Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
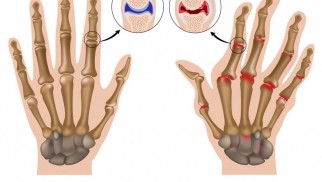
What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis and Why Is It a Problem?
Have you ever wondered why some people suffer from chronic joint pain and stiffness? The answer might be Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), a long-term autoimmune disorder that affects millions worldwide.
- Chronic Inflammation: RA causes the immune system to mistakenly attack healthy joint tissue, leading to inflammation.
- Joint Damage: Over time, untreated inflammation can cause permanent joint damage and deformities.
- Beyond the Joints: RA doesn’t just affect the joints; it can also harm the skin, lungs, heart, and eyes.
- Daily Struggles: Many people with RA experience severe pain, swelling, and reduced mobility, impacting their quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Recognizing RA early can help in managing its progression. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Joint Stiffness: Most noticeable in the morning or after inactivity.
- Swelling & Pain: Affected joints may feel warm and tender.
- Fatigue & Weakness: The body’s immune response can lead to extreme tiredness.
- Decreased Mobility: Over time, simple activities like gripping objects or walking can become difficult.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The exact cause of RA is still unclear, but experts believe a combination of genetics and environmental factors play a role.
- Genetic Factors: People with a family history of RA are at a higher risk.
- Immune System Malfunction: The immune system attacks the body’s own joint tissues.
- Environmental Triggers: Infections, smoking, and stress can trigger or worsen symptoms.
- Hormonal Influence: RA is more common in women, suggesting hormones may play a role.
Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Without proper management, RA can lead to serious complications:
- Joint Deformities: The damage caused by RA can lead to permanent joint deformities.
- Organ Involvement: RA may affect the lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
- Mental Health Impact: Chronic pain and disability can cause depression and anxiety.
- Reduced Life Expectancy: Severe cases of RA have been linked to a shorter lifespan.
How Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Treated?
Although there is no cure for RA, treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and managing symptoms.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants help control pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can improve mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be needed.
Deltasone (Prednisolone): A Powerful Solution for Rheumatoid Arthritis
One of the most effective medications for RA is Deltasone (Prednisolone), a corticosteroid that helps reduce inflammation and pain.
- Fast-Acting Relief: Deltasone works quickly to reduce swelling and joint stiffness.
- Suppresses the Immune Response: Helps prevent the immune system from attacking the joints.
- Improves Mobility: Patients experience better movement and less pain.
- Short-Term & Long-Term Use: While effective, long-term use requires monitoring due to potential side effects.
Living with rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, but with proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their quality of life. Early diagnosis and the right medication, such as Deltasone (Prednisolone), can make a significant difference in reducing pain and inflammation, allowing individuals to lead more active and fulfilling lives.
Article Post: Editorial Team of RXShop.md
(Updated at Mar 14 / 2025)
