Navigating Acute and Chronic Urticaria: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
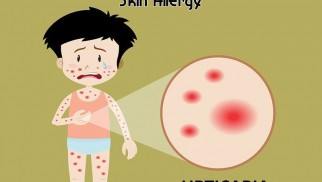
What Is Urticaria,and Why Does It Occur?
Urticaria, commonly referred to as hives, is a condition characterized by the sudden appearance of itchy, red, or skin-colored welts on the surface of the skin. But what causes these outbreaks, and why do they differ in duration and severity? Urticaria can manifest in two distinct forms: acute and chronic. Let’s explore each type, their triggers, symptoms, and management strategies.
Understanding Acute Urticaria
Acute urticaria is a short-term condition that typically resolves within six weeks.
It’s often triggered by:
- Allergic reactions to foods such as nuts, shellfish, and eggs.
- Insect bites or stings.
- Certain medications, like antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Viral infections or illnesses.
- Exposure to physical stimuli, including sunlight, heat, or cold.
Symptoms of acute urticaria include:
- Red, raised welts that may merge to form larger patches.
- Intense itching or a burning sensation.
- Swelling in some areas, particularly around the eyes, lips, or hands.
Management involves identifying and avoiding the trigger, using antihistamines, and applying soothing creams to reduce discomfort.
Exploring Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria persists for more than six weeks and can continue for months or even years. Unlike acute urticaria, the triggers are often harder to pinpoint, and in many cases, the cause remains idiopathic (unknown).
Common characteristics of chronic urticaria include:
- Recurring hives, often without a clear pattern.
- Persistent swelling and itching that interferes with daily life.
- Triggers that may include stress, hormonal changes, or underlying autoimmune conditions.
Chronic urticaria may require more complex management, including:
- Regular use of antihistamines or corticosteroids to control symptoms.
- Lifestyle adjustments to reduce stress and avoid known triggers.
- Consultation with a healthcare provider to investigate potential underlying causes.
Practical tips for managing urticaria at home
Managing urticaria effectively often requires combining medical treatment with self-care strategies. Here are some practical tips to alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
- Use cool compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected area can help reduce itching and swelling.
- Opt for loose clothing: Wearing lightweight, loose-fitting clothes made of breathable fabrics can prevent irritation.
- Avoid harsh soaps: Stick to gentle, hypoallergenic cleansers to reduce the risk of skin irritation.
- Keep a symptom diary: Tracking your diet, activities, and environmental exposures can help identify potential triggers.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports overall skin health and reduces dryness.
Addressing the Problem with Periactin Cyproheptadine
Periactin Cyproheptadine, an antihistamine, has proven effective in managing both acute and chronic urticaria. By blocking histamine receptors, it helps alleviate itching, reduce swelling, and prevent the formation of new hives. Its sedative properties can also aid in improving sleep quality for patients experiencing discomfort.
This medication may be particularly useful in cases where conventional antihistamines fail to provide relief. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment, as Periactin Cyproheptadine may have side effects or interact with other medications.
Conclusion
Effective management of urticaria depends on accurate diagnosis, trigger identification, and appropriate treatment. Whether dealing with the short-term inconvenience of acute hives or the long-term challenges of chronic urticaria, taking proactive steps can significantly improve one’s quality of life. Relief is possible with proper care and, when needed, the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Faride Ramos, MD
(Updated at Jan 15 / 2025)

