technique of the test consists in applying small drops containing various allergens to the skin of the forearm. Then a minimal superficial puncture of the skin is performed ("prick" means an injection), and then, 20 minutes after application, a visual analysis of the reaction occurred. In the existing allergy, a blistering reaction occurs at the site of application of the culprit allergen. The size of the blister determines the degree of reaction.
It is advisable to carry out skin testing for patients with pollinosis in the autumn-winter period after stopping the use of antiallergic drugs, as while taking antihistamines, the skin becomes "blocked" and the tests may show a false negative result.
If necessary, the patient can be appointed a blood test for the presence of allergic antibodies to a wide variety of allergens. This analysis can be done to patients of any age, regardless of the treatment and the phase of the disease.
Pollinosis treatment

Is it possible to get rid of hay fever forever? Unfortunately, currently, there is still no medicine that could completely cure this disease. Modern medicine also cannot change the genotype that forms the disease. But it can significantly alleviate the suffering of a patient with hay fever. In addition, there is a special method of non-drug therapy that can significantly reduce or even prevent the manifestations of the disease, prevent the progression of the disease (in particular, the transition of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis to bronchial asthma), and in some cases remove the manifestations of hay fever for many years. The correct treatment for pollinosis is selected and carried out only by an allergist-immunologist.
Drug treatment of pollinosis
The first-line treatment implies the exclusion of the exposure to the allergen or its minimization: staying mostly indoors during the flowering season, mounting window filters, keeping doors and windows closed during the high pollen season, and so on. Besides, the first help that can be taken during the whole allergy season is the use of antihistamine drugs, i.e. medicines that block the allergic reaction. Preferably, it should be modern medications such as Fexofenadine (Allegra or generic versions). But in the severe course of the disease, first-generation antihistamines such as Cyproheptadine (Periactin or generic versions) are preferable. A doctor can also prescribe corticosteroids, usually, applied topically as a nasal spray, for instance, Fluticasone (Flomist or generic versions).
Non-drug treatment of hay fever
Another way of treating confirmed pollinosis is allergen-specific (ASIT) or specific (SIT) immunotherapy.

To date, it is the most successful and effective way of treating hay fever, which allows not only to influence the emerging symptoms of the disease, but also to make the seasonal allergy disappear for several years, or its manifestations become minimal. However, it is a costly procedure that must be done by a qualified specialist because it is not the drug that is introduced, but the source of the disease itself.
ASIT is the only pathogenetic method for the treatment of pollinosis. ASIT allows you to change the response of the immune system to the allergen, to make sure that contact with the allergen during the flowering season does not cause an allergic reaction in the patient's body. This is achieved by dosed administration to the patient according to a specific method of increasing concentrations of the allergen - from the very minimum, initially not causing any manifestations, to high concentrations. During ASIT, a restructuring occurs in the immune system and it ceases to react painfully to an incoming allergen. This treatment has a lot of nuances, which can be safe and effective only in the competent hands of a specialist. To achieve a lasting effect in accordance with international standards, the treatment should be carried out within 3-5 years. In this case, various techniques are used. Possibly pre-seasonal injection of the allergen (subcutaneously, into the arm) for several months, 2-3 injections per week; it is possible to use an allergen of a prolonged nature, which is injected less often - at the stage of dialing a dose once a week, then once a month. It is possible to carry out sublingual (sublingual) ASIT, when the patient, according to a certain scheme, drips the allergen on his own at home under the tongue, and periodically comes to the allergist-immunologist to control and correct the therapy. This method is also applicable to small patients from 5 years of age.
The ASIT method is chosen by an allergist-immunologist, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient, i.e. based on medical indications/contraindications and which method is more convenient for the patient.
Prevention of pollinosis

Prevention of the development of hay fever is simple:
- If possible, during the flowering period, move to another climatic area;
- During an exacerbation, unless absolutely necessary, do not go outside, exclude country walks, especially in windy weather;
- Outdoor walks only in the evening, preferably after rain or in cloudy weather;
- Regular wet cleaning of the apartment, moistening window screens;
- Removal of carpets, carpets, soft toys from living quarters;
- Exclusion of any herbal medicine (treatment with herbal ingredients), adherence to the diet, exclusion of honey and other beekeeping products, in case of allergy to tree pollen;
- Exclusion during the dusting season of any fruits of trees, raw carrots, in case of allergy to pollen of cereal grasses
- Exclusion from the diet of food grains (including bread, cereals, bran, etc.), in case of allergy to Compositae pollen;
- Exclusion from the unrefined sunflower oil, mayonnaise, chicory, melons, and gourds.
Post by: John Johansson, allergist, Amsterdam, Netherlands
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)
Periactin articles:
Some of the trademarks used in this Web Site appear for identification purposes only.
All orders are reviewed by a licensed physician and pharmacist before being dispensed and shipped.
The statements contained herein are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The statements are for informational purposes only and is it not meant to replace the services or recommendations of a physician or qualified health care practitioner. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist.