Fungal Infections Explained: Key Insights and Treatments
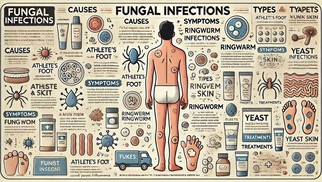

Fungal infections are common conditions caused by fungi, a type of microorganism found in the environment. While many fungi coexist harmlessly with humans, some can lead to infections under specific conditions. This article delves into the causes, types, and management of fungal infections, including effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
What is the Main Cause of Fungal Infection?
Fungal infections occur when certain types of fungi invade and multiply in the body. The primary causes are diverse but interconnected. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients, or people living with HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to fungal infections. Fungi also thrive in warm, damp environments, making places like locker rooms, swimming pools, and tight-fitting shoes ideal breeding grounds. Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the body, allowing fungi to proliferate. Additionally, direct contact with contaminated surfaces, infected individuals, or animals can lead to infections. Underlying health conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and hormonal changes also increase susceptibility to fungal infections, particularly on the skin.
What are 5 Common Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections can affect various parts of the body, from the skin to internal organs. Among the most prevalent are athlete’s foot, ringworm, yeast infections, jock itch, and nail fungus. Athlete’s foot, for example, typically affects the feet, causing itching, burning, and cracked skin. Ringworm manifests as red, circular, and scaly patches on the skin, despite its misleading name that suggests the presence of worms. Yeast infections, caused by Candida species, often occur in the mouth, genital area, or skin folds, presenting as white patches or severe itching. Jock itch affects the groin area and is characterized by red, itchy, and flaky skin, particularly in those who sweat excessively. Nail fungus, on the other hand, causes fingernails or toenails to thicken, discolor, and become brittle.
Fungal Infections on the Skin
Skin fungal infections are among the most frequent types of fungal conditions. They occur when fungi grow on the surface or outer layers of the skin. These infections often present as red, scaly, or flaky patches, accompanied by itching and a burning sensation. In some cases, the skin may crack, peel, or develop blisters. Risk factors for these infections include wearing tight or non-breathable clothing, poor hygiene, excessive sweating, and sharing personal items like towels or razors.
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing skin fungal infections. Keeping the skin clean and dry, wearing breathable fabrics, and avoiding walking barefoot in communal areas are essential measures. When infections do occur, treatment typically involves topical antifungals in the form of creams, sprays, or ointments. For severe or widespread infections, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. Maintaining good hygiene and adopting lifestyle adjustments, such as wearing loose, breathable clothing, can significantly aid recovery.
How to Remove Fungus in the Body?
Removing fungus from the body involves a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Topical antifungal medications are commonly used for localized infections, such as those affecting the skin, scalp, or nails. These medications work by directly targeting the fungi and inhibiting their growth. For more persistent or systemic infections, oral antifungals like fluconazole or itraconazole may be prescribed. These medications act from within the body to eliminate fungal growth.
In addition to medical treatments, home remedies and lifestyle changes can enhance recovery. Maintaining dryness in affected areas is vital since fungi thrive in moist environments. Applying natural antifungal substances like tea tree oil, coconut oil, or diluted apple cider vinegar can provide additional support. Boosting the immune system through a healthy diet rich in garlic, yogurt, and turmeric can also help combat fungal infections. Reducing sugar intake is recommended, as fungi such as Candida feed on sugar, exacerbating the infection.
Good hygiene practices are essential to prevent the spread of fungal infections. Washing hands regularly, avoiding the sharing of personal items, and cleaning footwear and clothing thoroughly can minimize the risk of reinfection. In extreme cases, such as severe nail fungus, surgical removal of the affected nail may be necessary.
Treatment with Diflucan
Diflucan, also known as fluconazole, is a widely used antifungal medication effective in treating various fungal infections. It belongs to the azole class of antifungals, which work by inhibiting the synthesis of fungal cell membranes, ultimately leading to the death of the fungus. Diflucan is particularly effective against Candida infections, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and systemic candidiasis. Additionally, it is used to treat other fungal conditions such as cryptococcal meningitis and certain dermatophyte infections.
One of the advantages of Diflucan is its versatility. It is available in various forms, including tablets, oral suspensions, and intravenous preparations, making it suitable for both mild and severe infections. For uncomplicated infections like vaginal candidiasis, a single dose of Diflucan is often sufficient to resolve symptoms. In more severe or systemic infections, longer treatment durations and higher doses may be required, as determined by a healthcare provider.
Diflucan’s safety profile is generally favorable, but like all medications, it can cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, headache, and abdominal discomfort. Rarely, it may lead to liver toxicity or allergic reactions, so it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and report any unusual symptoms to a doctor. Patients with liver conditions or those taking other medications should inform their healthcare provider to avoid potential drug interactions.
Overall, Diflucan is a reliable and convenient option for treating fungal infections, especially when prompt and effective treatment is needed. Its broad-spectrum efficacy and ease of use make it a cornerstone in antifungal therapy, providing relief and preventing complications associated with fungal diseases.
When to See a Doctor?
While many fungal infections can be managed with over-the-counter remedies, some situations warrant medical attention. If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, or if the infection spreads to multiple body parts, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Signs of systemic infection, such as fever, fatigue, or difficulty breathing, require immediate medical intervention. Individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions should seek professional advice promptly to ensure effective treatment and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Fungal infections are a widespread health concern, but they are generally manageable with prompt and appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of fungal infections. If you suspect a fungal infection, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing complications and ensuring a quick recovery.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Faride Ramos, MD
(Updated at Jan 2 / 2025)

