Understanding Ulcerative Colitis: Causes, Flare-ups, and Living with the Condition
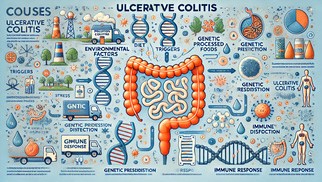
What is the Main Cause of Ulcerative Colitis?
Despite extensive research, the precise cause of ulcerative colitis is not fully understood. However, scientists have identified several contributing factors:
- Genetics: Ulcerative colitis tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Certain genetic mutations are associated with an increased risk of developing the disease, particularly those linked to immune system regulation.
- Immune System Dysfunction: In ulcerative colitis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the healthy tissues of the colon, causing inflammation. This autoimmune response is thought to be triggered by an abnormal reaction to gut bacteria or other environmental factors.
- Environmental Influences: While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, environmental factors such as diet, stress, and exposure to certain pathogens may act as triggers. Smoking, for example, has been found to have a protective effect against ulcerative colitis, though the exact reasons remain unclear.
- Microbiome Imbalance: The gut microbiome—the collection of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms living in the digestive tract—is crucial for maintaining intestinal health. An imbalance in the microbiome, known as dysbiosis, may contribute to the development of ulcerative colitis.
What Causes Colitis Flare-ups?
Flare-ups in ulcerative colitis refer to periods when symptoms worsen or return after a period of remission. These episodes can vary in severity and duration, and their causes are often multifaceted:
- Dietary Triggers: Certain foods, such as spicy dishes, high-fiber vegetables, caffeine, and alcohol, can irritate the digestive tract and trigger flare-ups in some individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify specific dietary triggers.
- Stress: Emotional and physical stress can exacerbate symptoms. While stress does not cause ulcerative colitis, it can influence the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
- Medication Non-Adherence: Skipping prescribed medications or altering dosages without consulting a healthcare provider can lead to a resurgence of symptoms.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections in the gastrointestinal tract can provoke an immune response, leading to inflammation and symptom exacerbation.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and aspirin may irritate the intestinal lining, potentially triggering flare-ups.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during menstruation or pregnancy, can influence symptoms in women with ulcerative colitis.
How Does Colitis Affect Your Life?
Living with ulcerative colitis can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. The disease’s symptoms, both physical and emotional, present unique challenges:
- Physical Symptoms: Persistent diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue can make daily activities difficult. Frequent bathroom trips may interfere with work, social engagements, and travel plans.
- Emotional Impact: Chronic illnesses like ulcerative colitis can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. The unpredictability of flare-ups can increase stress levels, further complicating symptom management.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: The inflammation in the colon can interfere with nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals. This may result in anemia, weight loss, and other health issues.
- Social and Work Life: The need for proximity to a restroom can limit social activities and professional opportunities. Many individuals with ulcerative colitis struggle with explaining their condition to others or feel embarrassed about their symptoms.
- Impact on Relationships: Managing a chronic condition can strain personal relationships, especially when symptoms disrupt plans or require special accommodations.
- Financial Burden: The costs associated with treatment, medications, and frequent doctor visits can be significant, adding to the stress of living with the disease.
What Causes Colitis in Humans?
Understanding the underlying causes of colitis in humans requires a closer look at the interplay between genetic, immune, and environmental factors. While some overlap exists with ulcerative colitis, other forms of colitis—such as infectious, ischemic, and microscopic colitis—have distinct causes:
- Infectious Colitis: Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can lead to inflammation of the colon. Common pathogens include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Clostridium difficile (C. difficile).
- Ischemic Colitis: Reduced blood flow to the colon, often due to atherosclerosis or blood clots, can cause ischemic colitis. This condition is more common in older adults.
- Microscopic Colitis: This form of colitis involves inflammation visible only under a microscope. It is often associated with autoimmune conditions and may be triggered by medications such as NSAIDs and proton pump inhibitors.
- Diet and Lifestyle: While not a direct cause, diets high in processed foods and low in fiber may increase the risk of colitis by promoting gut inflammation.
- Allergic Reactions: In some cases, food allergies or intolerances can lead to colitis-like symptoms. This is more common in infants and young children.
Treating Ulcerative Colitis with Asacol
One of the most commonly prescribed medications for managing ulcerative colitis is Asacol. This drug belongs to a class of medications known as aminosalicylates and is designed to reduce inflammation in the lining of the colon.
- Mechanism of Action: Asacol contains the active ingredient mesalamine, which works directly in the colon to inhibit the production of inflammatory chemicals. This helps to reduce swelling, pain, and the frequency of diarrhea.
- Usage: Asacol is typically prescribed for both the induction of remission during a flare-up and maintenance therapy to prevent future episodes. The medication is taken orally, and the dosage may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
- Benefits: Regular use of Asacol can help achieve and maintain remission, allowing individuals to regain control over their symptoms and improve their quality of life. It is especially effective for mild to moderate cases of ulcerative colitis.
- Potential Side Effects: While generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea, headache, or abdominal discomfort. It is essential to communicate with a healthcare provider if any adverse effects occur.
- Combination Therapy: In some cases, Asacol may be used in conjunction with other medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, to achieve optimal results. Patients should always follow their doctor’s guidance and adhere to the prescribed treatment plan.
By reducing inflammation and promoting healing in the colon, Asacol plays a crucial role in the management of ulcerative colitis, helping patients lead more comfortable and fulfilling lives.
Managing and Living with Ulcerative Colitis
Effective management of ulcerative colitis involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. Here are some strategies to help individuals cope with the disease:
- Medical Treatment: Medications such as aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly used to reduce inflammation and maintain remission. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the colon.
- Dietary Changes: Working with a dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan can help manage symptoms. Small, frequent meals and a focus on easily digestible foods are often recommended.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and counseling can reduce stress levels and improve emotional well-being.
- Support Networks: Joining support groups or connecting with others who have ulcerative colitis can provide valuable insights and emotional encouragement.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring disease progression and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion
Ulcerative colitis is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a nuanced approach to diagnosis and treatment. While its exact cause remains elusive, advances in research have shed light on the genetic, immune, and environmental factors involved. Understanding the triggers of flare-ups and the ways in which colitis affects daily life can empower individuals to manage the disease effectively. With proper medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support, those living with ulcerative colitis can lead fulfilling and productive lives despite the challenges posed by the condition.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Faride Ramos, MD
(Updated at Jan 5 / 2025)